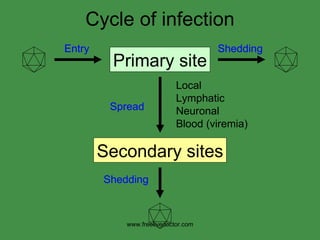
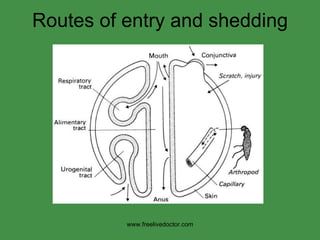
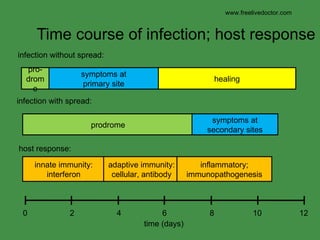
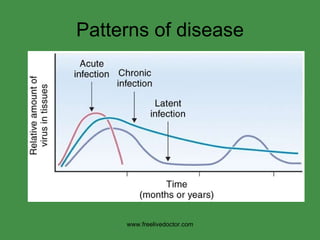
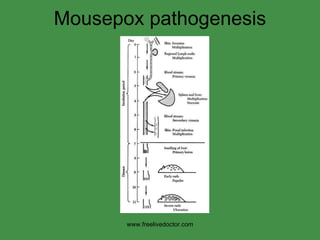
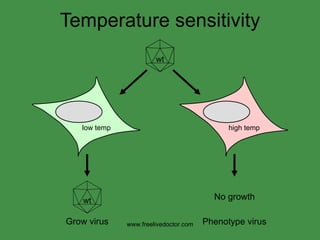
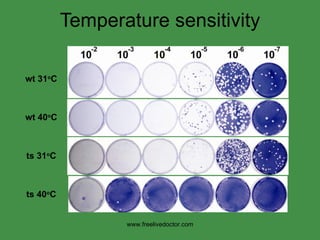
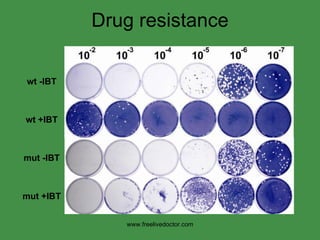
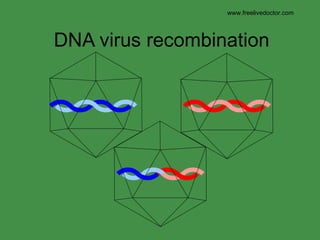
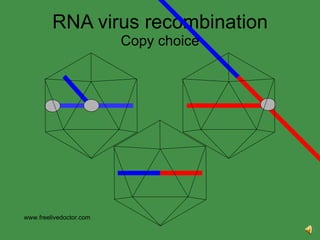
The document discusses viral pathogenesis and genetics. It describes the cycle of viral infection as entry into host cells, primary replication at the infection site, spread within the host, and shedding/transmission. It also discusses the effects of viruses on cells and the host organism. The genetic principles of viruses are explained as mutation, selection, and recombination, which impact viral evolution, management, and experimental study.