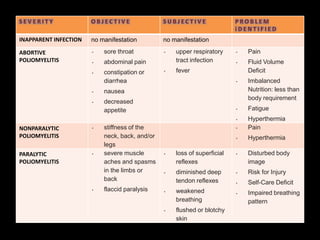
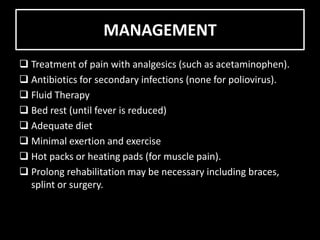
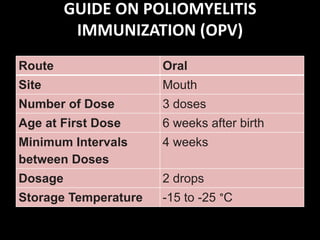
Poliomyelitis is an infectious disease caused by a poliovirus that primarily affects the spinal cord. It was once a global disease but through vaccination efforts, now only exists in a few countries in Africa and Asia. The virus is transmitted via the fecal-oral route. It enters the body through the mouth and may cause a range of symptoms from none to paralysis depending on if it infects the spinal cord. Treatment focuses on symptoms and rehabilitation while vaccination is the best prevention method.