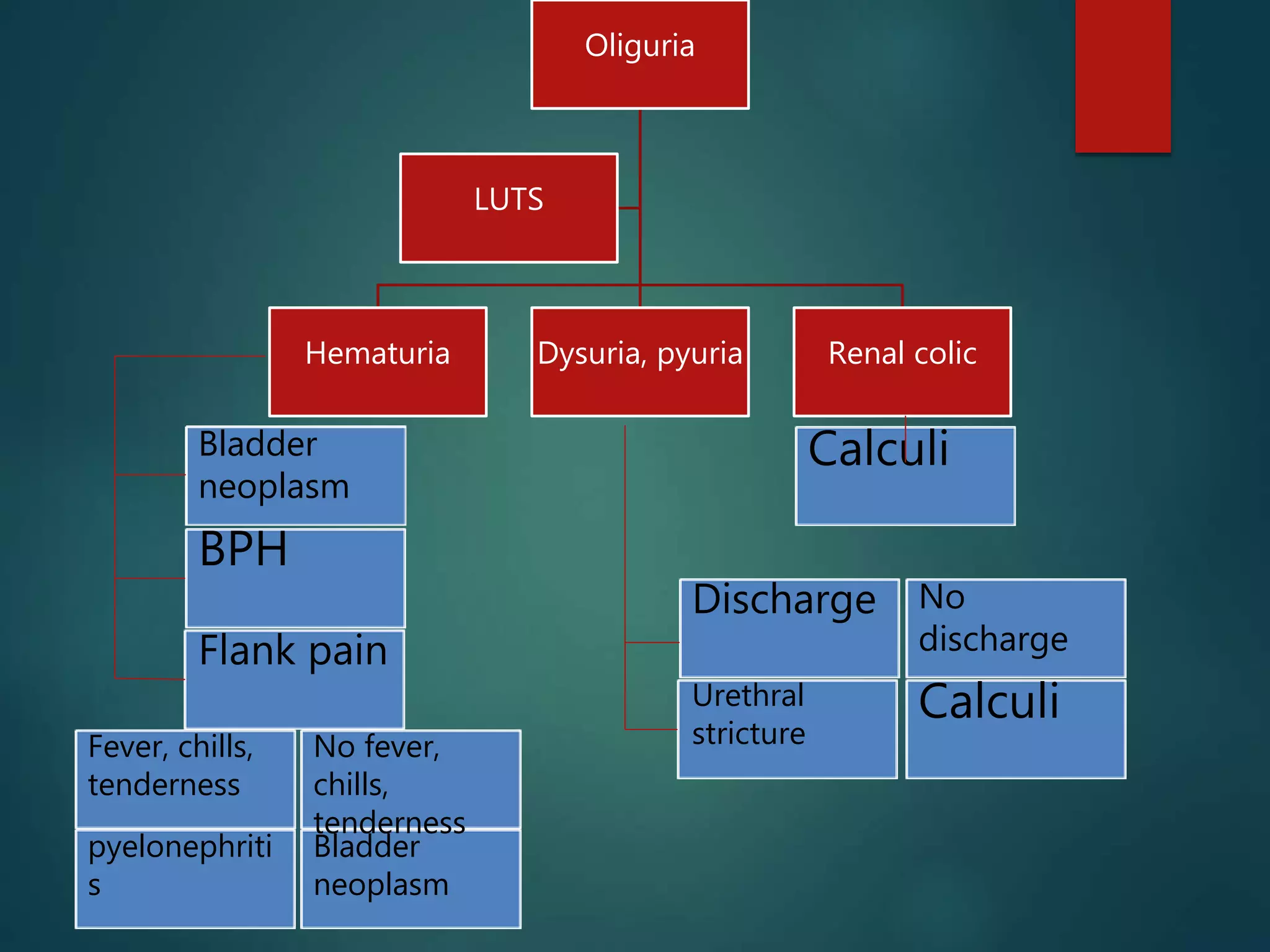
Oliguria is a low urine output defined as less than 1 mL/kg/hr in infants, less than 0.5 mL/kg/hr in children, and less than 300 mL daily in adults. It indicates an underlying disorder and can lead to acute renal failure if left untreated. Anuria is even less urine output at less than 50 mL/day. Causes of oliguria and anuria include pre-renal (low blood volume), renal (kidney damage), and post-renal (urinary tract obstruction). Evaluation and management depends on determining the cause through history, physical exam, urinalysis, and blood tests to guide volume replacement or other interventions to prevent further kidney injury.