Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX





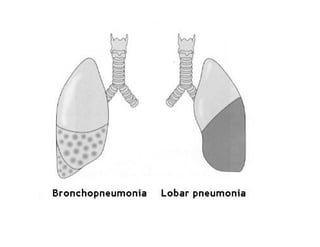


















Pneumonia is an acute inflammation of the lung parenchyma that presents with inflammatory infiltrate in the alveoli. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or other pathogens. Pneumonia is classified based on its etiology, morphology, whether it was community or hospital acquired, and the patient's immune status. The most common types are bronchopneumonia, which often affects young children and the elderly, and lobar pneumonia, typically caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in previously healthy adults. Complications can include abscess formation, empyema, scarring or systemic infection.























