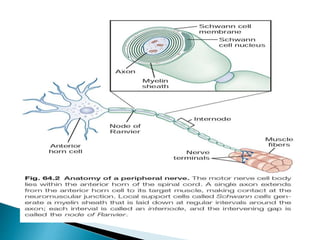
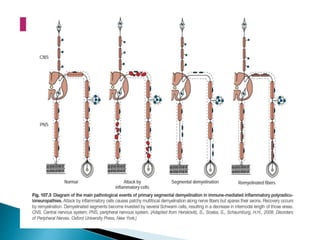
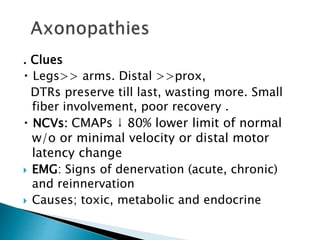
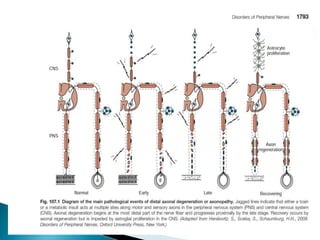
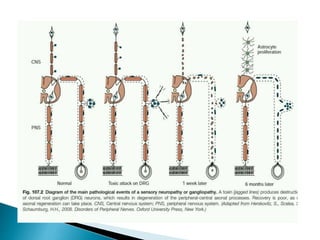
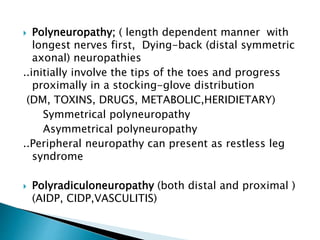
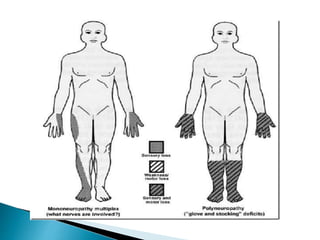
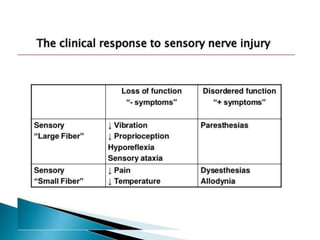
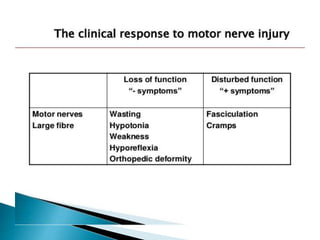
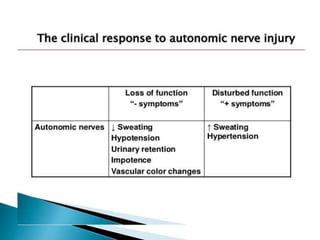
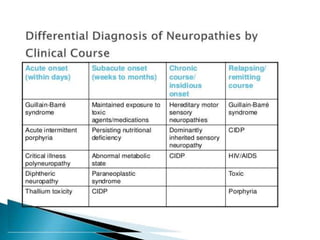
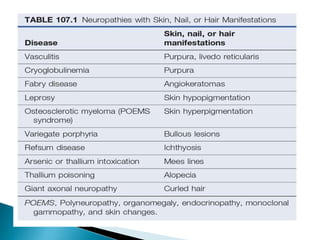
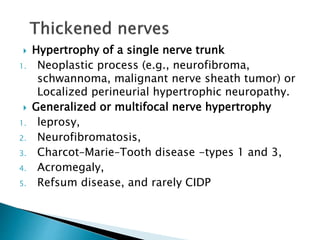
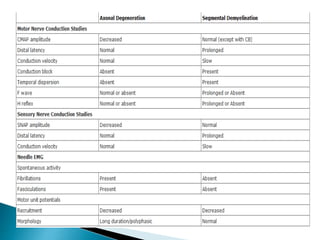
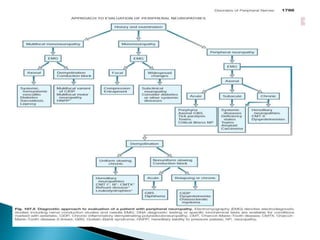
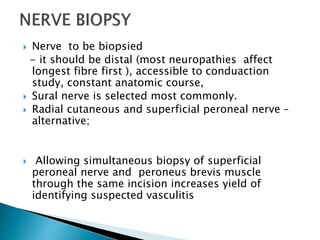
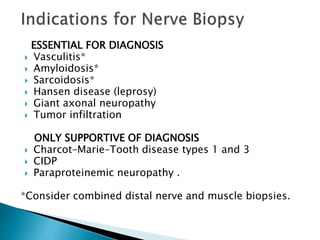
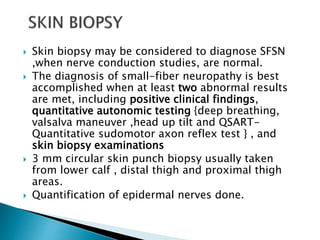
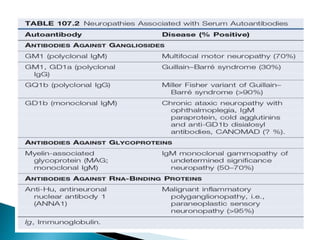
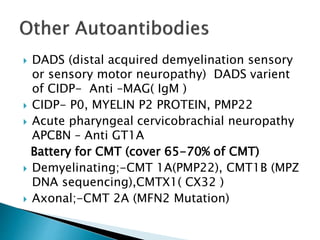
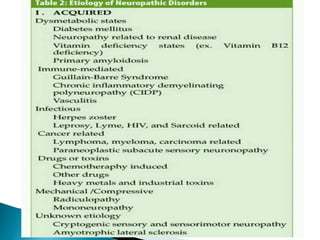
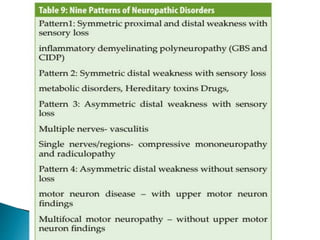
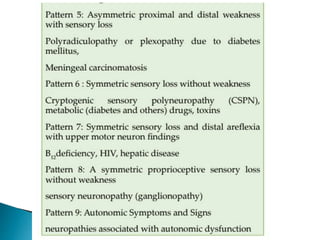
Peripheral neuropathies are common neurological disorders caused by dysfunction of peripheral nerves. A systematic diagnostic approach involving detailed history, physical exam, electrodiagnostic studies, and possibly additional testing is recommended to determine the nature and location of nerve lesions. Diagnostic tests should not be ordered without understanding their significance. Biopsy may be needed in some cases to confirm diagnoses like vasculitis or amyloidosis. Treatment involves managing underlying causes, IVIG or immunomodulators for rapidly progressive neuropathies, and symptomatic treatments like antidepressants, antiepileptics, and topical agents.