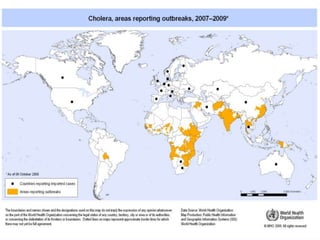
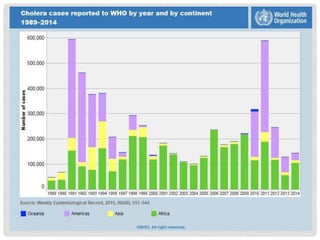
This document discusses cholera, an acute diarrheal disease caused by Vibrio cholerae bacteria. It covers the epidemiology, prevention, and control of cholera globally and in India. Key points include that cholera causes a sudden onset of watery diarrhea and dehydration. If untreated, case fatality can be 30-40%. Transmission is related to inadequate water and sanitation. Prevention and control involves early detection, oral rehydration therapy, antibiotic treatment, vaccination, health education, and improving water quality, sanitation, and hygiene. The National Diarrheal Disease Control Programme was established in India to prevent deaths from dehydration through oral rehydration therapy.