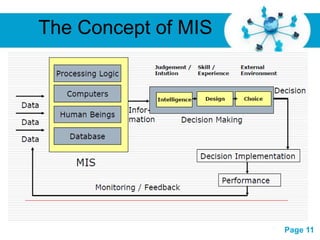
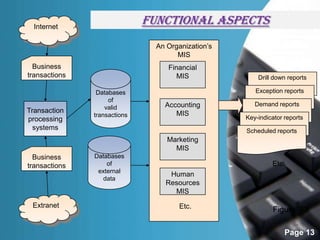
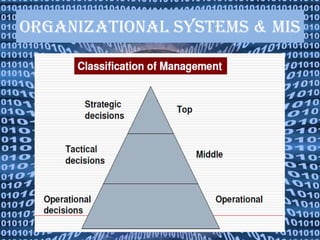
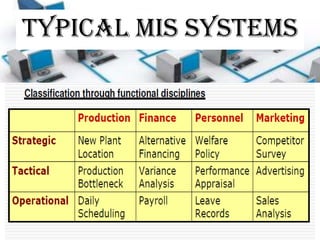
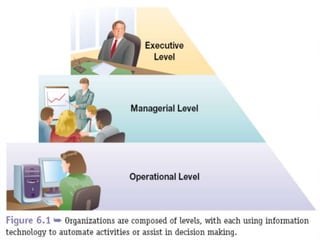
The document provides information about management information systems (MIS). It defines MIS as a system designed to supply information required for effective management of an organization. MIS processes data into information which is then communicated to departments for decision making. The objectives of MIS are to make the right information available at the right time, place and cost. MIS provides advantages like coordination, access to data, and improved techniques. It outputs scheduled, key indicator, demand and exception reports. MIS supports different levels of management and their varying information needs.