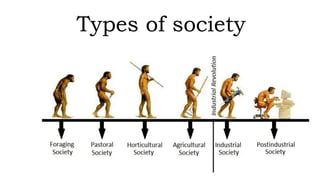
The document defines and discusses the key concepts of society. It begins by defining society as a group of people and their relationships. It describes some key elements and characteristics of society, including mutual interaction, interdependence, cooperation, and a pattern of social control. The document then discusses different types of societies, including tribal societies characterized by kinship and nomadism, agrarian societies focused on agriculture, and industrial societies with specialized division of labor and impersonal relationships.