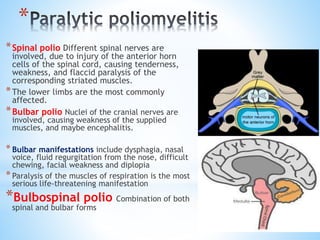
Poliomyelitis, primarily affecting children and young adults, is an acute viral infectious disease transmitted via fecal-oral or oro-oral routes, with a 6 to 20-day incubation period. It presents in three patterns: abortive polio, nonparalytic, and paralytic forms, with paralytic cases leading to severe complications, especially in older individuals. Immunization, through either inactivated or oral vaccines, effectively prevents polio, but some survivors may develop post-polio syndrome years later, characterized by new muscle weakness and fatigue.