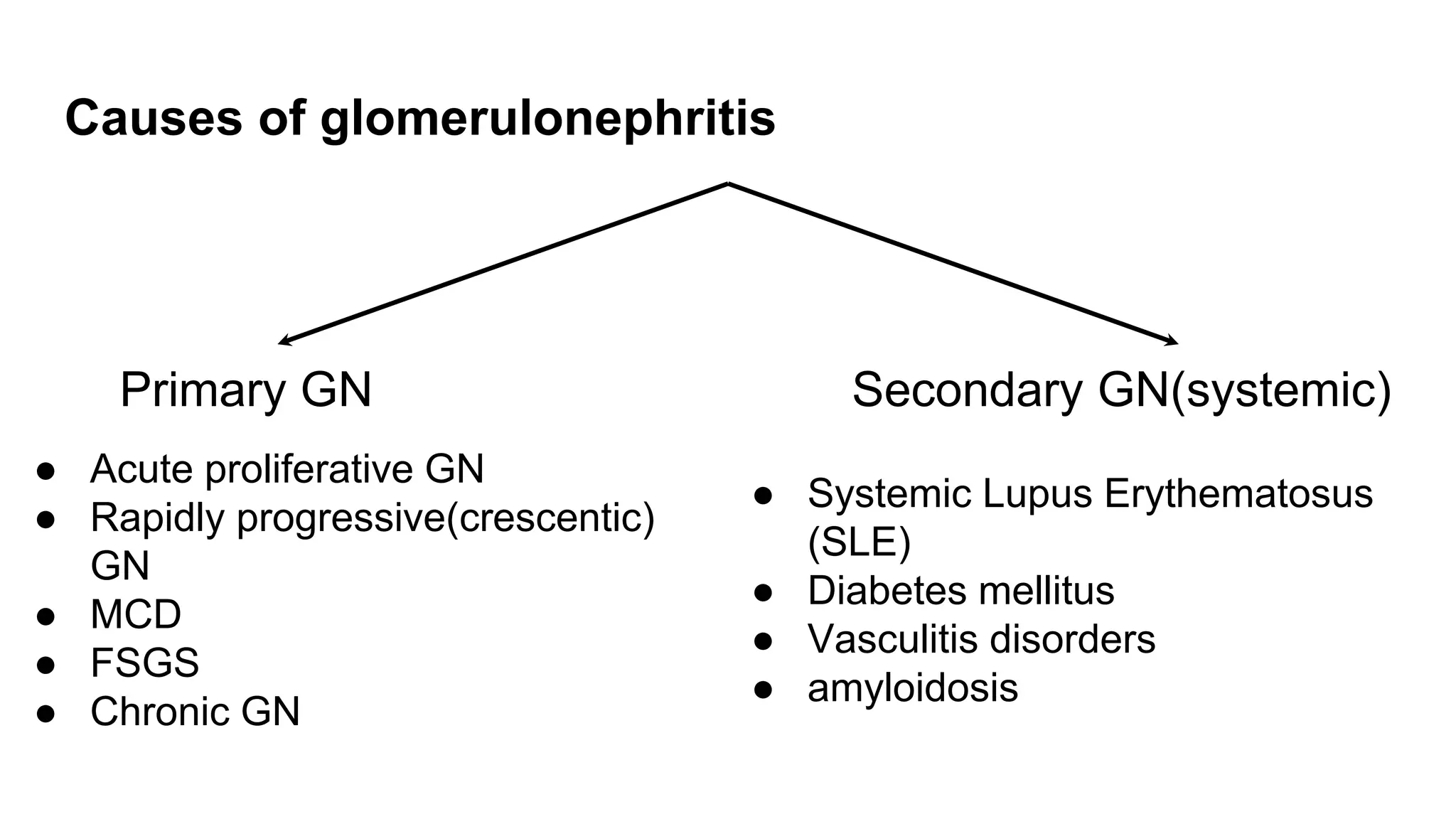
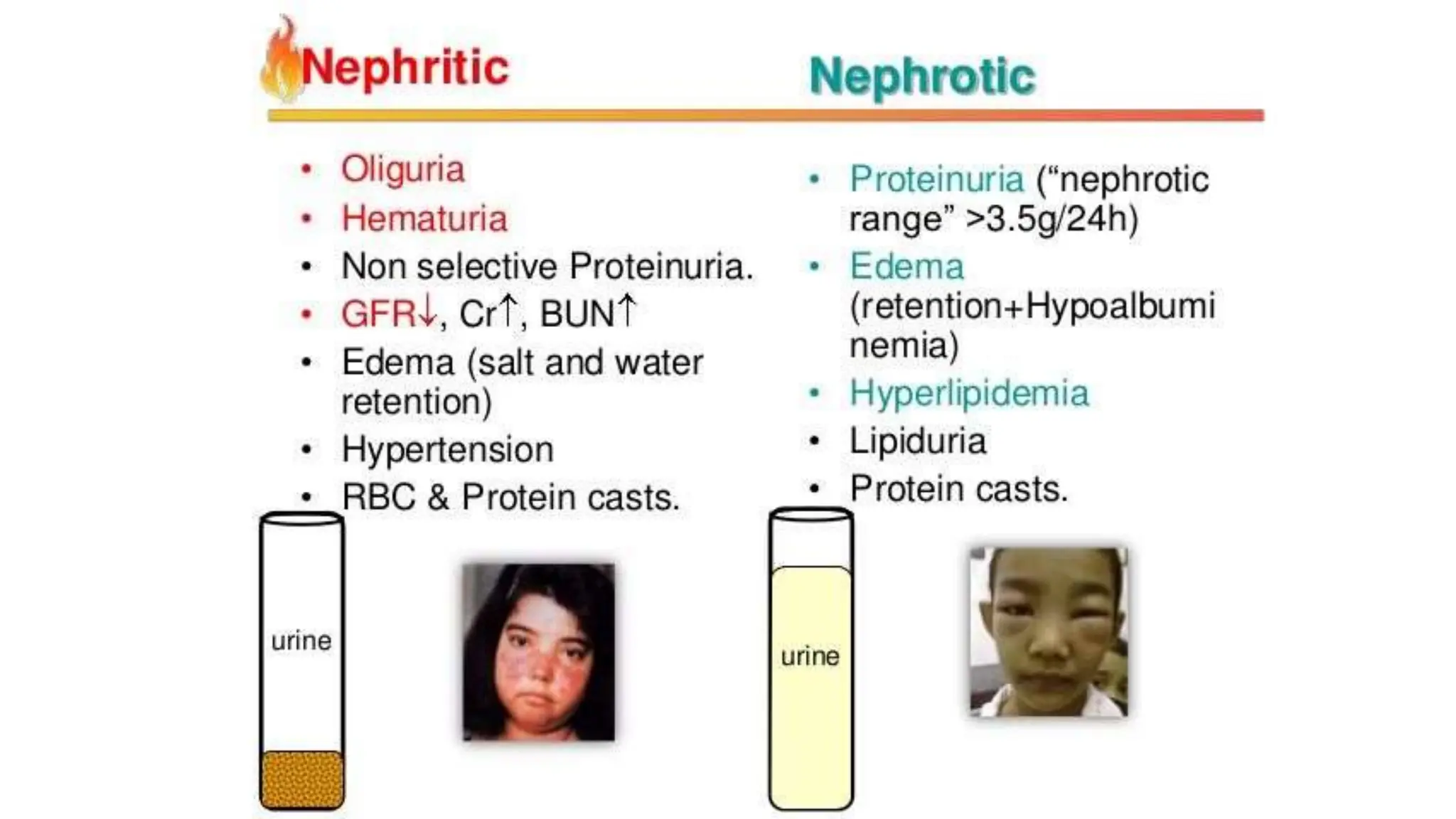
The document provides a detailed overview of nephritic syndrome and related glomerular diseases, including their causes, pathogenesis, and clinical features. It discusses conditions such as post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, emphasizing the immune response and potential complications. Diagnosis and treatment options are reviewed, with a focus on supportive care and management of symptoms.