This document provides an overview of poliomyelitis (polio), including its introduction, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Some key points:
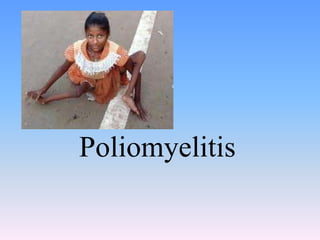
- Polio is a viral infection that can cause paralysis. It was first described in 1799 and primarily infects the gastrointestinal tract.
- Through vaccination efforts starting in the 1950s, polio has been eliminated in most developed countries. Global eradication efforts have reduced endemic countries from 125 to 3 between 1988-2012.
- Polio spreads through the fecal-oral route or oral secretions. There is no animal reservoir - humans are the only known carrier. Vaccines including both inactivated (Salk) and