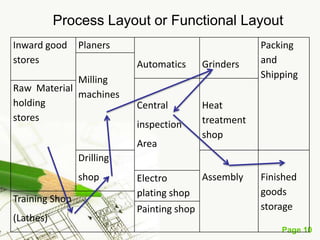
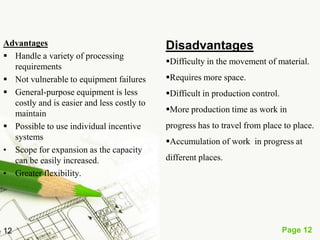
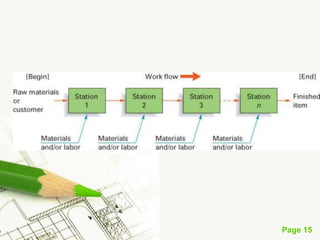
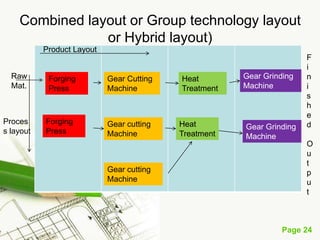
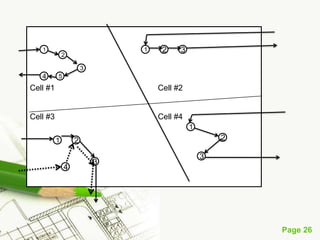
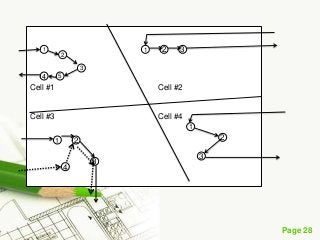
The document discusses different types of plant layouts. It defines plant layout as the arrangement of machines, equipment, and tools to allow for the efficient flow of materials through the production process. The objectives of a good layout are to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve productivity and employee satisfaction. The main types of layouts discussed are process layout, product layout, fixed position layout, and group technology/cellular layout. Process layout groups machines by function, while product layout arranges them in linear sequence of operations.