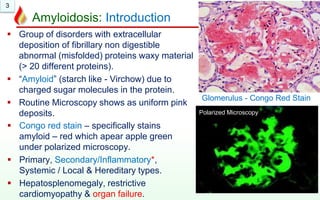
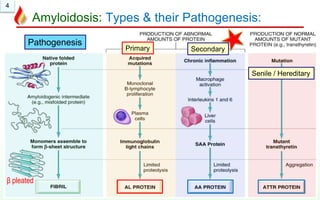
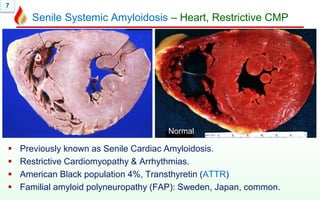
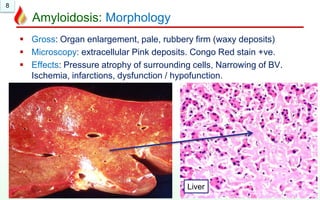
The document discusses amyloidosis, a group of disorders involving the deposition of abnormal proteins outside cells. There are different types including primary, secondary, systemic, localized, and hereditary amyloidosis. Secondary amyloidosis is the most common type and is caused by chronic inflammation. Clinically, amyloidosis can lead to organ enlargement and failure of the liver, kidneys, brain, and heart. Under the microscope, amyloid deposits appear as extracellular pink proteins that stain positive with Congo red and appear apple green under polarized microscopy.