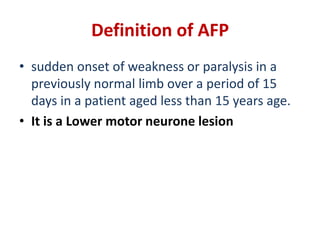
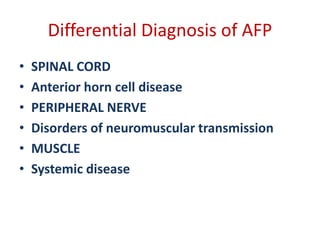
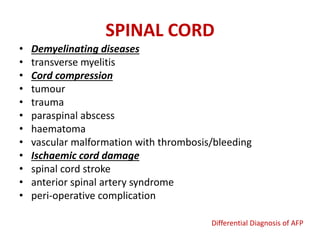
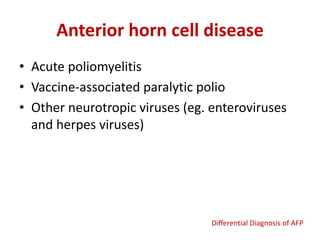
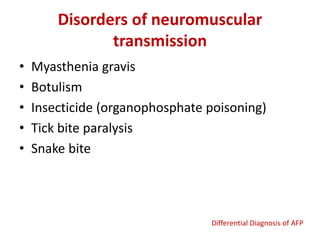
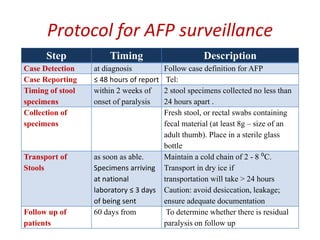
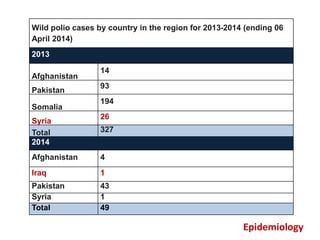
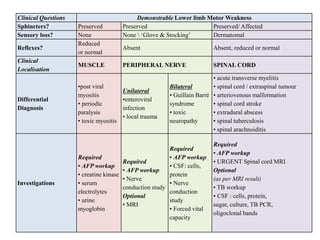
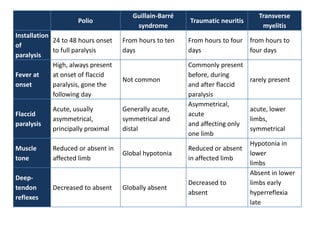
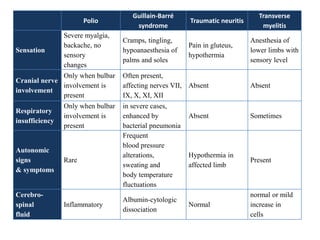
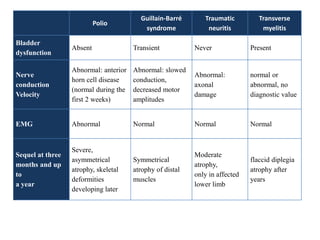
Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) is defined as sudden onset of weakness or paralysis in a previously normal limb over 15 days in patients under 15 years old. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is the most common cause of AFP and is an acute acquired inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. It has an annual incidence of 0.6 to 2.4 cases per 100,000 people and usually occurs 2-4 weeks after a respiratory or GI infection. GBS is diagnosed through CSF analysis showing elevated proteins and electrophysiological studies showing demyelination. Treatment involves monitoring, IVIG or plasma exchange to shorten recovery time, and PICU care if respiratory involvement is present.