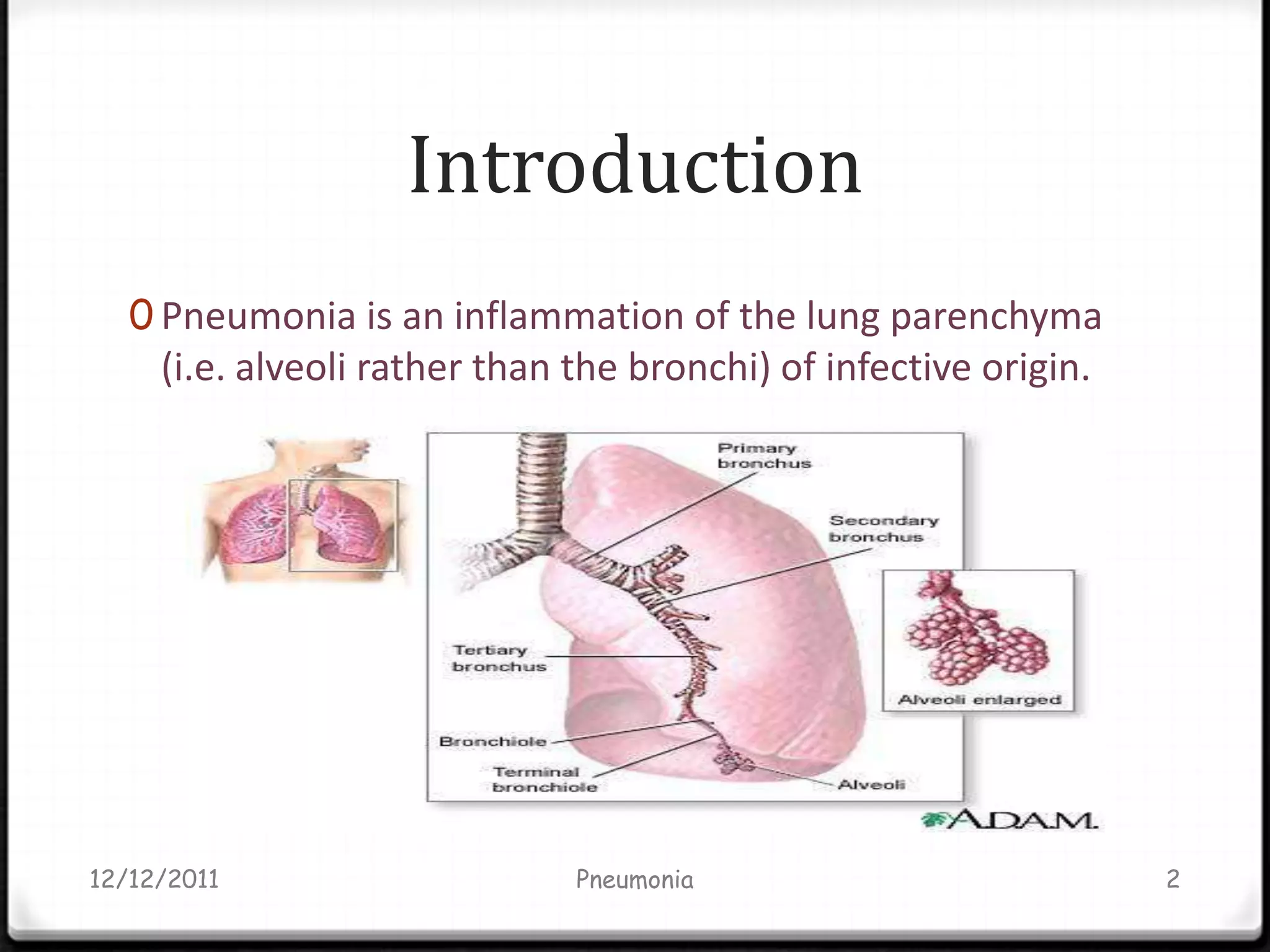
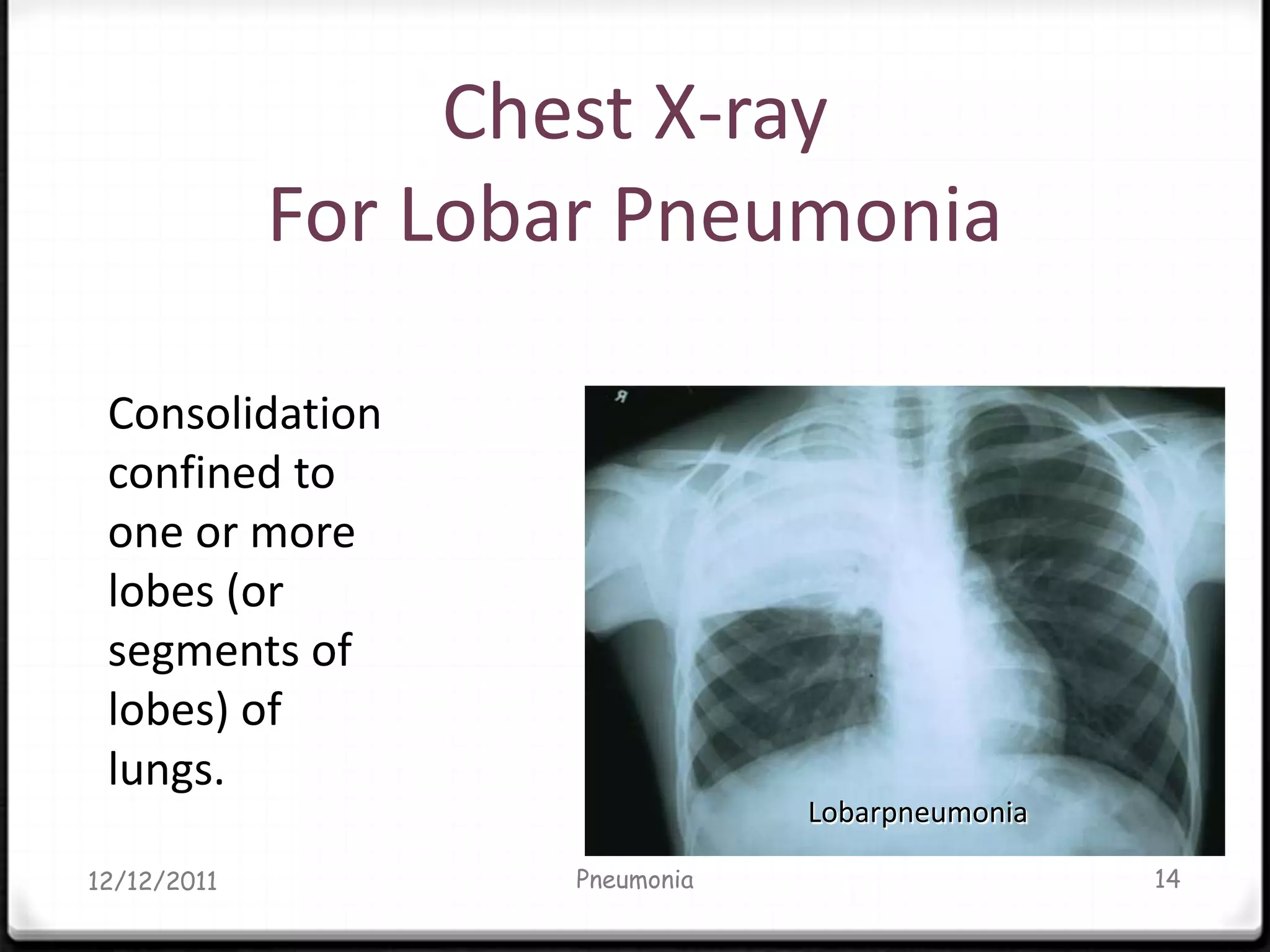
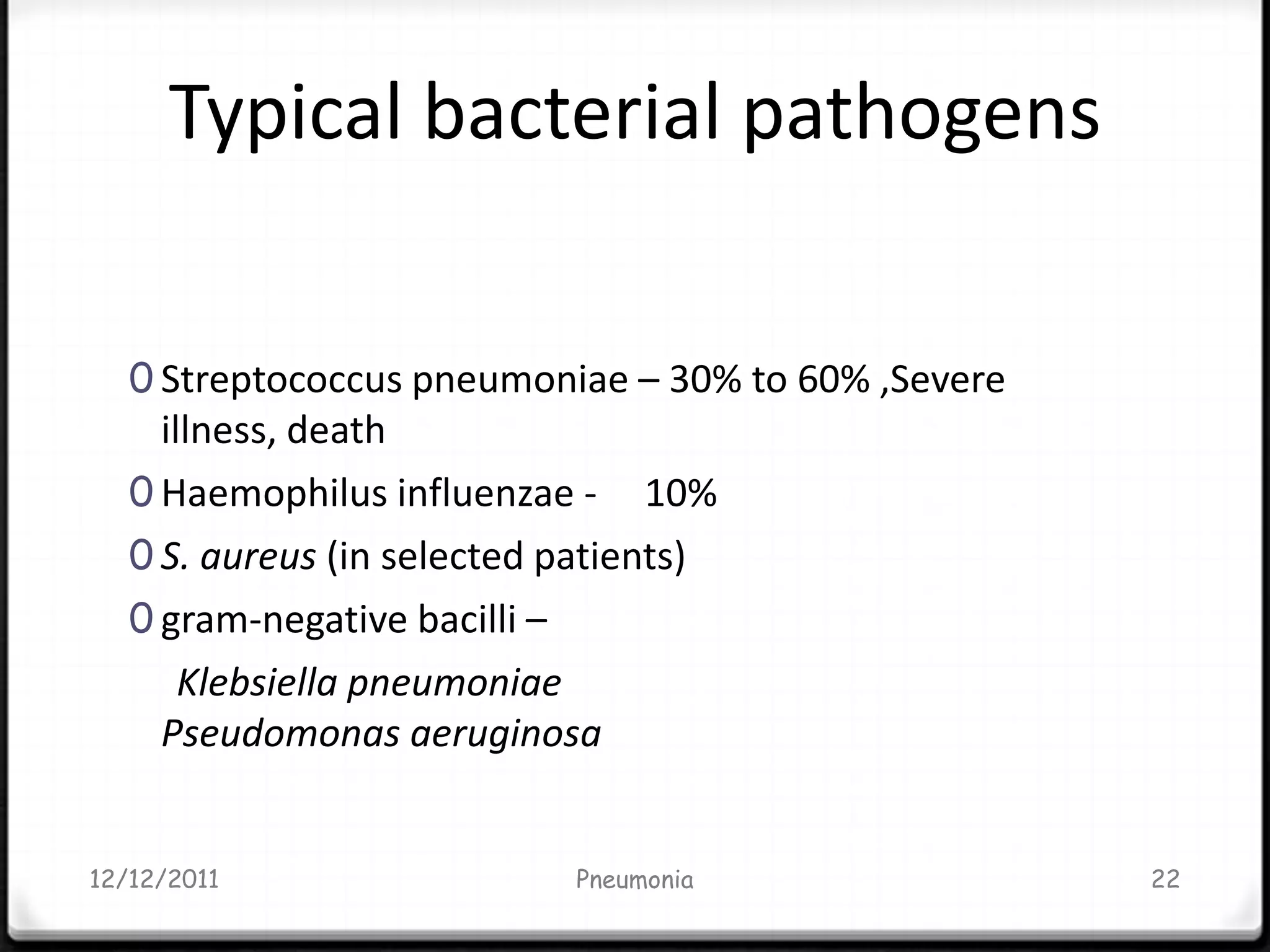
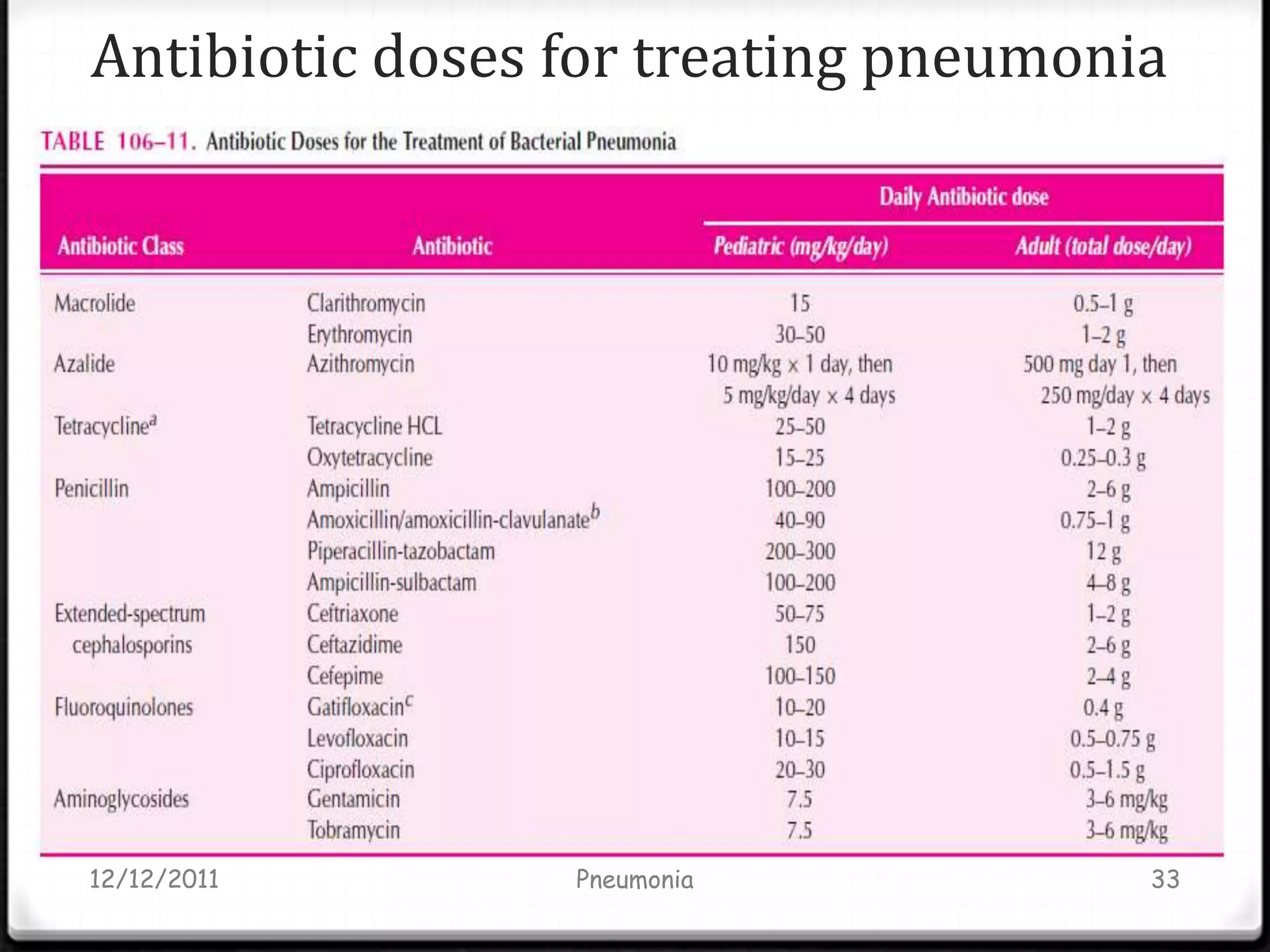
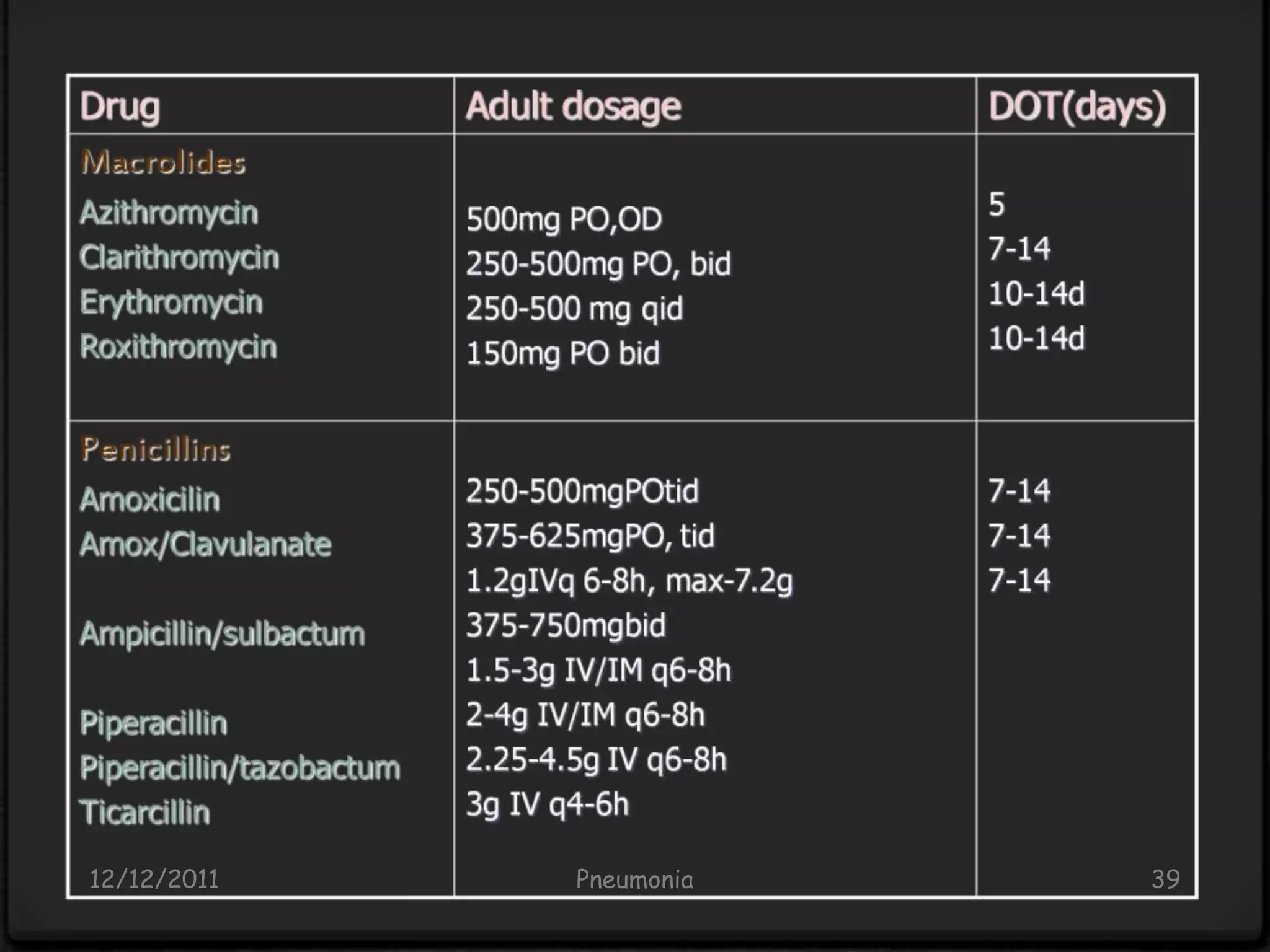
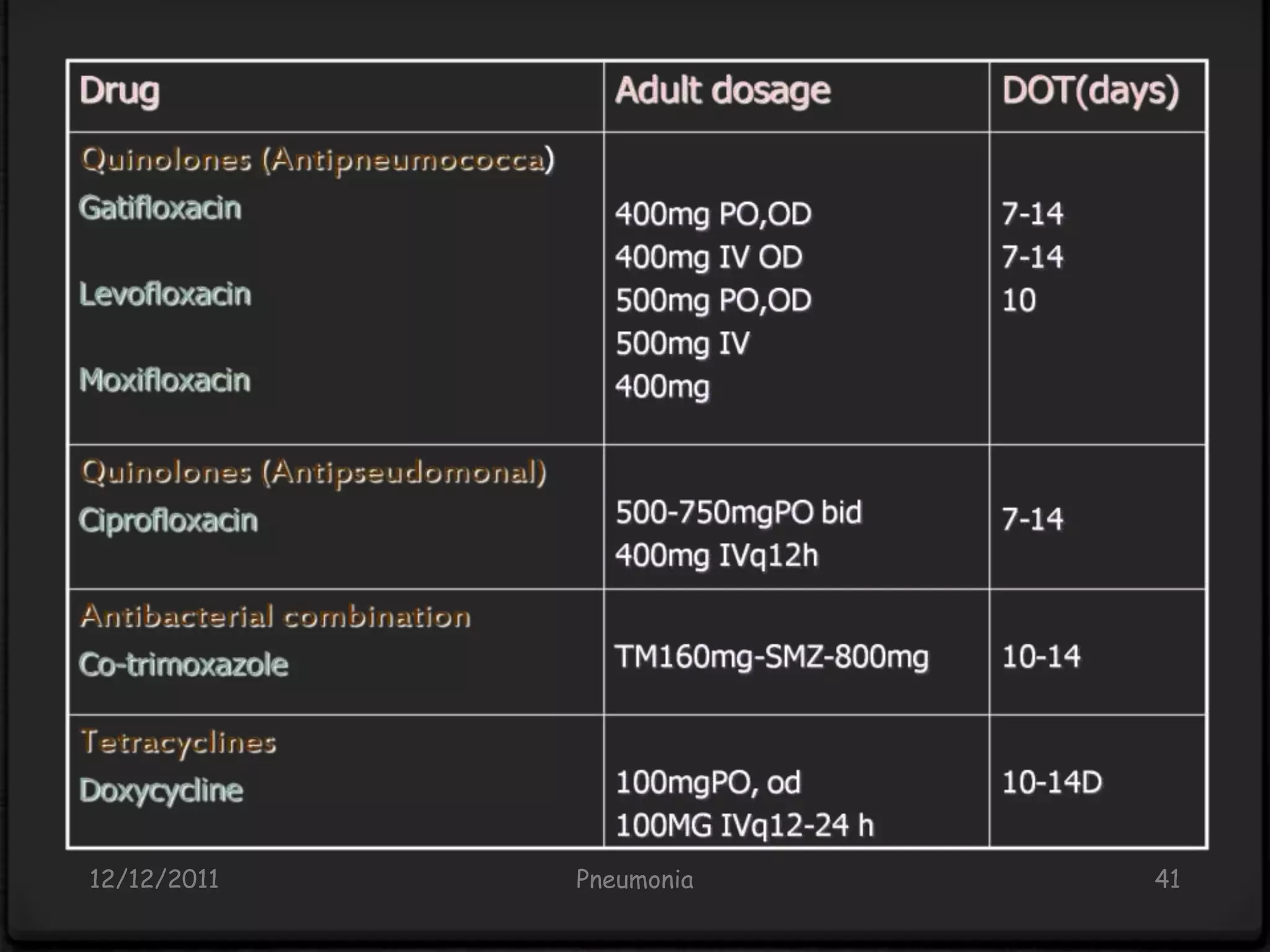
Pneumonia is an inflammatory lung condition caused by infection, usually bacterial or viral. It is characterized by consolidation of the lungs due to inflammatory exudate, bacteria, and white blood cells filling the alveoli. Pneumonia can be classified as lobar or bronchopneumonia based on location in the lungs and as community-acquired or hospital-acquired based on where infection was contracted. Treatment involves use of antibiotics to eradicate the infecting organism as well as supportive care like oxygen supplementation. Antibiotic selection is based on suspected pathogen, patient age and health status, and severity of illness.