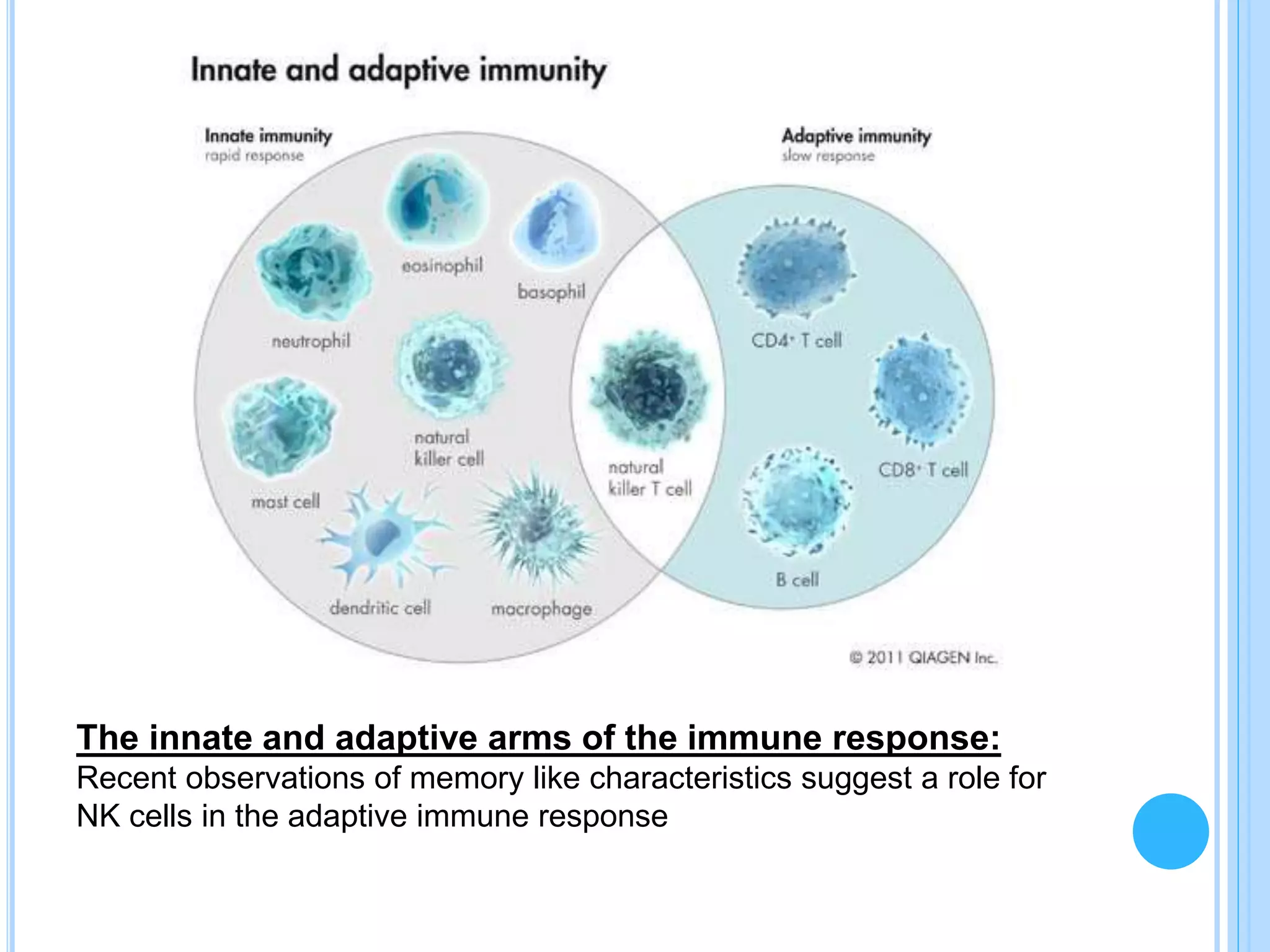
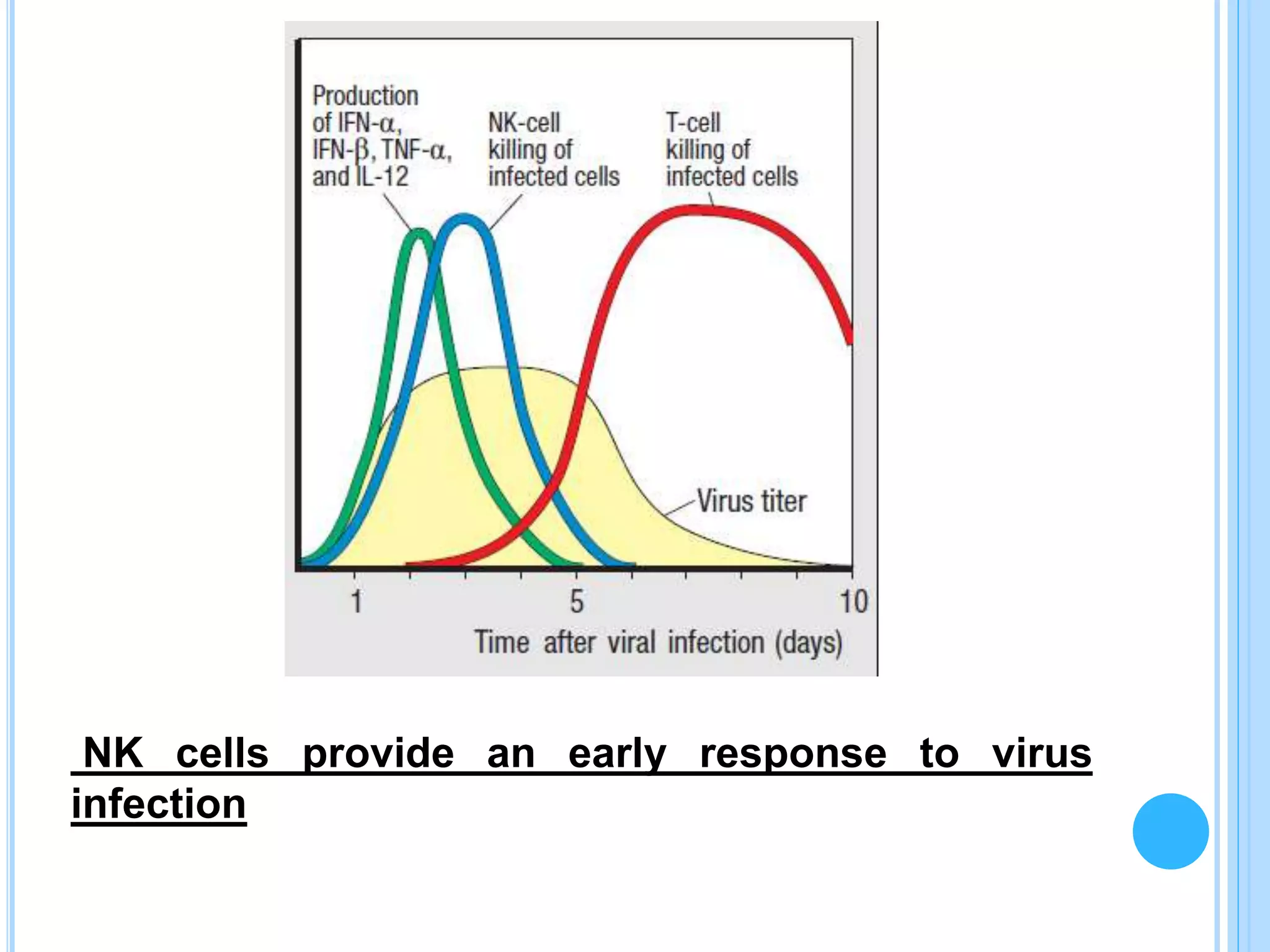
NK cells are lymphocytes that constitute 5-10% of cells in human peripheral blood. They play an important role in the innate immune response by killing infected or abnormal cells. NK cells are divided into two main subpopulations, CD56dim NK cells which are highly cytotoxic and mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and CD56bright NK cells which rapidly produce cytokines and chemokines upon activation. A specialized NK cell population in the uterus, uterine NK cells, help form the placenta during pregnancy by enlarging blood vessels to supply the growing fetus.