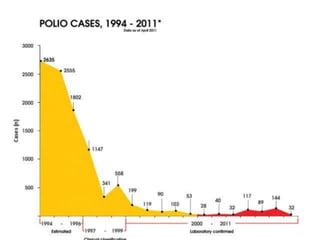
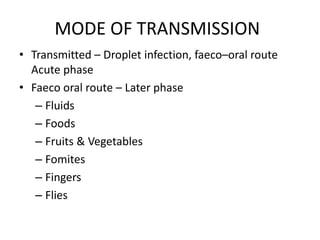
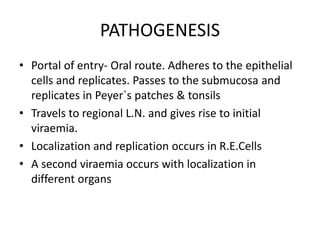
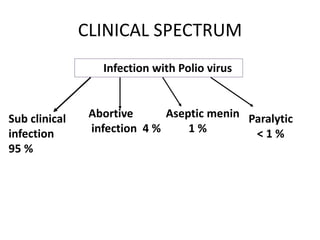
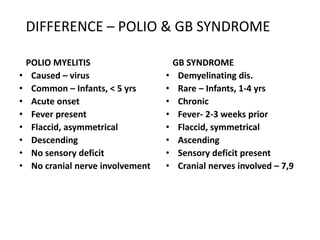
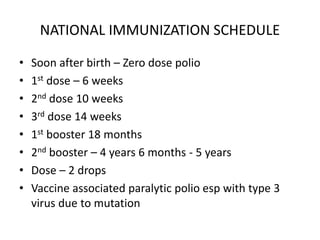
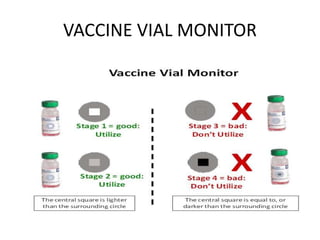
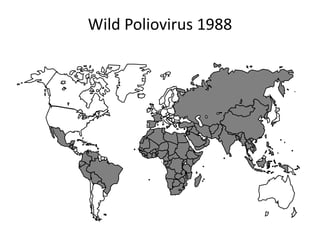
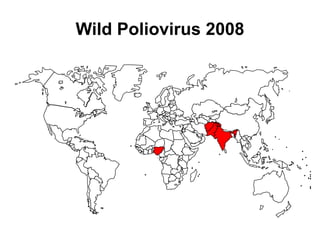
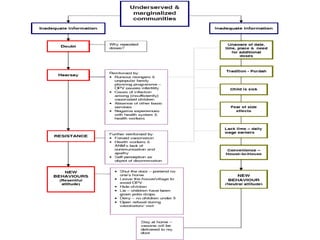
Poliomyelitis is an acute viral infection that mainly affects children and can cause paralysis. It is caused by three serotypes of the poliovirus. While most infections are mild or asymptomatic, the virus can infect the central nervous system in rare cases and cause paralysis. Global efforts aim to eradicate polio through high routine immunization coverage, supplemental immunization activities like pulse polio campaigns, acute flaccid paralysis surveillance to detect cases, and mop-up immunization in high-risk areas. Combined, these strategies have helped eliminate wild poliovirus from many countries.