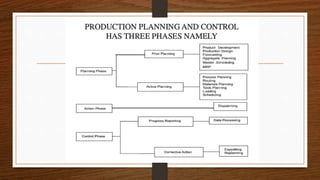
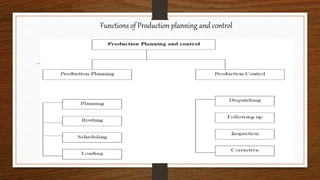
Production planning and control aims to efficiently utilize resources like materials, people, and facilities to transform raw materials into finished products in an optimal manner. It involves planning, coordinating, and controlling all production activities from procurement to shipping. The key objectives are proper coordination of activities, better control, ensuring uninterrupted production, capacity utilization, and timely delivery. The main stages are planning, action, and control. Important functions include production planning like estimating, routing, and scheduling, as well as production control functions like dispatching, follow up, and inspection. A master production schedule is a production plan that states what will be made, how many units, and when, to coordinate activities and resources.