1. Polyuria is defined as urine output greater than 5 ml/kg/hr or 2 L/m2/day. Causes include increased fluid intake, increased urinary solute excretion, and impaired urinary concentration.
2. Evaluation of polyuria involves obtaining a detailed history, clinical examination, and investigations including a 24-hour urine output measurement and urine and serum analysis.
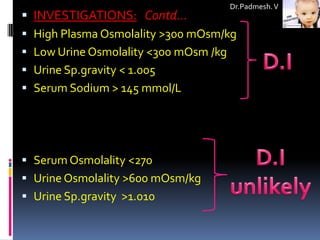
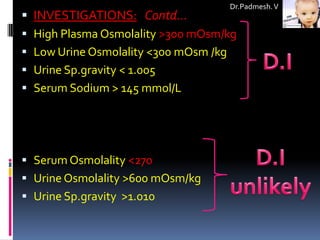
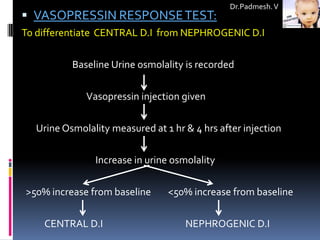
3. Distinguishing between central and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus involves tests like the water deprivation test and vasopressin response test.