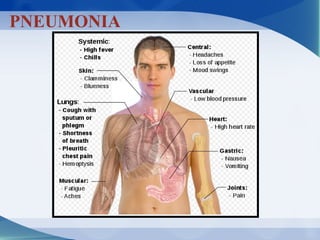
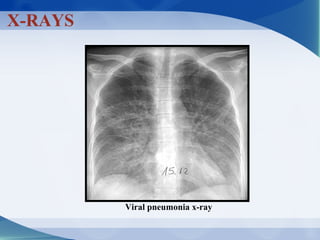
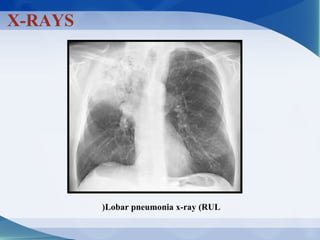
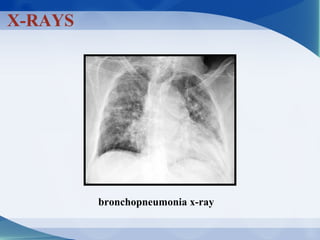
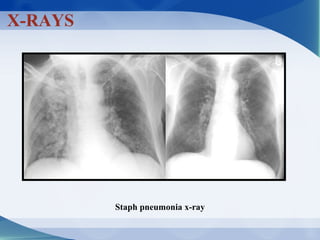
Pneumonia can be classified in several ways, including by anatomical location (lobar, bronchopneumonia, interstitial), etiology (bacterial, viral, fungal, mycobacterial, parasitic, non-infectious), and age of the patient. Common causative pathogens vary by age group. Hospitalization is often required for young children, immunocompromised patients, or those with severe symptoms. Recurrent pneumonia can be caused by hereditary disorders impacting immunity or airway function. Bacterial pneumonia results in different pathology depending on the invading organism. Viral pneumonia predisposes to secondary bacterial infection by disrupting host defenses.