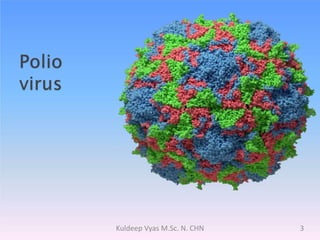
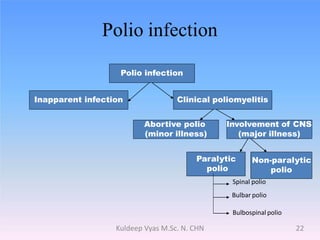
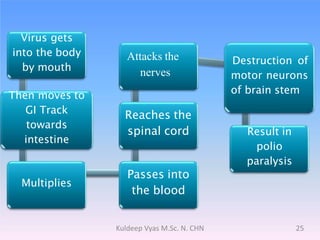
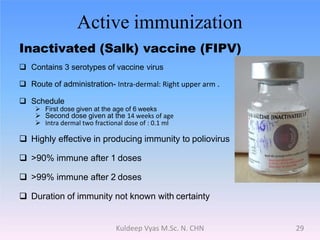
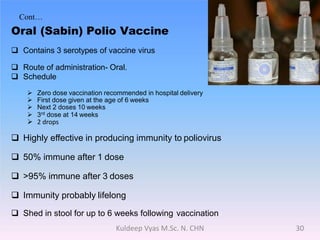
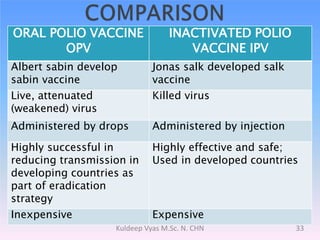
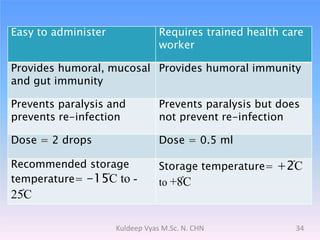
Poliomyelitis is caused by the poliovirus, which infects the gastrointestinal tract and sometimes spreads to the central nervous system. It primarily affects children under 5 years old and can cause a spectrum of symptoms from mild illness to paralysis. While polio was eradicated in many countries through vaccination programs, cases persisted in some developing nations until as recently as 2011 in India. The document discusses the history, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of poliomyelitis.