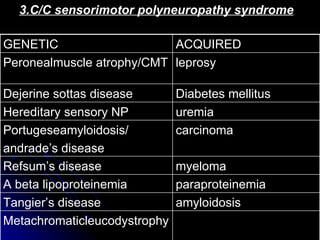
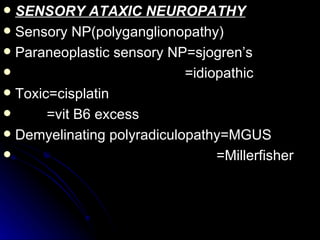
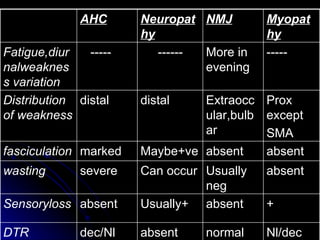
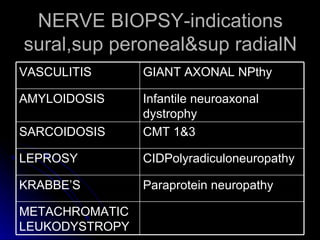
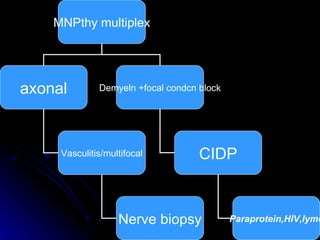
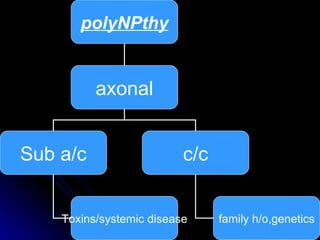
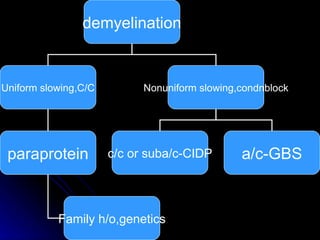
This document provides an overview of peripheral neuropathy, including:
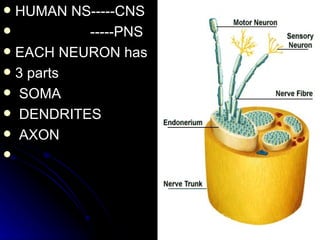
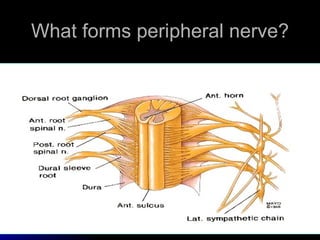
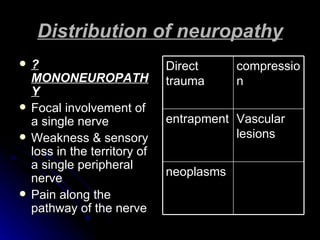
1. It describes the anatomy of peripheral nerves and different types of peripheral neuropathies such as mononeuropathy, mononeuropathy multiplex, polyneuropathy, polyradiculopathy, and plexopathy.
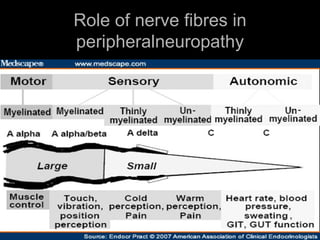
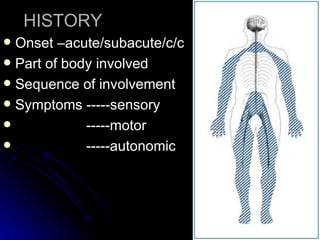
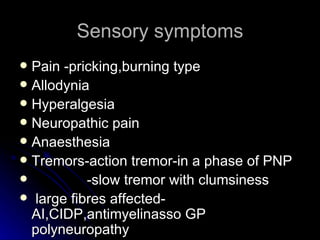
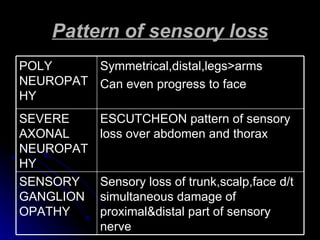
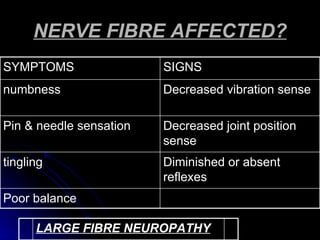
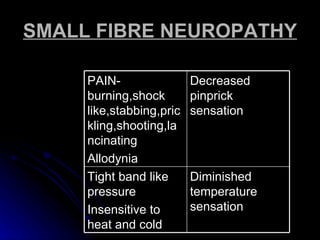
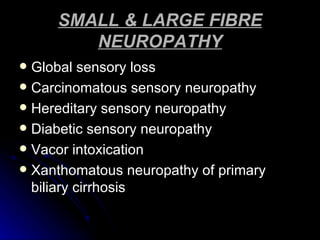
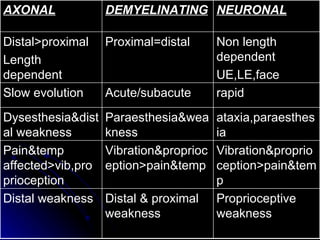
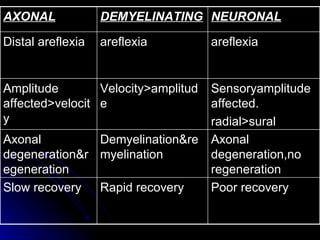
2. It outlines the various clinical presentations of peripheral neuropathy including sensory, motor, and autonomic symptoms as well as patterns of nerve fiber involvement.
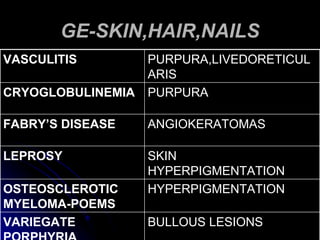
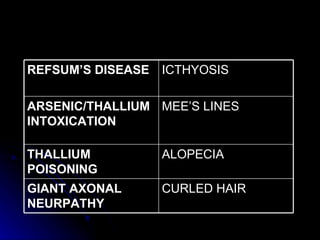
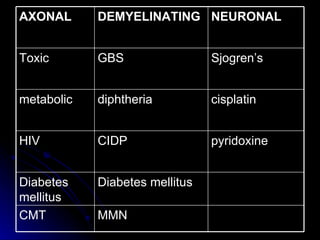
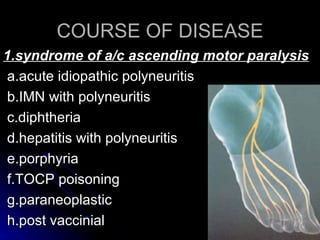
3. It discusses the etiology, clinical course, investigations and management of different peripheral neuropathies.