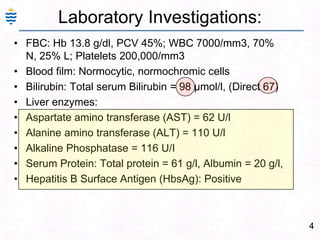
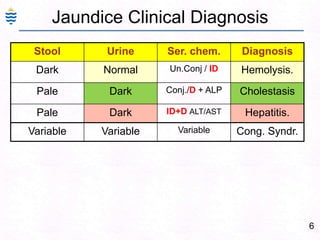
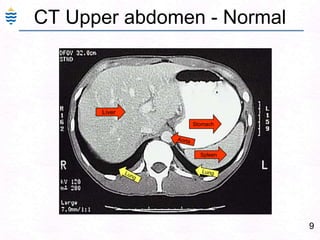
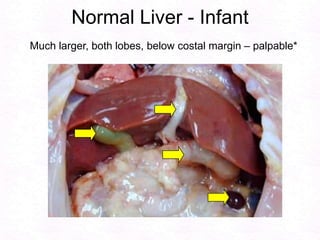
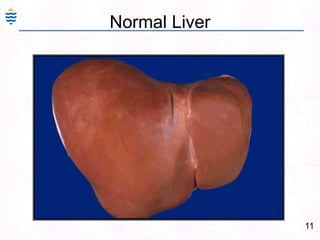
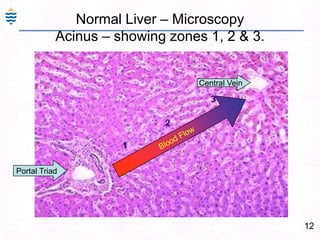
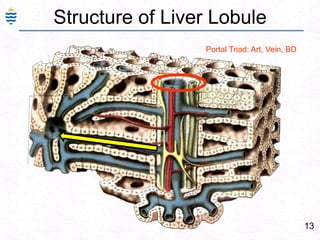
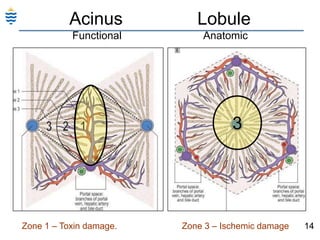
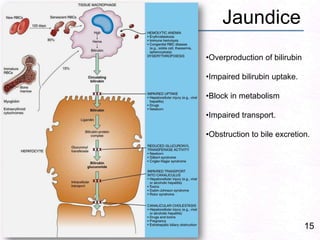
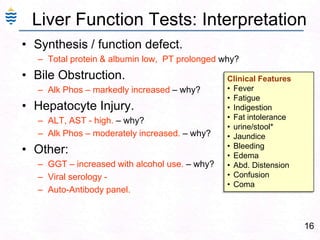
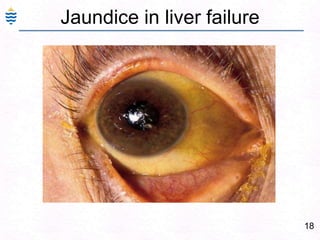
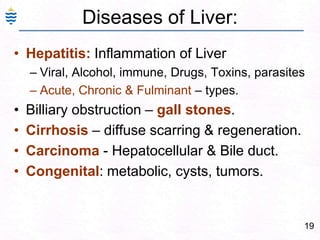
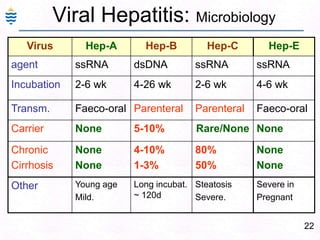
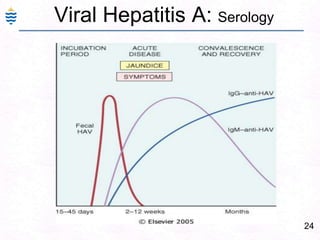
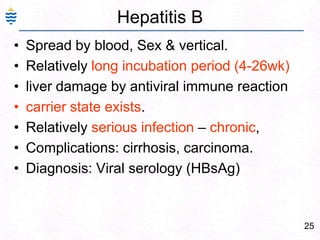
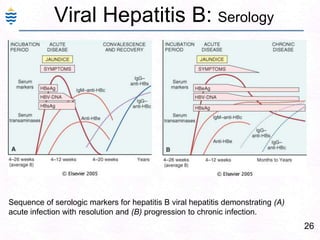
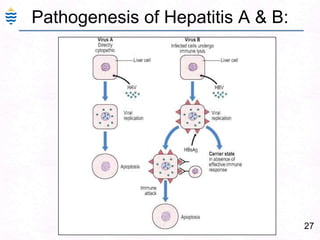
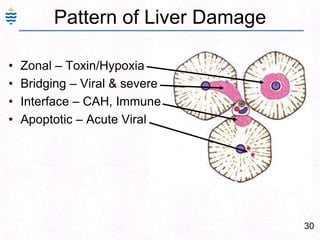
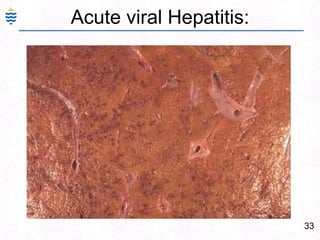
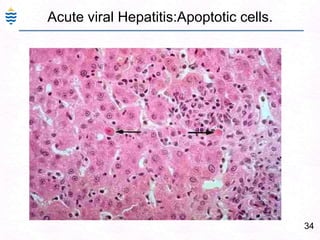
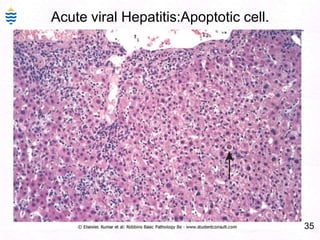
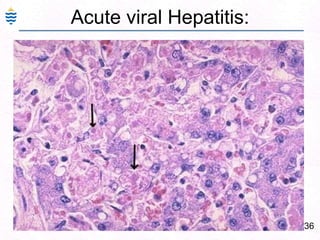
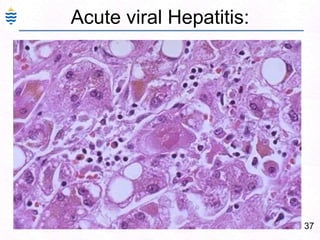
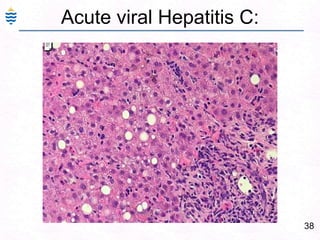
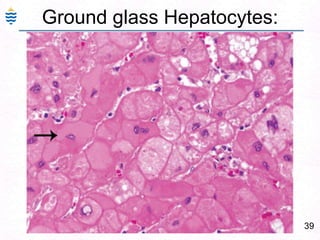
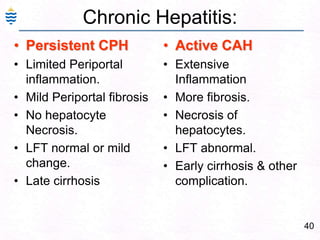
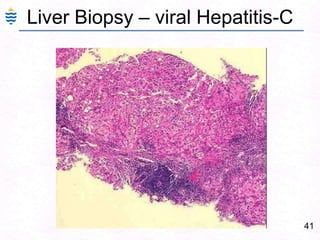
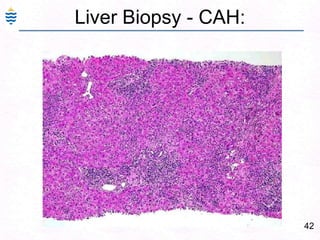
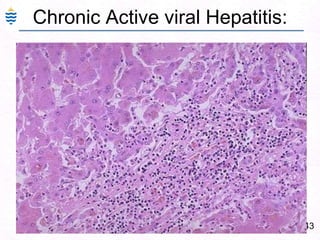
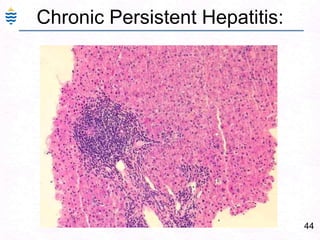
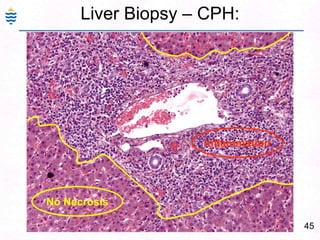
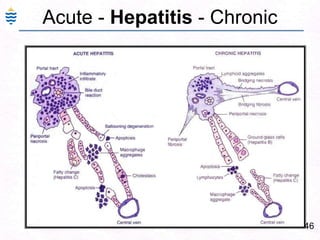
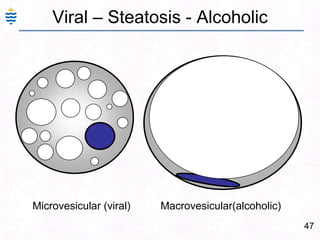
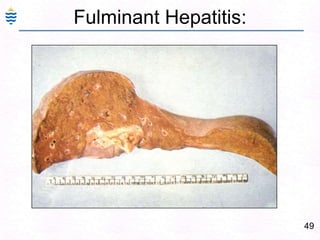
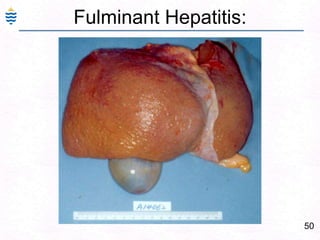
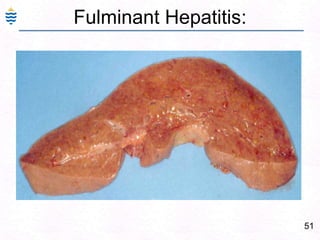
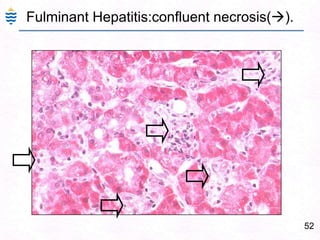
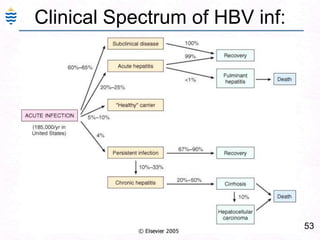
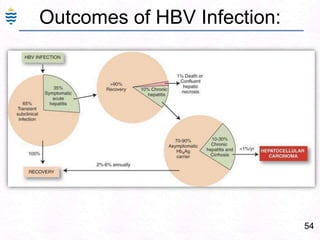
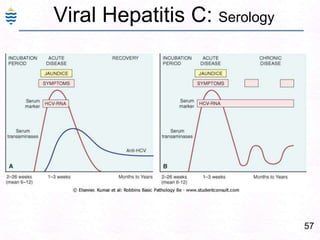
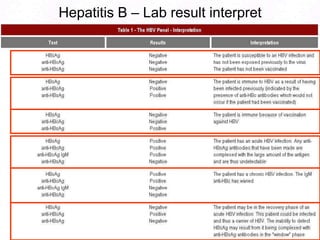
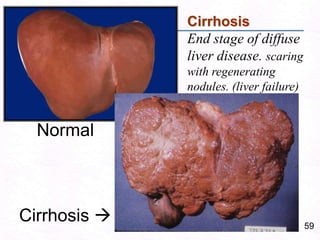
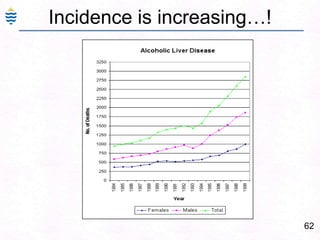
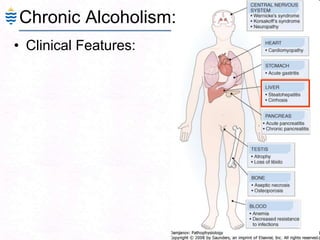
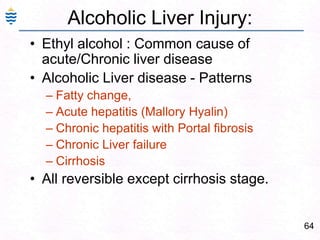
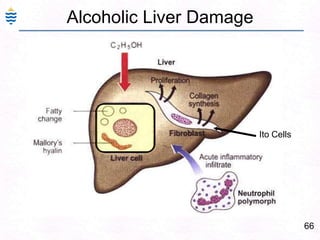
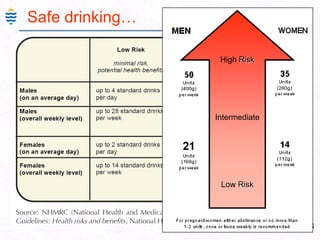
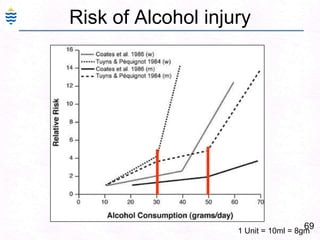
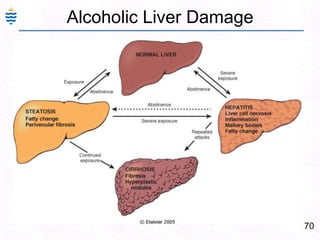
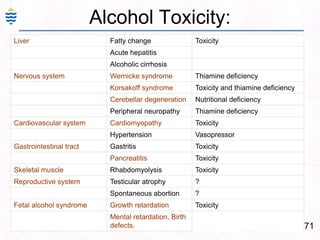
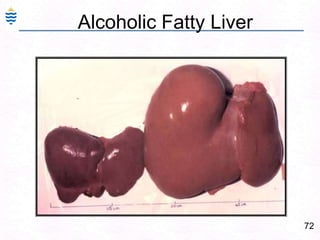
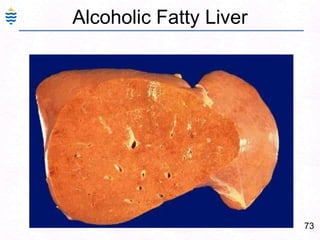
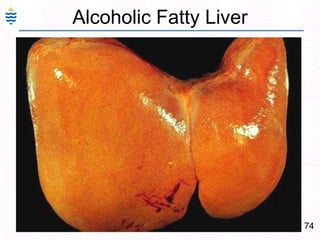
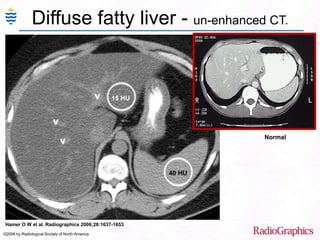
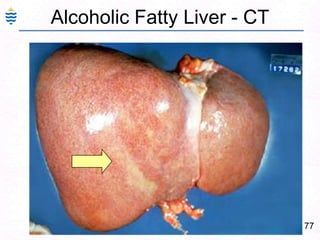
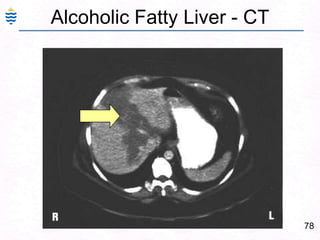
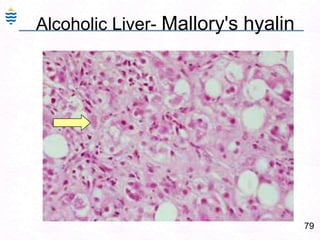
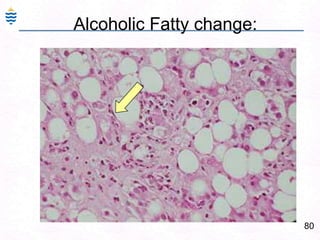
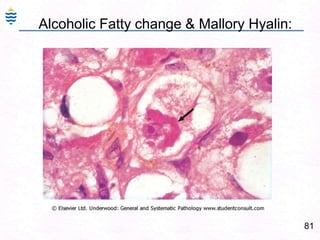
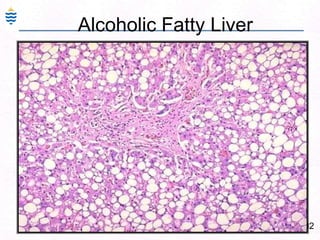
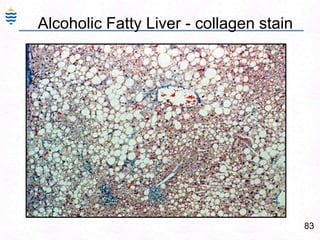
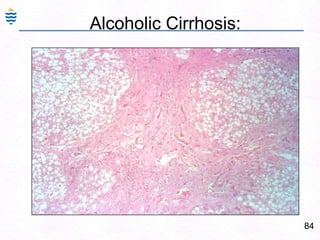
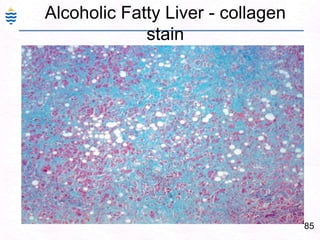
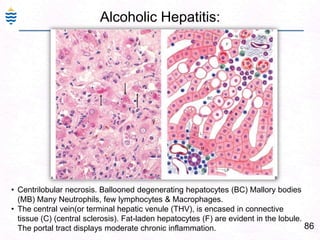
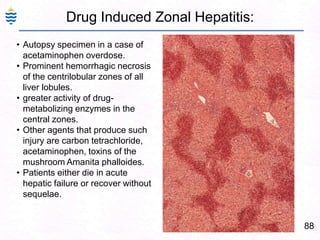
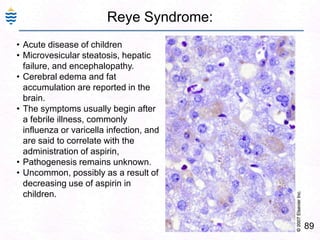
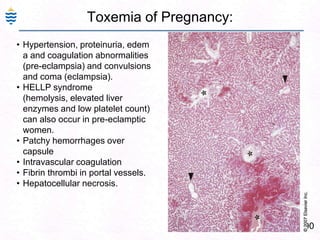
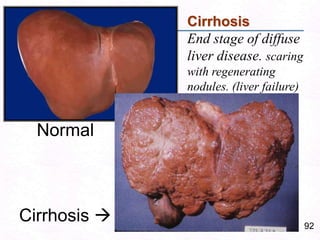
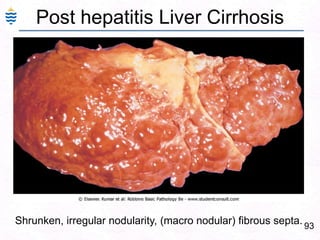
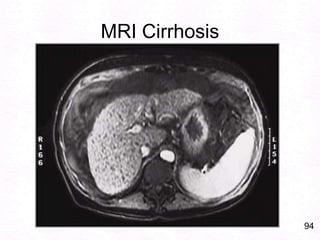
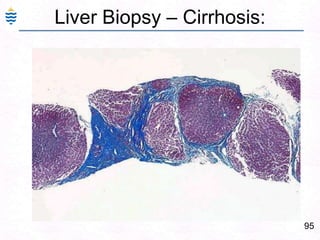
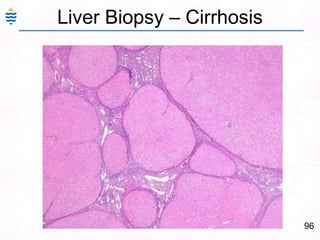
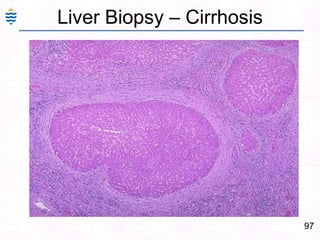
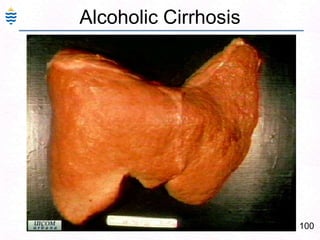
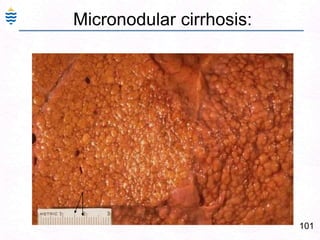
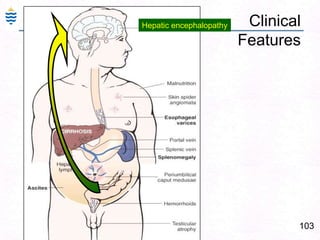
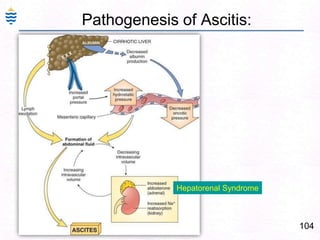
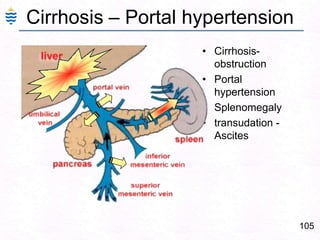
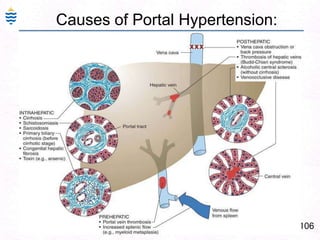
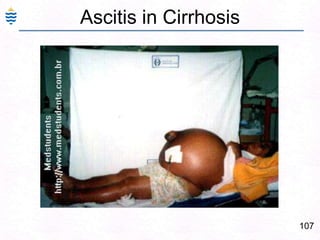
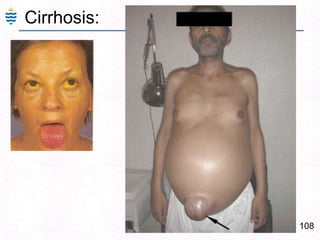
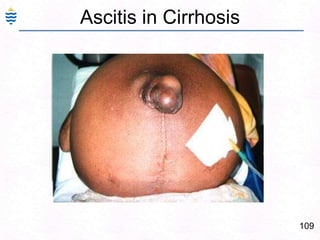
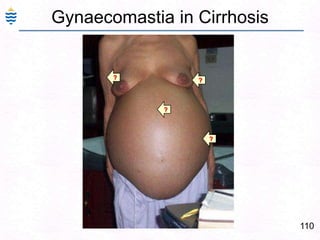
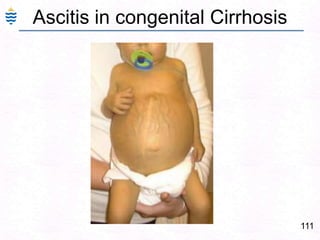
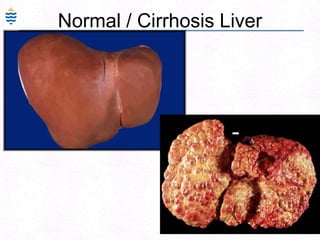
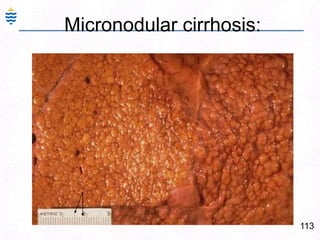
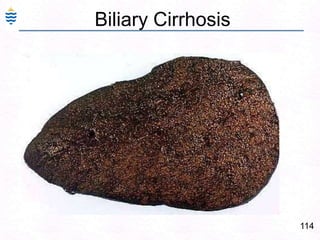
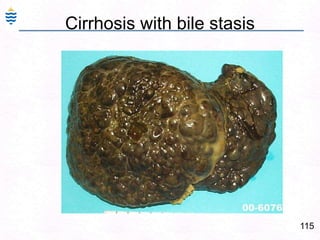
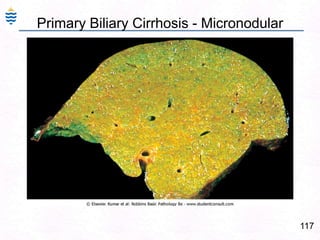
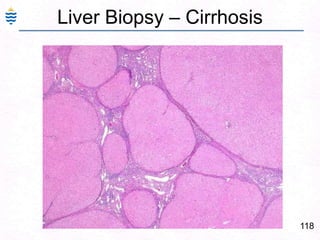
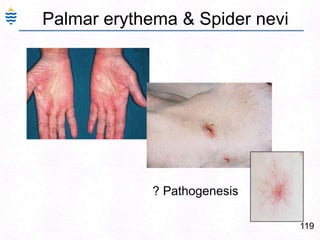
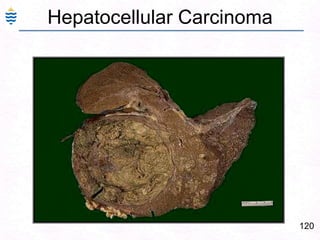
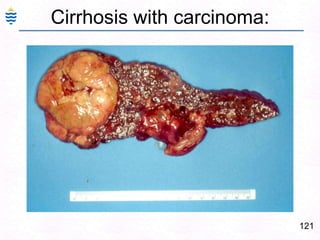
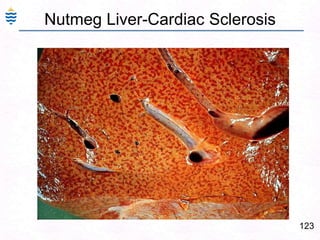
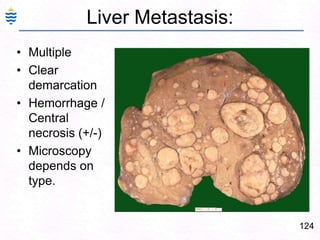
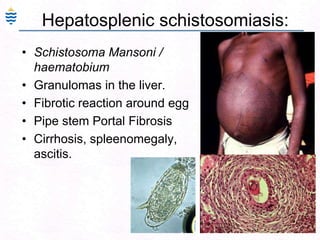
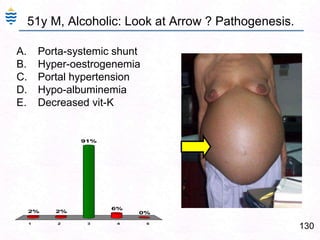
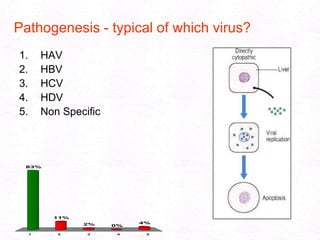
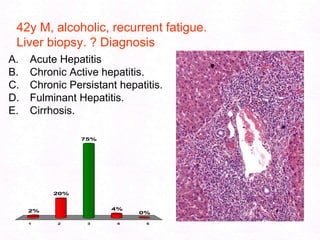
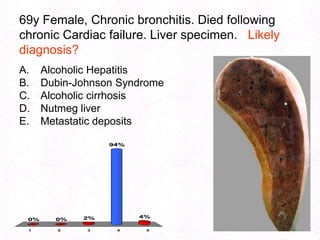
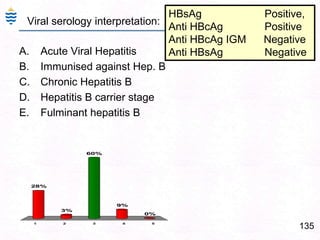
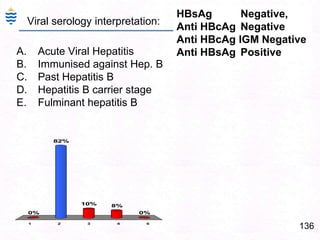
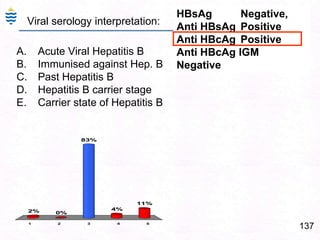
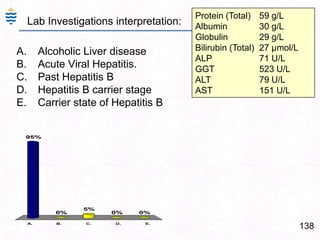
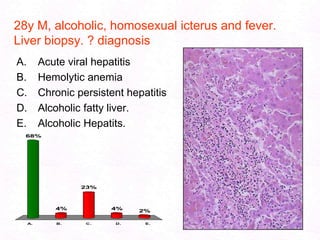
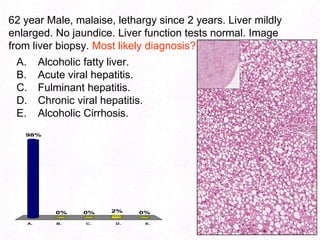
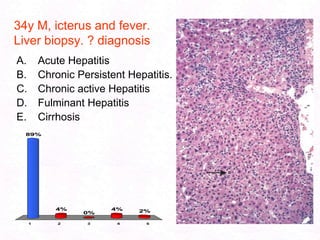
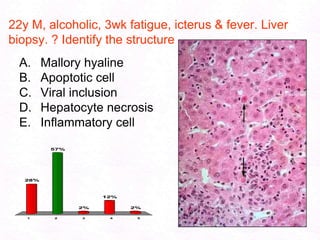
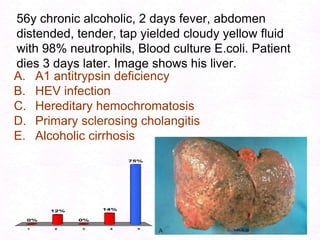
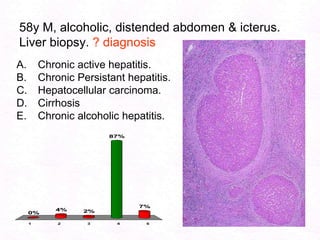
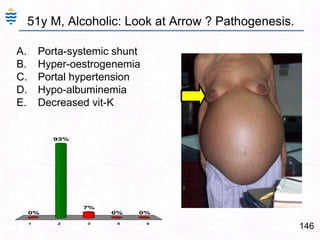
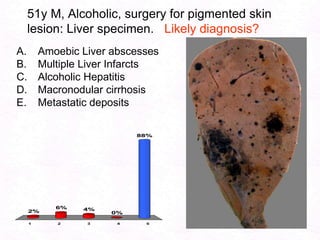
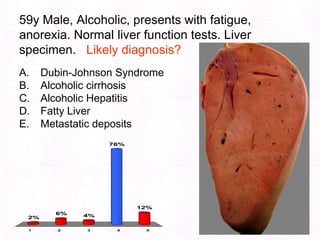
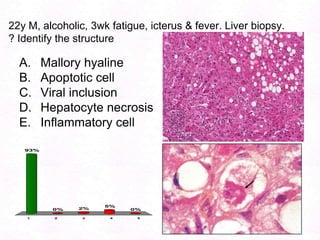
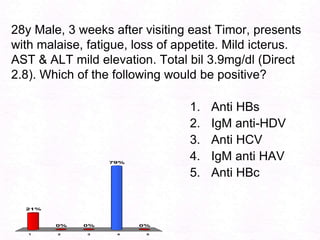
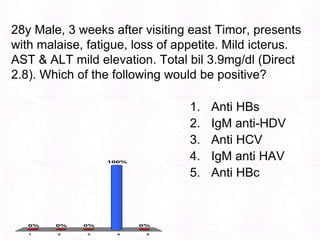
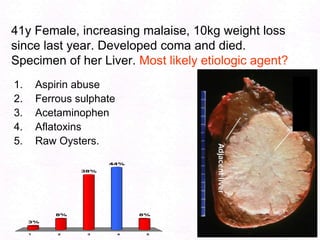
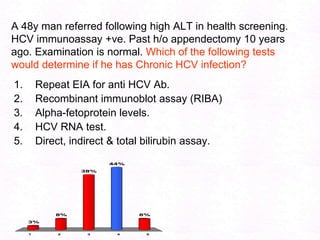
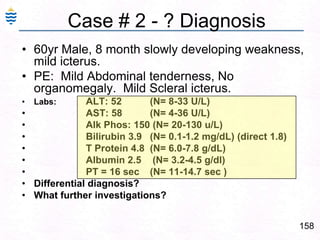
George, a 62-year-old farmer, presents with fatigue and yellowing of the eyes for 2 weeks. He reports weight loss but no other symptoms. Laboratory tests show elevated bilirubin and liver enzymes with positive hepatitis B surface antigen. The doctor considers diagnoses including acute or chronic hepatitis B, alcoholic liver disease, and other causes of jaundice. A liver biopsy may be needed to confirm chronic hepatitis B as the cause of the patient's chronic condition and symptoms.