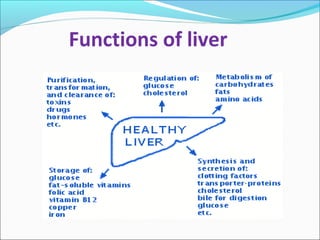
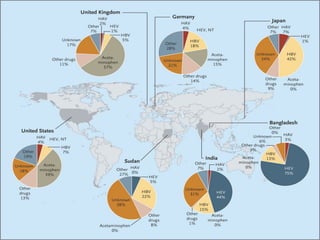
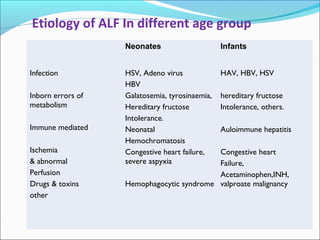
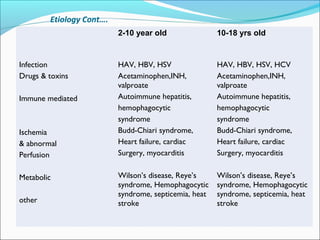
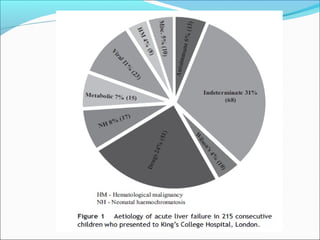
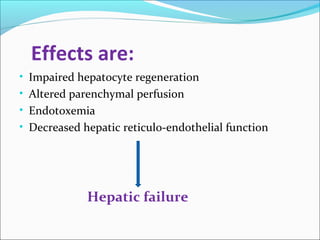
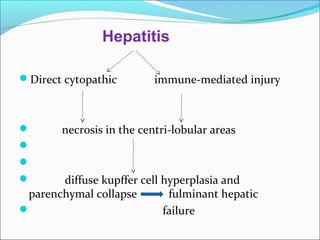
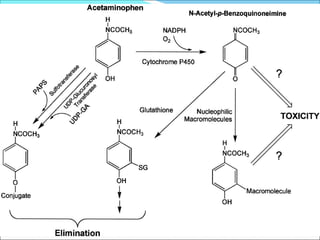
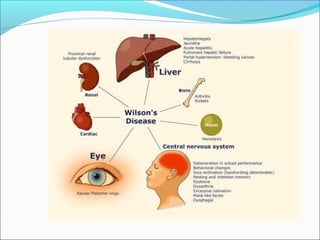
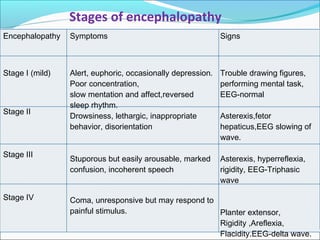
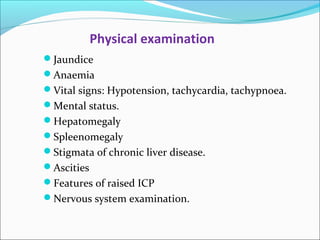
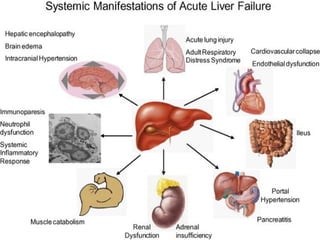
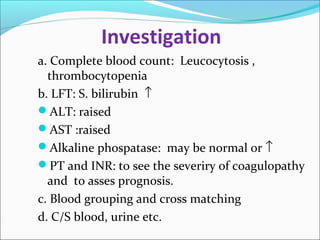
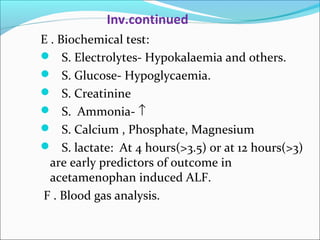
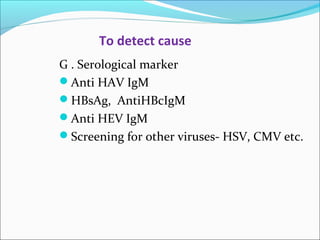
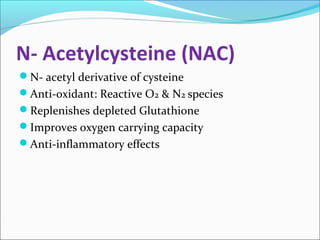
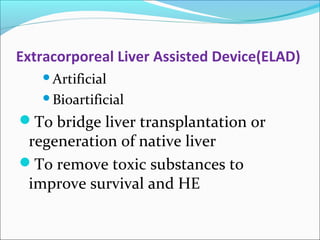
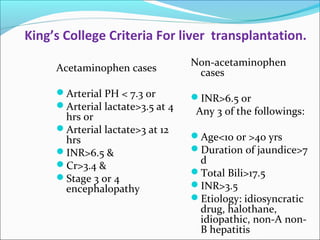
The document defines acute liver failure in children and discusses its causes, presentation, management, and complications. Acute liver failure is characterized by liver dysfunction within 8 weeks without preexisting liver disease and includes coagulopathy and hepatic encephalopathy. Common causes include viral hepatitis, acetaminophen toxicity, and idiosyncratic drug reactions. Management involves supportive care to maintain organ function, treatment of specific causes, and potentially liver transplantation for severe cases.