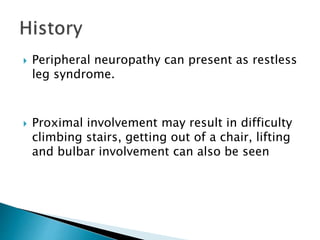
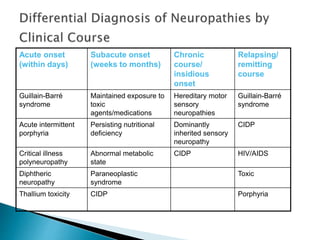
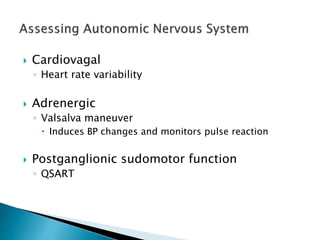
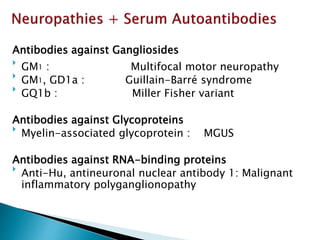
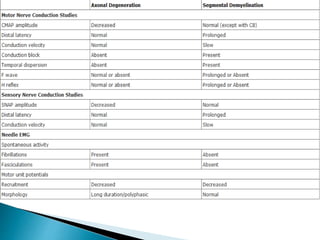
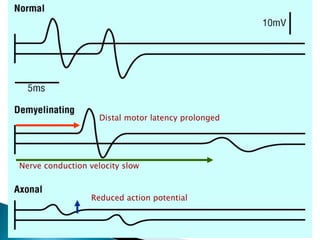
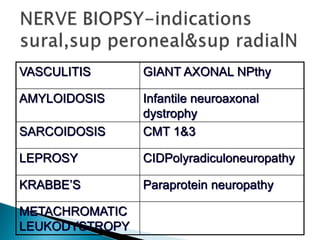
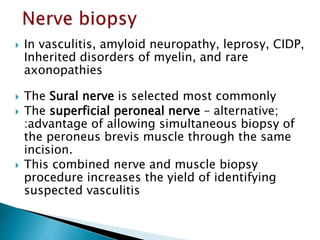
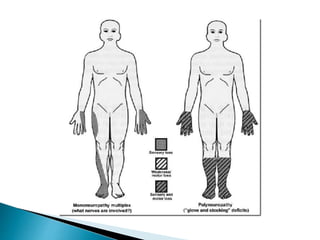
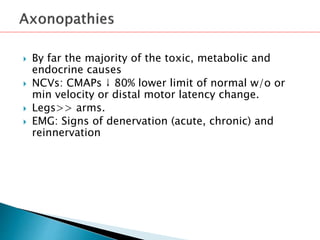
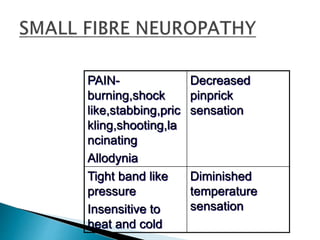
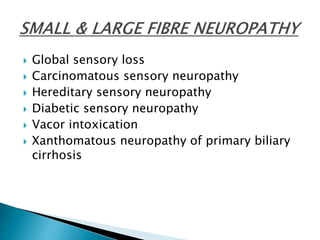
This document provides an overview of peripheral neuropathies. It discusses that peripheral neuropathies can involve sensory nerves, motor nerves, or both, and may affect single or multiple nerves. The document then covers the clinical presentation and classification of different types of neuropathies, including those that primarily affect the cell body, myelin, or axon. It also lists common causes of peripheral neuropathies like diabetes, paraproteinemia, alcohol misuse, and discusses their prevalence. The temporal course, symptoms, and assessment of peripheral neuropathies are discussed in detail.
















![ DM
hypothyroidism
chronic renal failure
liver disease
intestinal
malabsorption
malignancy
connective tissue
diseases
[HIV]
drug use
Vitamin B6 toxicity
alcohol and dietary
habits
•Weight loss, malaise, and anorexia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peripheral-neuropathy-160215171345/85/Peripheral-neuropathy-32-320.jpg)