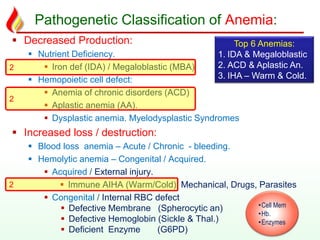
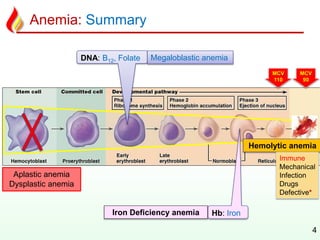
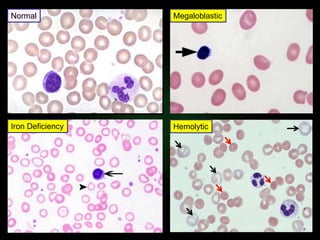
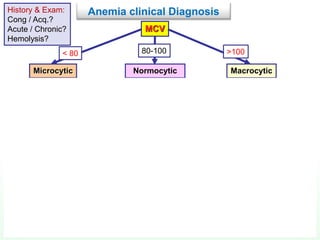
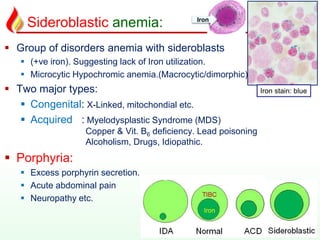
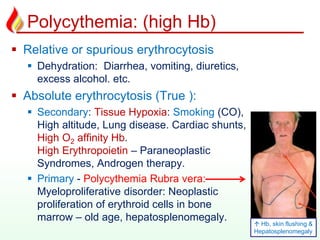
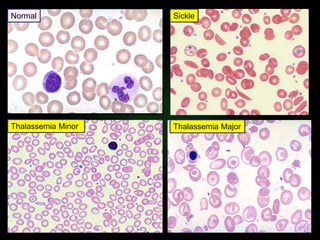
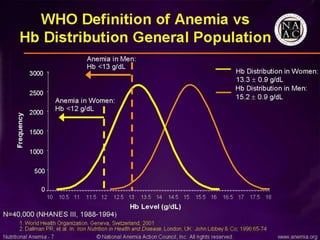
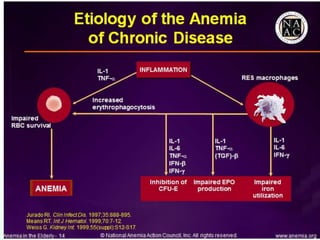
This document discusses various types of anemia classified by their pathogenetic mechanisms. The top 6 anemias are discussed in more detail and include iron deficiency anemia, megaloblastic anemia, anemia of chronic disease, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, and thalassemia. Diagnostic indicators are provided for differentiating between anemia types based on mean corpuscular volume, reticulocyte count, iron studies, and peripheral blood smears. Common causes, clinical manifestations, and treatments are summarized for several specific anemia conditions.