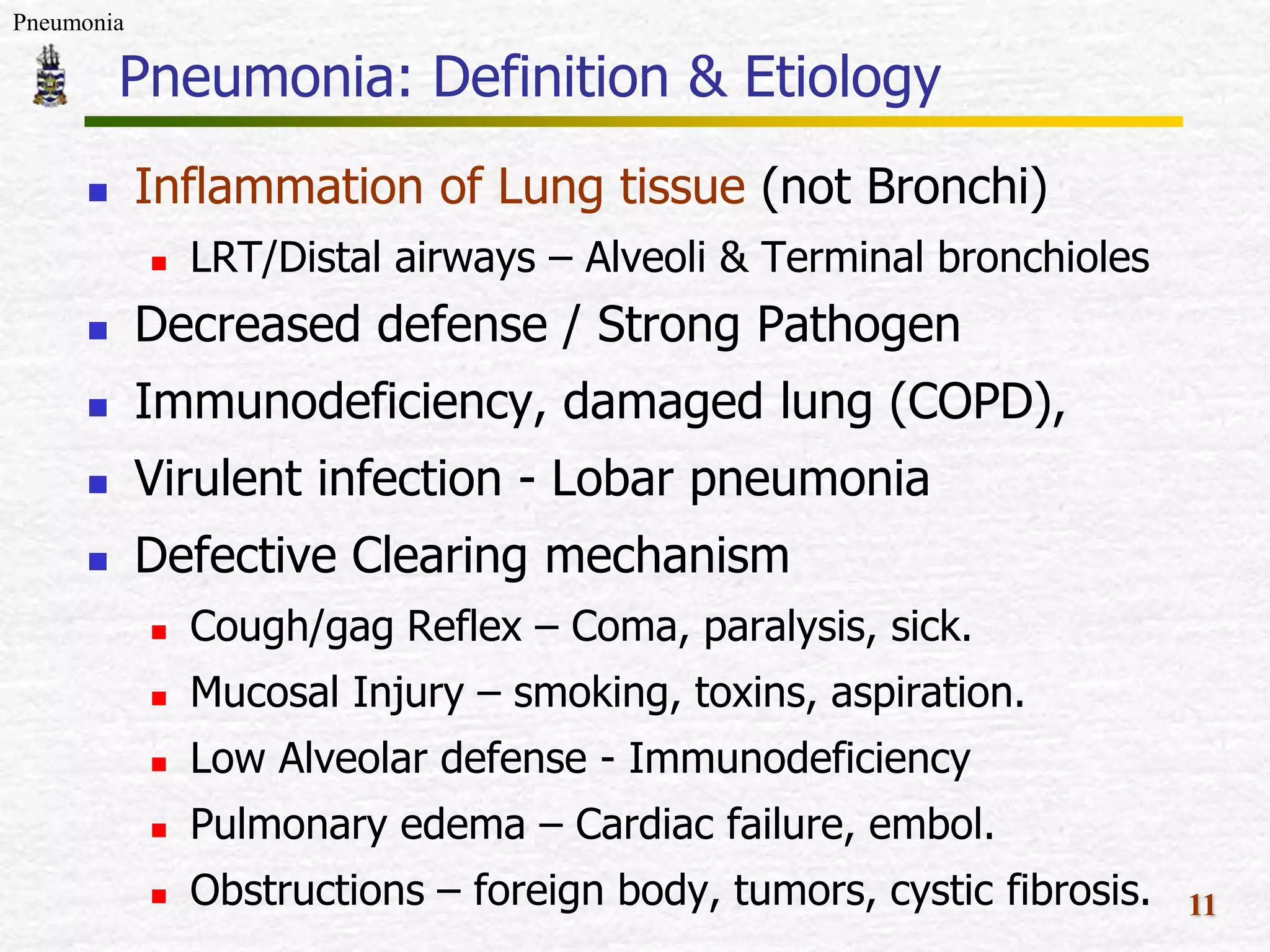
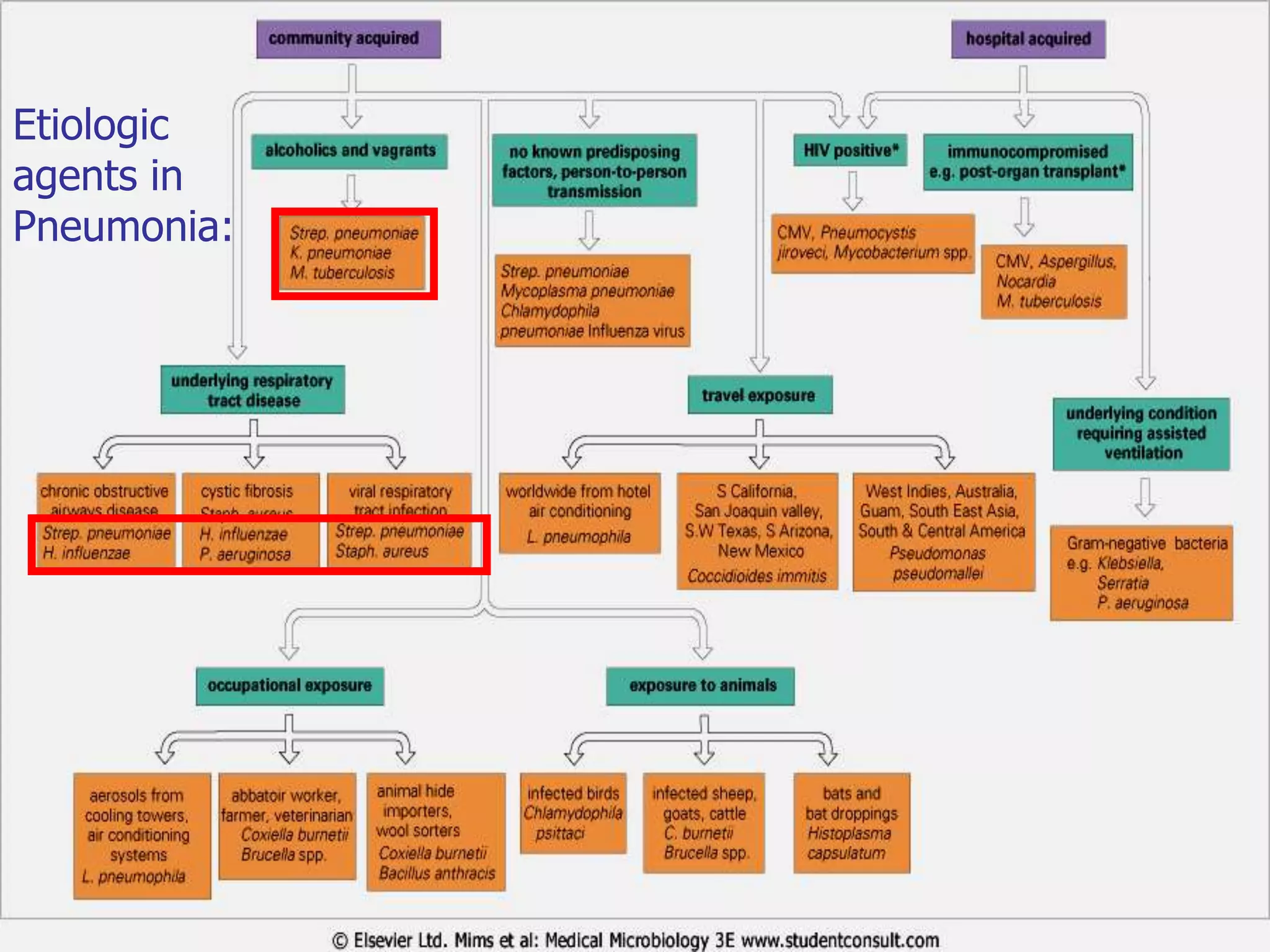
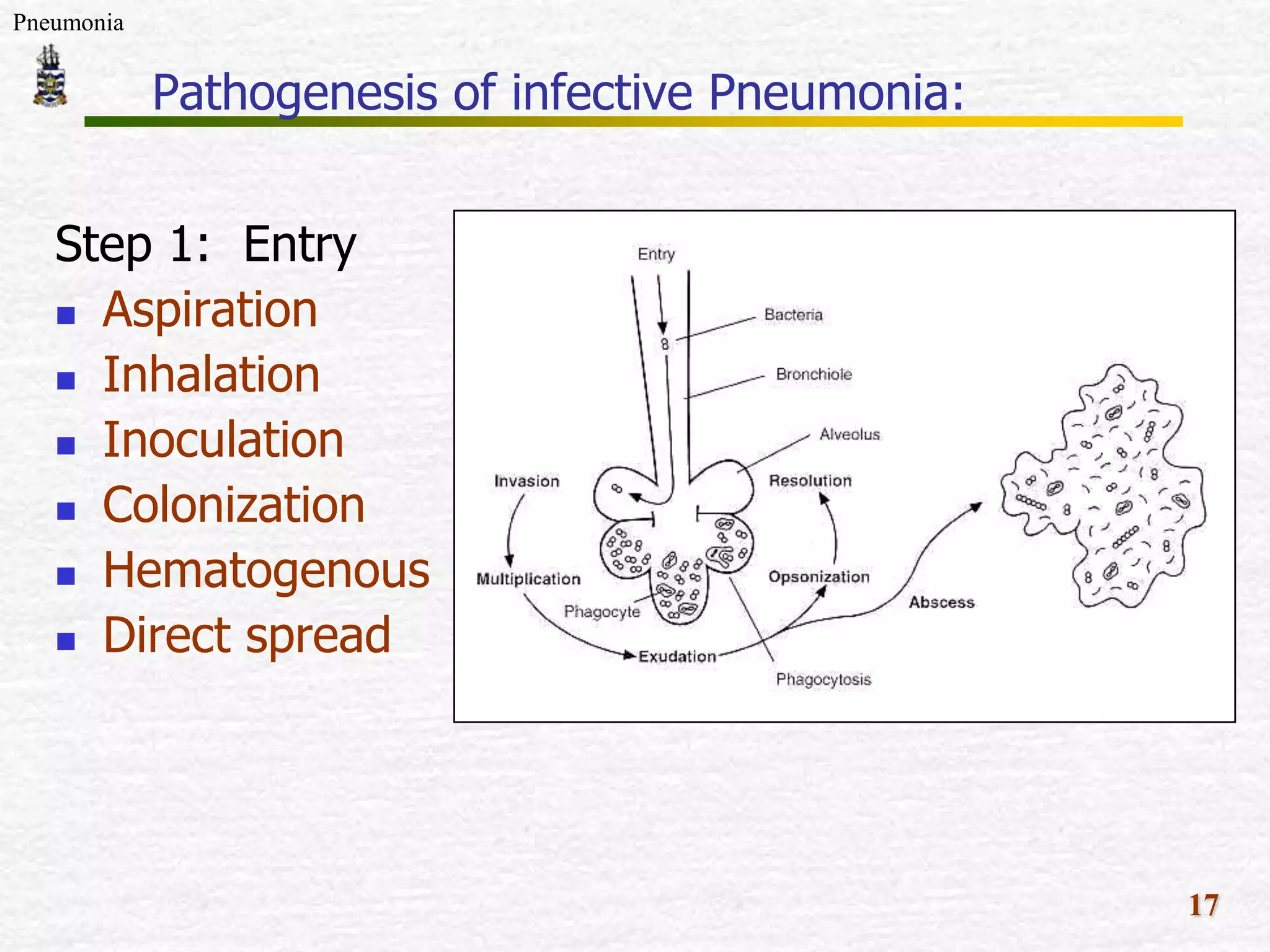
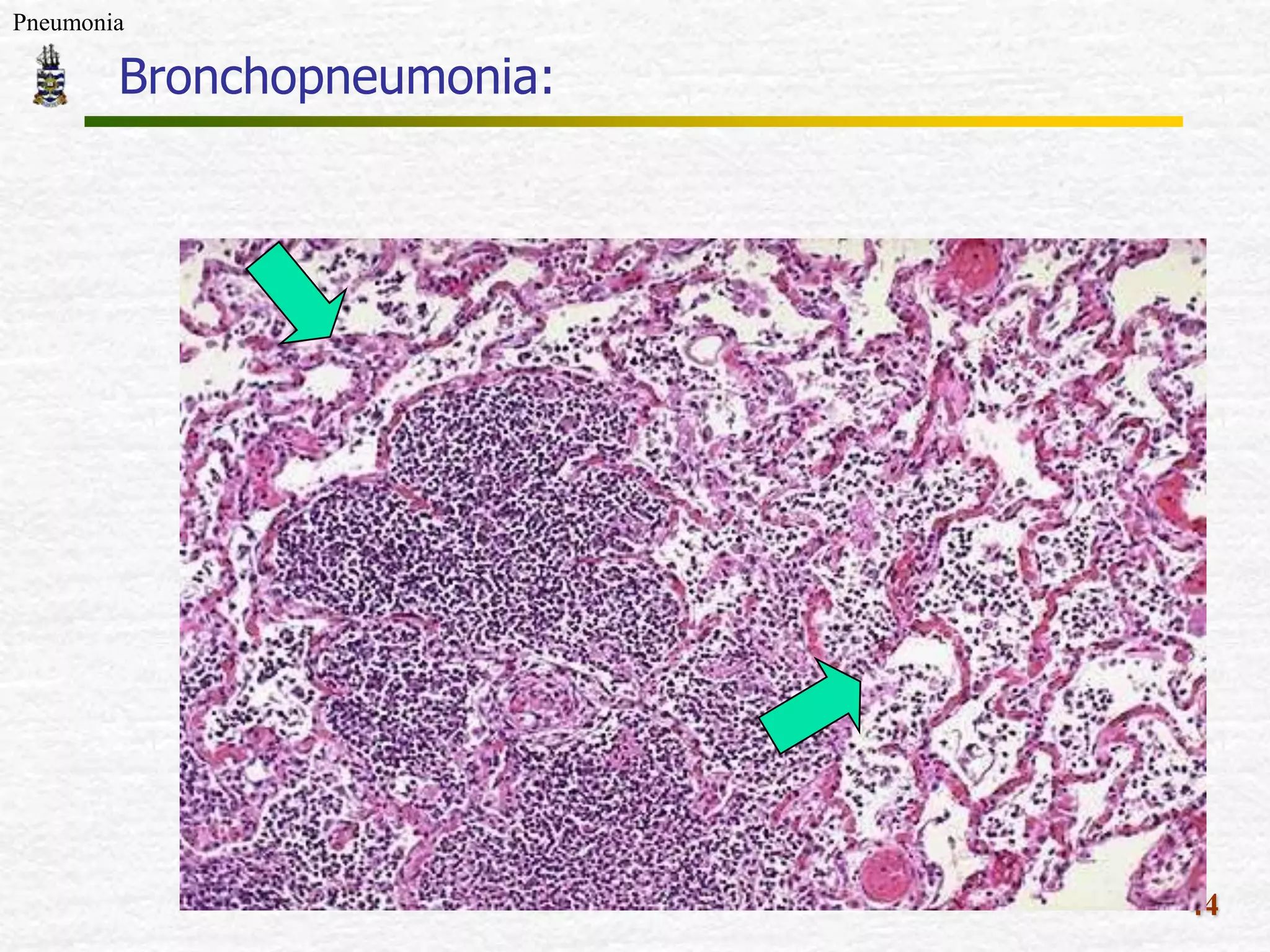
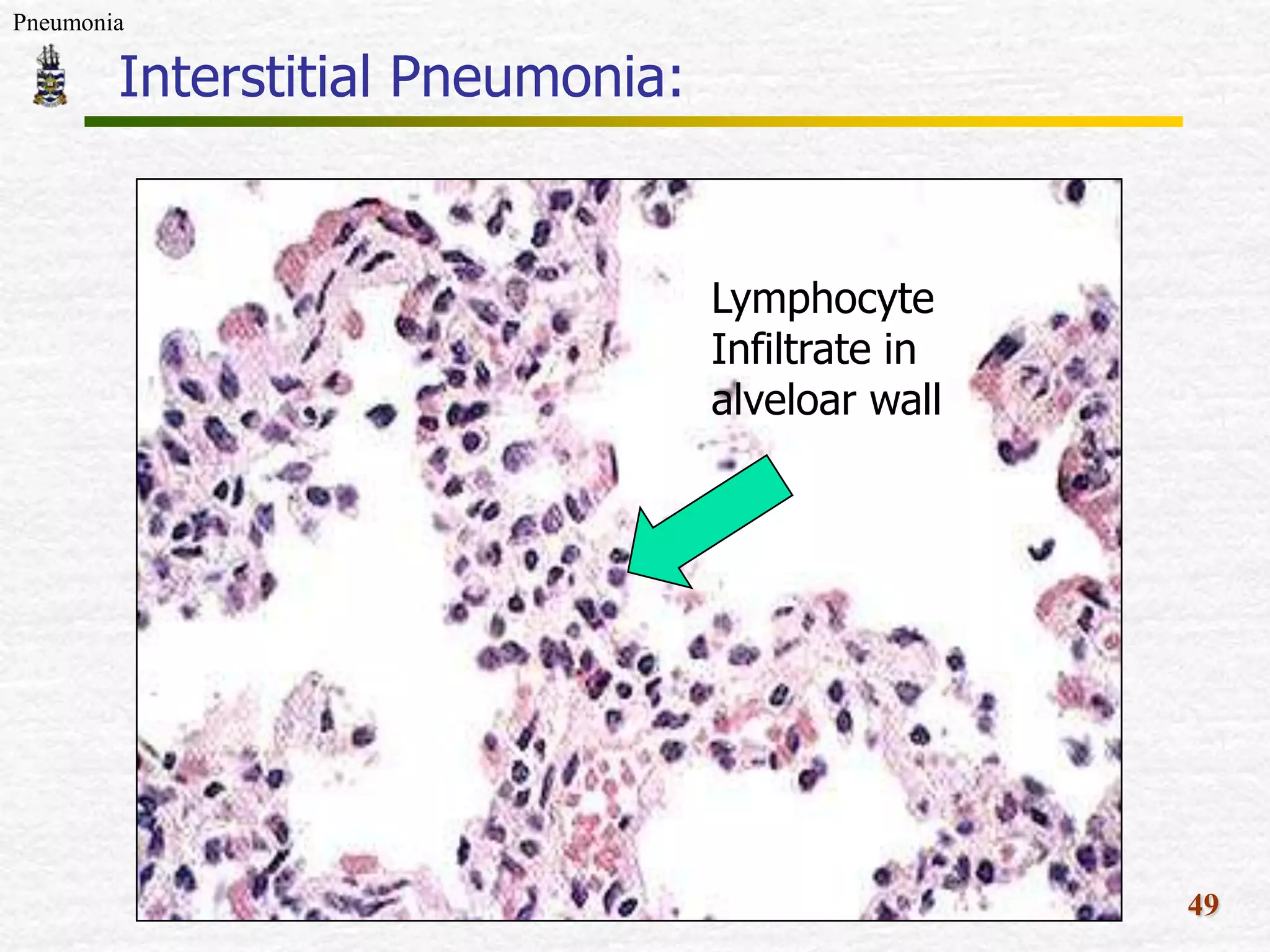
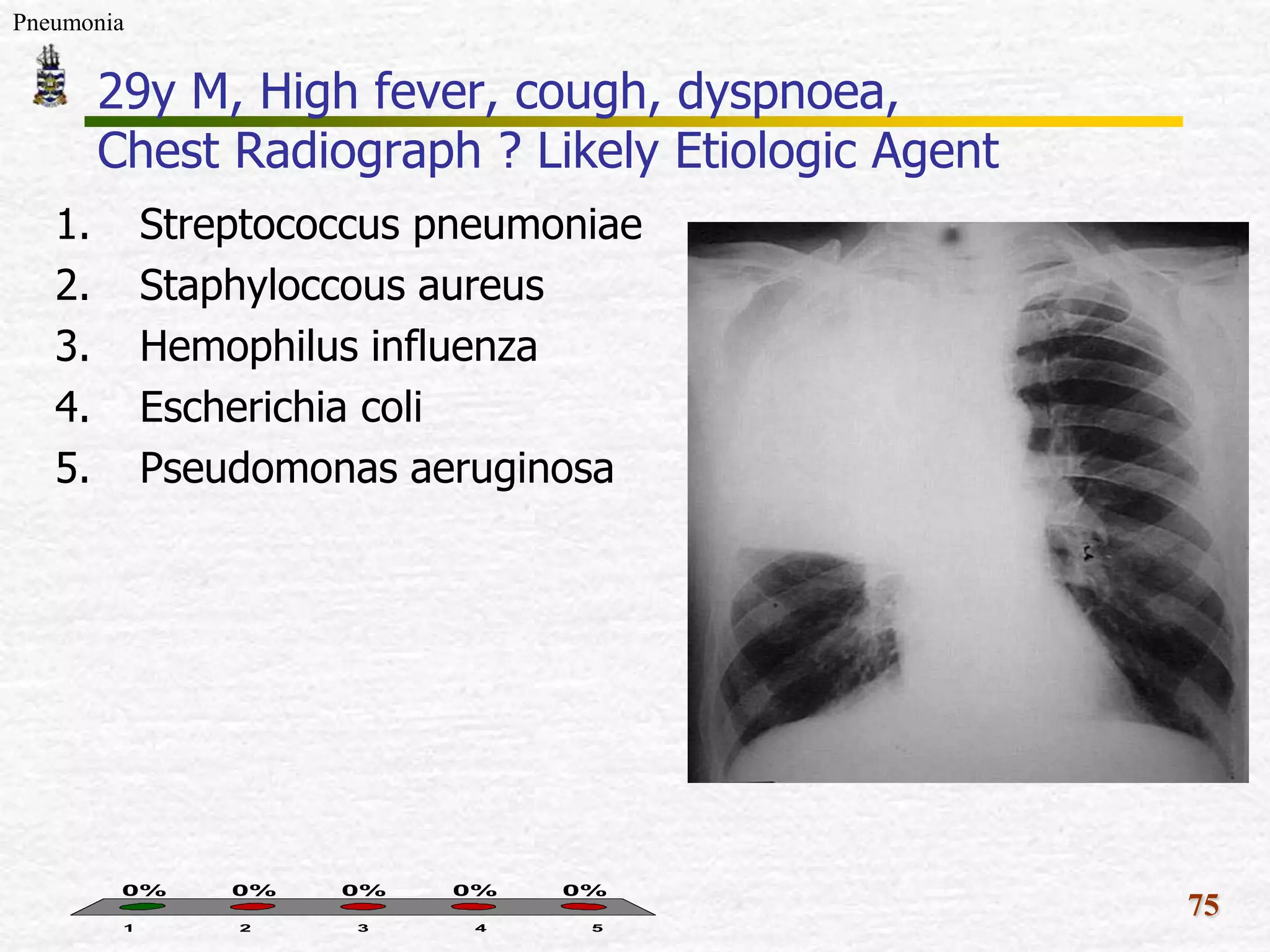
The document discusses Mr. Turner, a 38-year-old Vietnamese cane farmer who presents to the emergency department with pneumonia, having high fever, shortness of breath, and cough. It lists potential differential diagnoses for his condition and asks questions to further evaluate his medical history and risk factors. The pathogenesis of pneumonia is also briefly outlined, noting how pathogens can enter the lungs and cause inflammation.













































































![Pneumonia
Laboratory findings
Leukocytes 19.0 x 109/L (19 000/µL)
Haemoglobin 7.1 mmol/L (11.5 g/dL)
Haematocrit 0.35 (35 mL/dL)
Platelets 195 x 109/L (195 000 /µL)
C-reactive protein 279.4 mg/dL [<5]
Blood urea nitrogen 6.6 nmol/L (9.0 mg/dL)
Creatinine 95 µmol/L (1.1 mg/dL)
Sodium 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L)
Potassium 4.56 mmol/L (4.56 mEq/L)
Glucose 6.8 mmol/L (121.4 mg/dL)
PaO2 62.1 mmHg
PaCO2 33.8 mmHg
sat O2 91.2%
pH 7.41
87](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpc-4-1-5-rs-pneum-pathlec-view-100707013900-phpapp01/75/Pathology-of-Pneumonia-87-2048.jpg)






![Pneumonia
Hospital Day 3 laboratory findings
Leukocytes 22.4 x 109/L (22 400/µL)
Haemoglobin 6.1 mmol/L (9.8 g/dL)
Haematocrit 0.30 (35 mL/dL)
Platelets 395 x 109/L (39 500/µL)
C-reactive protein 394.2 mg/dL [<5]
Blood urea nitrogen 16.6 nmol/L(22.7 mg/dL)
Creatinine 145 µmol/L (1.7 mg/dL)
Sodium 138 mmol/L (138 mEq/L)
Potassium 3.88 mmol/L (3.88 mEq/L)
Glucose 8.2 mmol/L (146.4 mg/dL)
PaO2 55.2 mmHg
PaCO2 30.1 mmHg
sat O2 86.9%
pH 7.46
94](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpc-4-1-5-rs-pneum-pathlec-view-100707013900-phpapp01/75/Pathology-of-Pneumonia-94-2048.jpg)


