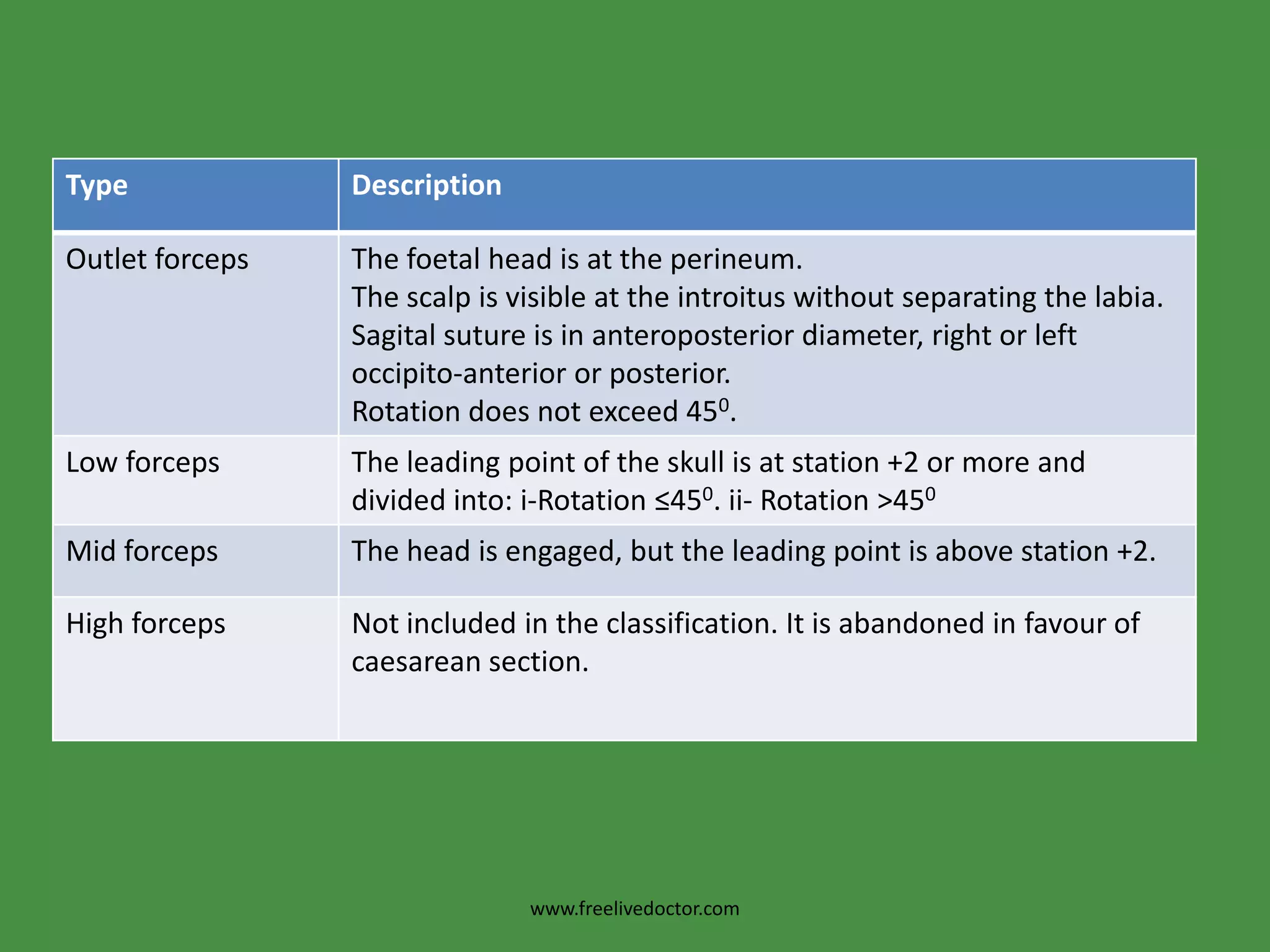
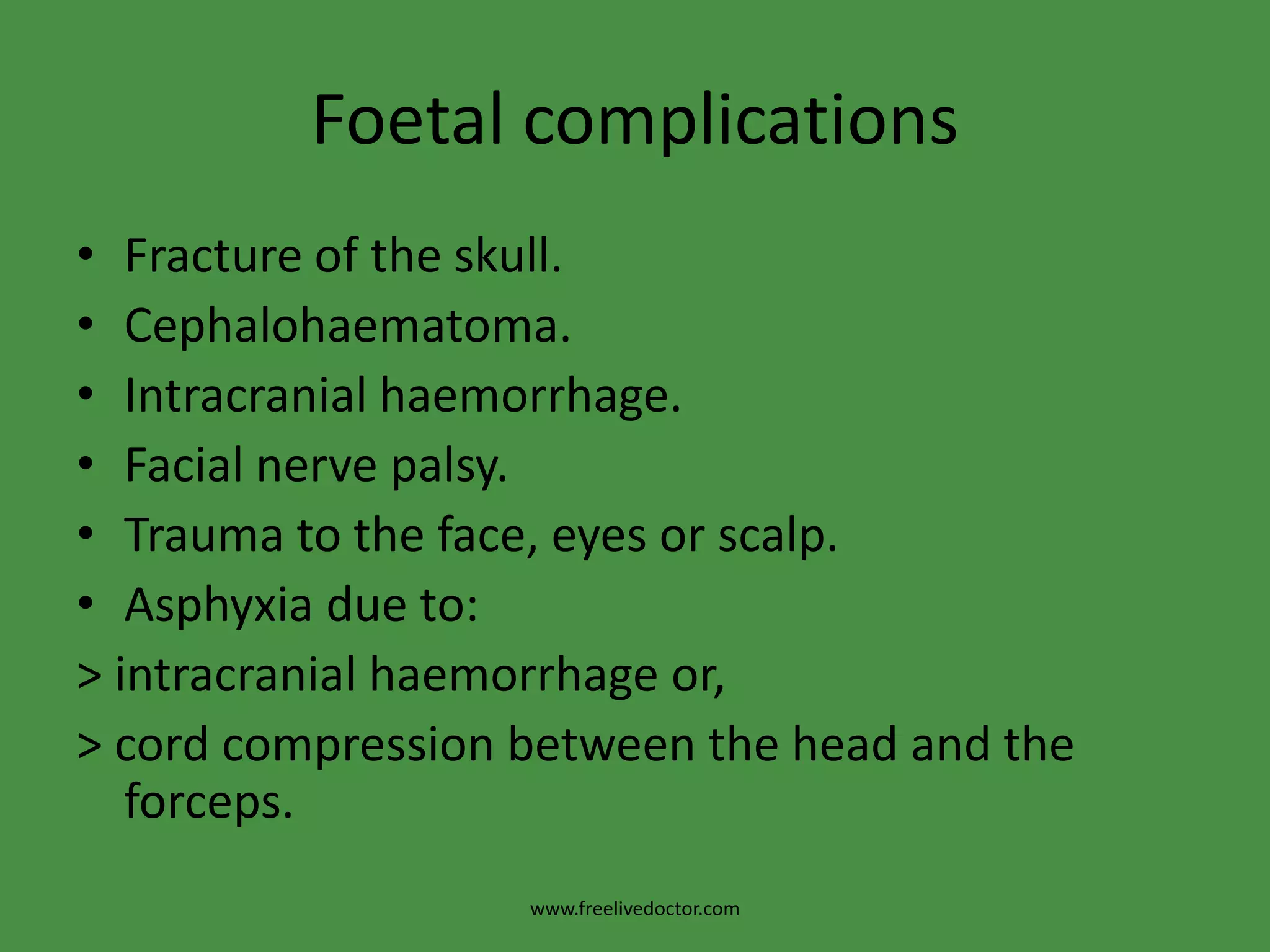
This document discusses obstetric forceps, which are metal instruments used to extract a baby's head during delivery. It describes different types of forceps and their proper application techniques. Forceps are indicated for prolonged second stage of labor, maternal distress, or fetal distress. Correct application involves inserting one blade along each side of the baby's head. Potential complications include laceration, hemorrhage, nerve injury, or problems for the baby such as skull fractures. Failure to deliver with forceps may require removal and assessment to determine if cesarean section is needed.