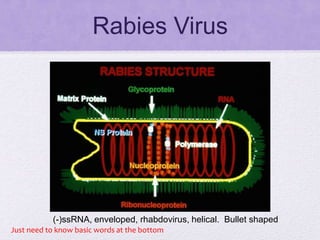
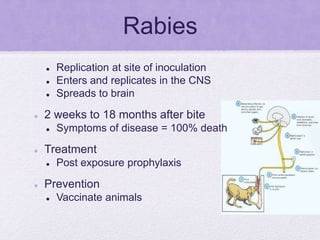
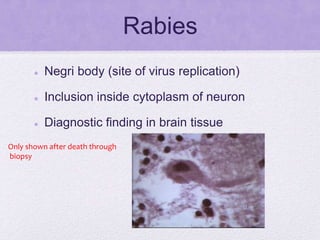
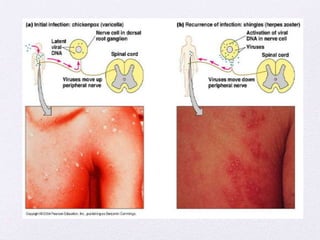
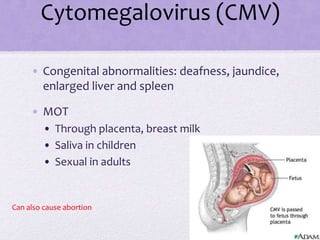
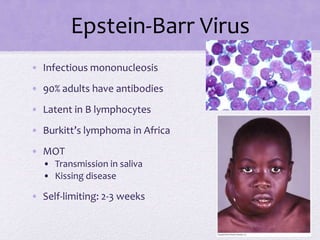
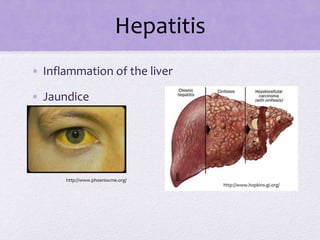
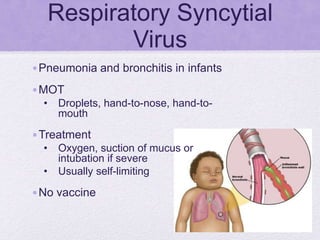
This document summarizes several viral pathogens including herpes viruses, hepatitis viruses, human papillomavirus, influenza virus, paramyxoviruses, enteroviruses, norovirus, arboviruses, HIV, Ebola virus, and hantavirus. It describes their viral structure, transmission methods, symptoms, treatments, and prevention methods. Key details provided on herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, varicella zoster virus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis A, B, and C viruses, influenza virus antigenic drift and shift, measles, mumps, respiratory syncytial virus, poliovirus, rotavirus, dengue,








![Togavirus
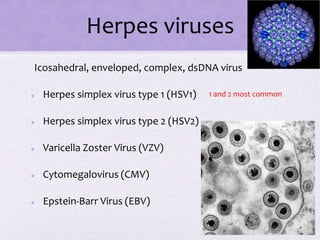
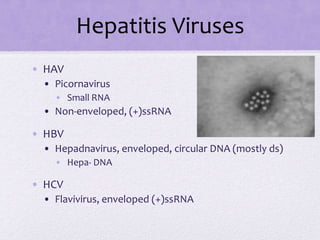
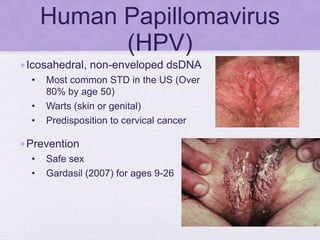
• Icosahedral, enveloped, (+)ssRNA
• Rubella
• Eastern Equine Encephalitis (arbovirus
[transmitted by insects])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/viralpathogens-140409143213-phpapp01/85/9-Viral-Pathogens-26-320.jpg)