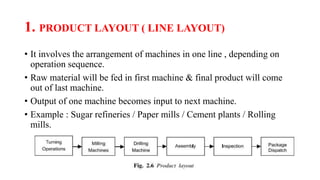
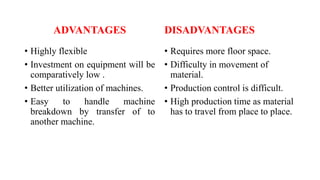
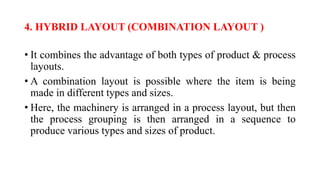
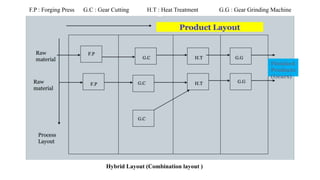
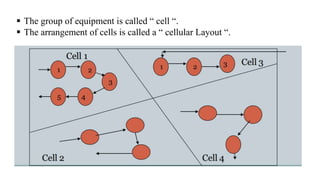
The document discusses different types of plant layouts. It describes plant layout as the physical arrangement of production facilities, including equipment, personnel, storage, and materials handling. The main types of layouts discussed are product layout, process layout, fixed position layout, hybrid layout, and cellular layout. Product layout arranges machines in a straight line by operation sequence, while process layout groups machines by function into departments. Hybrid layout combines aspects of product and process layouts. Cellular layout uses group technology to cluster equipment for similar parts into cells. The objectives and principles of effective plant layouts are also outlined.