1pneumonia
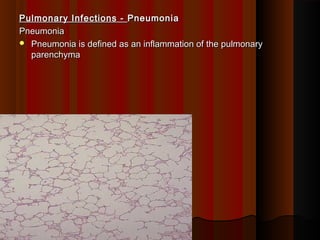
- 1. Pulmonary Infections -Pulmonary Infections - PneumoniaPneumonia PneumoniaPneumonia Pneumonia is defined as an inflammation of the pulmonaryPneumonia is defined as an inflammation of the pulmonary parenchymaparenchyma
- 2. ClassificationClassification A) According to immune statusA) According to immune status Primary Pneumonia: Community acquiredPrimary Pneumonia: Community acquired Secondary Pneumonia (occurs in compromised host or Lungs)Secondary Pneumonia (occurs in compromised host or Lungs) BronchopneumoniaBronchopneumonia Nosocomial Pneumonia (hospital acquired)Nosocomial Pneumonia (hospital acquired) Aspiration pneumoniaAspiration pneumonia Pneumonia in the immmunocompromised patientPneumonia in the immmunocompromised patient
- 3. ClassificationClassification B) Anatomical classificationB) Anatomical classification Lobar PneumoniaLobar Pneumonia Lobular Pneumonia (bronchopneumonia if bilateral)Lobular Pneumonia (bronchopneumonia if bilateral) Interstitial PneumoniaInterstitial Pneumonia C)Aetiological classificationC)Aetiological classification Infective-Bacteria, Virus, Fungi, Protozoa etc.Infective-Bacteria, Virus, Fungi, Protozoa etc. AllergicAllergic Chemical agents: Irritant gases and liquid e.g. ammonia, vomitusChemical agents: Irritant gases and liquid e.g. ammonia, vomitus Physical agents: RadiationPhysical agents: Radiation
- 4. Predisposing factorsPredisposing factors • A number of potent defense mechanisms clear or destroy anyA number of potent defense mechanisms clear or destroy any bacteria inhaled with air or accidently deposited in the airwaybacteria inhaled with air or accidently deposited in the airway passage.passage. The following 3 defense mechanisms play vital role in preventing fromThe following 3 defense mechanisms play vital role in preventing from any sort of micro organisms infection that reaches our airwayany sort of micro organisms infection that reaches our airway passages.passages. a. Nasal clearancea. Nasal clearance b. Tracheobronchial clearanceb. Tracheobronchial clearance c. Alveolar clearancec. Alveolar clearance
- 5. a.a.Nasal clearanceNasal clearance Particles including inhaled microorganisms are cleared byParticles including inhaled microorganisms are cleared by sneezing or blowing from the nose. Those microorganisms whichsneezing or blowing from the nose. Those microorganisms which manage to escape down are swallowed.manage to escape down are swallowed. b.b.Tracheobronchial clearanceTracheobronchial clearance Due to mucociliary action any particles or mocroorganismsDue to mucociliary action any particles or mocroorganisms deposited in the tracheobronchial tree are eventually either swalloweddeposited in the tracheobronchial tree are eventually either swallowed or expectorated.or expectorated.
- 6. c. Alveolar clearancec. Alveolar clearance Any bacteria or solid particles deposited in the alveoli areAny bacteria or solid particles deposited in the alveoli are phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages.phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages. Some of the particles are carried to regional lymph nodes and viaSome of the particles are carried to regional lymph nodes and via the blood stream, they reach other parts of the body.the blood stream, they reach other parts of the body.
- 7. Pathogenesis of PneumoniaPathogenesis of Pneumonia Pneumonia may occurPneumonia may occur When these defense mechanisms are impaired Or whenever theWhen these defense mechanisms are impaired Or whenever the resistant of the host in general is lowered.resistant of the host in general is lowered. Infection of lung tissueInfection of lung tissue Following factors may interfere with clearing mechanisms.Following factors may interfere with clearing mechanisms. Loss or suppression of cough reflexLoss or suppression of cough reflex - due to coma, drugs, anaesthesia, neuromuscular disorders.- due to coma, drugs, anaesthesia, neuromuscular disorders. These condition can lead to aspiration of gastric contents too.These condition can lead to aspiration of gastric contents too.
- 8. Injury to mucociliary apparatusInjury to mucociliary apparatus This can be due to cigarette smoking, due to inhalation of hot orThis can be due to cigarette smoking, due to inhalation of hot or corrosive gasses, viral diseases, or genetic diseases.corrosive gasses, viral diseases, or genetic diseases. Interference with phagocytic or bactericidal action ofInterference with phagocytic or bactericidal action of alveolar macrophagesalveolar macrophages This can be due to alcohol, tobacco, smoke, anoxia, or oxygenThis can be due to alcohol, tobacco, smoke, anoxia, or oxygen intoxication.intoxication.
- 9. Pulmonary congestion & oedemaPulmonary congestion & oedema Accumulations of secretionsAccumulations of secretions – cystic fibrosis &– cystic fibrosis & bronchial obstructionbronchial obstruction
- 10. LOBAR PNEUMONIALOBAR PNEUMONIA : -: - When a part of lobe, entire lobe or lobes of one or both lungs areWhen a part of lobe, entire lobe or lobes of one or both lungs are involvedinvolved Etiology: -Etiology: - Streptococcus PneumoniaeStreptococcus Pneumoniae StaphylococcalStaphylococcal H. InfluenzaeH. Influenzae Pseudomonas.Pseudomonas.
- 11. 4 sequences or stages4 sequences or stages 1. Stage of Congestion1. Stage of Congestion : - Lasts for 1 – 2 days.: - Lasts for 1 – 2 days. MicroMicro Dilated & congested blood vessels with oedema fluid filled in air sacsDilated & congested blood vessels with oedema fluid filled in air sacs (alveoli) with plenty of bacteria & a few neutrophil(alveoli) with plenty of bacteria & a few neutrophil Gross : -Gross : -Lobe is enlarged, heavy, congested & exudes pink frothyLobe is enlarged, heavy, congested & exudes pink frothy fluid on cut surface.fluid on cut surface.
- 12. 2. Stage of Red Hepatization2. Stage of Red Hepatization : - Lasts – 2 – 4 days: - Lasts – 2 – 4 days MICRO : -MICRO : - Oedema fluid replaced by fibrin threads with markedOedema fluid replaced by fibrin threads with marked neutrophils & R.B.C., Neutrophils with engulfed bacteria & theneutrophils & R.B.C., Neutrophils with engulfed bacteria & the alveolar septa is less prominent than stage I.alveolar septa is less prominent than stage I. GROSS : -GROSS : - Liver like red, firm, airless. On cut section, red – pink,Liver like red, firm, airless. On cut section, red – pink, dry, granular to look at.dry, granular to look at.
- 13. 3. Stage of Grey Hepatization3. Stage of Grey Hepatization : - 4 – 8 days: - 4 – 8 days MICRO : -MICRO : - Due to R.B.C. disintegration and numerous fibrinDue to R.B.C. disintegration and numerous fibrin strands and their contraction causes a separation of exudates fromstrands and their contraction causes a separation of exudates from the alveolar walls.the alveolar walls. Exudates are now less rich in bacteria, Rbc and inflammatory cells.Exudates are now less rich in bacteria, Rbc and inflammatory cells. GROSS : -GROSS : - Firm, heavy with dry, granular and grey liver like.Firm, heavy with dry, granular and grey liver like. LessLess hyperaemiahyperaemia
- 14. 4. Stage of Resolution:4. Stage of Resolution: - 8 – 16 days.- 8 – 16 days. MICRO : -MICRO : - Consolidated exudate within the alveolar spaces undergoesConsolidated exudate within the alveolar spaces undergoes progressive enzymatic digestion to produce a granular semisolidprogressive enzymatic digestion to produce a granular semisolid debris that is either resorbed, ingested by macrophages or cougheddebris that is either resorbed, ingested by macrophages or coughed upup Lungs return to normalLungs return to normal
- 16. This is a lobarThis is a lobar pneumonia in whichpneumonia in which consolidation of theconsolidation of the entire left upper lobeentire left upper lobe has occurred.has occurred.
- 18. Clinical signs and symptomsClinical signs and symptoms i. Fever and chillsi. Fever and chills ii. Productive cough with yellow-green (pus) or rusty (bloody) sputumii. Productive cough with yellow-green (pus) or rusty (bloody) sputum iii. Tachypnea(abnormal rapid breathing)iii. Tachypnea(abnormal rapid breathing) iv. Pleuritic chest painiv. Pleuritic chest pain v. Decreased breath sounds, bronchial breath sounds ,v. Decreased breath sounds, bronchial breath sounds , crepitations(crackling sound), and dullness to percussioncrepitations(crackling sound), and dullness to percussion Nonspecific symptoms Most patients also have:Nonspecific symptoms Most patients also have: Fatigue, Myalgia(muscles pain), Abdominal pain, Anorexia,Fatigue, Myalgia(muscles pain), Abdominal pain, Anorexia, HeadacheHeadache
- 19. Lab: Elevated WBCLab: Elevated WBC countcount Chest x-rayChest x-ray i. Lobar: lobar or segmental consolidation (opacification)i. Lobar: lobar or segmental consolidation (opacification) ii. Bronchopneumonia: patchy opacificationii. Bronchopneumonia: patchy opacification iii. Pleural effusioniii. Pleural effusion Clinical keys: identification of the organism and early treatment withClinical keys: identification of the organism and early treatment with antibioticsantibiotics
- 20. X-Ray showing Right middle lobe pneumoniaX-Ray showing Right middle lobe pneumonia
- 21. Chest x-ray demonstrating complete right upper lobe consolidation, consistent with aChest x-ray demonstrating complete right upper lobe consolidation, consistent with a lobar pneumonia.lobar pneumonia.
- 24. BronchopneumoniaBronchopneumonia This is the inflammatory consolidation of the surrounding alveoli of theThis is the inflammatory consolidation of the surrounding alveoli of the terminal bronchioles leading to patchy solidification of lung.terminal bronchioles leading to patchy solidification of lung. Etiology : -Etiology : - StaphylococcusStaphylococcus Haemophilus influenza,Haemophilus influenza, pseudomonaspseudomonas & E.coli.& E.coli.
- 25. This is more common in elderly or children i.e extremes of age due toThis is more common in elderly or children i.e extremes of age due to viral or other bacterial infections.viral or other bacterial infections. Usually secondary to other conditions associated with local andUsually secondary to other conditions associated with local and general defense mechanisms:general defense mechanisms: - viral infections (influenza, measles)- viral infections (influenza, measles) - aspiration of food or vomitus- aspiration of food or vomitus - obstruction of a bronchus (foreign body or neoplasm)- obstruction of a bronchus (foreign body or neoplasm) - inhalation of irritant gases- inhalation of irritant gases - major surgery- major surgery - malnutrition- malnutrition
- 26. PATHOLOGYPATHOLOGY : -: - GROSS : -GROSS : - Patchy areas of consolidation in one or more lobes frequently bilateral andPatchy areas of consolidation in one or more lobes frequently bilateral and more often involving the lower zone due to gravitational reasons.more often involving the lower zone due to gravitational reasons.
- 27. Here is example of aHere is example of a bronchopneumonia. Thebronchopneumonia. The lighter areas that appearlighter areas that appear to be raised on cutto be raised on cut surface from thesurface from the surrounding lung are thesurrounding lung are the areas of consolidation ofareas of consolidation of the lung.the lung.
- 29. This radiographThis radiograph demonstrates patchydemonstrates patchy infiltrates consistent with ainfiltrates consistent with a bronchopneumonia from abronchopneumonia from a bacterial infection. Typicalbacterial infection. Typical organisms includeorganisms include Streptococcus pneumoniae,Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus,Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa,Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Hemophilus influenzae,Hemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae,Klebsiella pneumoniae, among others.among others.
- 32. Bronchopneumonia 1. Usually occurs in persons with pre existing lung disease 2. Common in extreme of age 3. Usually by staphylococci 4. Patchy consolidation involving one lobe or but often multilobular 5. Usually bi lateral & basal 6. Complete resolution uncommon, may lead to complications Lobar PneumoniaLobar Pneumonia 1.1. Usually occurs in healthyUsually occurs in healthy young adultyoung adult 2.2. Common in young ageCommon in young age 3.3. Usually by PneumococciUsually by Pneumococci 4.4. Lobar consolidationLobar consolidation involving large portion ofinvolving large portion of one lobe or entire lobeone lobe or entire lobe 5.5. Can effect any lobe – uni orCan effect any lobe – uni or bi lateralbi lateral 6.6. Complete resolution usuallyComplete resolution usually resolution takes placeresolution takes place
- 33. INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAINTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIA : -Atypical Pneumonia: -Atypical Pneumonia This is characterized by patchy inflammatory changes largelyThis is characterized by patchy inflammatory changes largely confined to interstitial tissues of lung without any alveolar exudate.confined to interstitial tissues of lung without any alveolar exudate. ETIOLOGYETIOLOGY : -: - Mycoplasma pneumonae, Respiratory syncytial virus (RV)Mycoplasma pneumonae, Respiratory syncytial virus (RV) Influenza virus, cytomegalo, pneumocystis jiroveci (pneumocystisInfluenza virus, cytomegalo, pneumocystis jiroveci (pneumocystis carinii )carinii ) More common in immunosuppressed state.More common in immunosuppressed state.
- 34. PATHOLOGYPATHOLOGY : -: - red blue colourred blue colour GROSS : -GROSS : - It may be patchy to massive involvement with heavyIt may be patchy to massive involvement with heavy congested &congested & subcrepitant lungs.subcrepitant lungs. Histo :Histo : Mainly interstitial infiltration of mononuclear cells with thickening ofMainly interstitial infiltration of mononuclear cells with thickening of alveolar septa.alveolar septa. Necrosis of bronchial epithelial lining & filled bronchiolar lumen withNecrosis of bronchial epithelial lining & filled bronchiolar lumen with secretions.secretions. A reactive change by multinuceated giant cells formation is shownA reactive change by multinuceated giant cells formation is shown by lining bronchiolar epithelium.by lining bronchiolar epithelium. Complications : -Complications : - Main complication is secondary bacterial infection or a reactiveMain complication is secondary bacterial infection or a reactive fibrosis of interstitial tissue.fibrosis of interstitial tissue.
- 35. Secondary bacterial infectionSecondary bacterial infection staphylococcistaphylococci
- 36. Nosocomial infection or Hospital acquired pneumoniaNosocomial infection or Hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP)(HAP):: - After 48 hours of admission to the hospital, often patients in ICU- After 48 hours of admission to the hospital, often patients in ICU - ↓ Local resistance to infection in lungs- ↓ Local resistance to infection in lungs - Intubation of respiratory tract- Intubation of respiratory tract - Altered normal flora due to antibiotics- Altered normal flora due to antibiotics - Mostly gram – negative enterobacteria or Staph aureus, E.coli,- Mostly gram – negative enterobacteria or Staph aureus, E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Bacteroides,Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Bacteroides,
- 37. Community acquired pneumoniaCommunity acquired pneumonia Commonest cause is due toCommonest cause is due to Streptococcus pneumoniae,Streptococcus pneumoniae, other areother are H. Influenzae,H. Influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae,Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis ,Moraxella catarrhalis , Staph. Aureus,Staph. Aureus, clamydia, etc.clamydia, etc.
- 38. The most common causes forThe most common causes for viral pneumoniaviral pneumonia are:are: InfluenzaInfluenza ParainfluenzaParainfluenza AdenovirusAdenovirus Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) - appears mostly in children- appears mostly in children CytomegalovirusCytomegalovirus - in immunocompromised hosts- in immunocompromised hosts
- 39. Modes of transmission of PneumoniaModes of transmission of Pneumonia Aspiration of organisms that colonize the oropharynx orAspiration of organisms that colonize the oropharynx or nasopharynxnasopharynx Inhalation of infectious agentsInhalation of infectious agents Haematogenous{formation of blood} spread from extra pulmonaryHaematogenous{formation of blood} spread from extra pulmonary sitesite Direct inoculation (tracheal intubations or stab wound to the chest) &Direct inoculation (tracheal intubations or stab wound to the chest) & contiguous spread from an adjacent site of infectioncontiguous spread from an adjacent site of infection
- 40. Complications of pneumoniaComplications of pneumonia Lung abscess formationLung abscess formation Pleural effusionPleural effusion Empyema{collection of pus in a cavity in the body}Empyema{collection of pus in a cavity in the body} Failure of resolution ⇒ intra-alveolar scarringFailure of resolution ⇒ intra-alveolar scarring Respiratory failureRespiratory failure Septicaemia and bacteraemiaSepticaemia and bacteraemia - Infective endocarditis- Infective endocarditis - Cerebral abscess / meningitis- Cerebral abscess / meningitis - Septic arthritis{pus formation in joints}- Septic arthritis{pus formation in joints} Fibrous scarring and pleural adhesionsFibrous scarring and pleural adhesions
- 41. Define Pneumonia & classify or causes of PneumoniaDefine Pneumonia & classify or causes of Pneumonia What are the complications of PneumoniaWhat are the complications of Pneumonia Give the pathogenesis of Lobar PneumoniaGive the pathogenesis of Lobar Pneumonia Give the morphology / stages of pneumoniaGive the morphology / stages of pneumonia Difference between lobar & bronchopneumoniaDifference between lobar & bronchopneumonia
