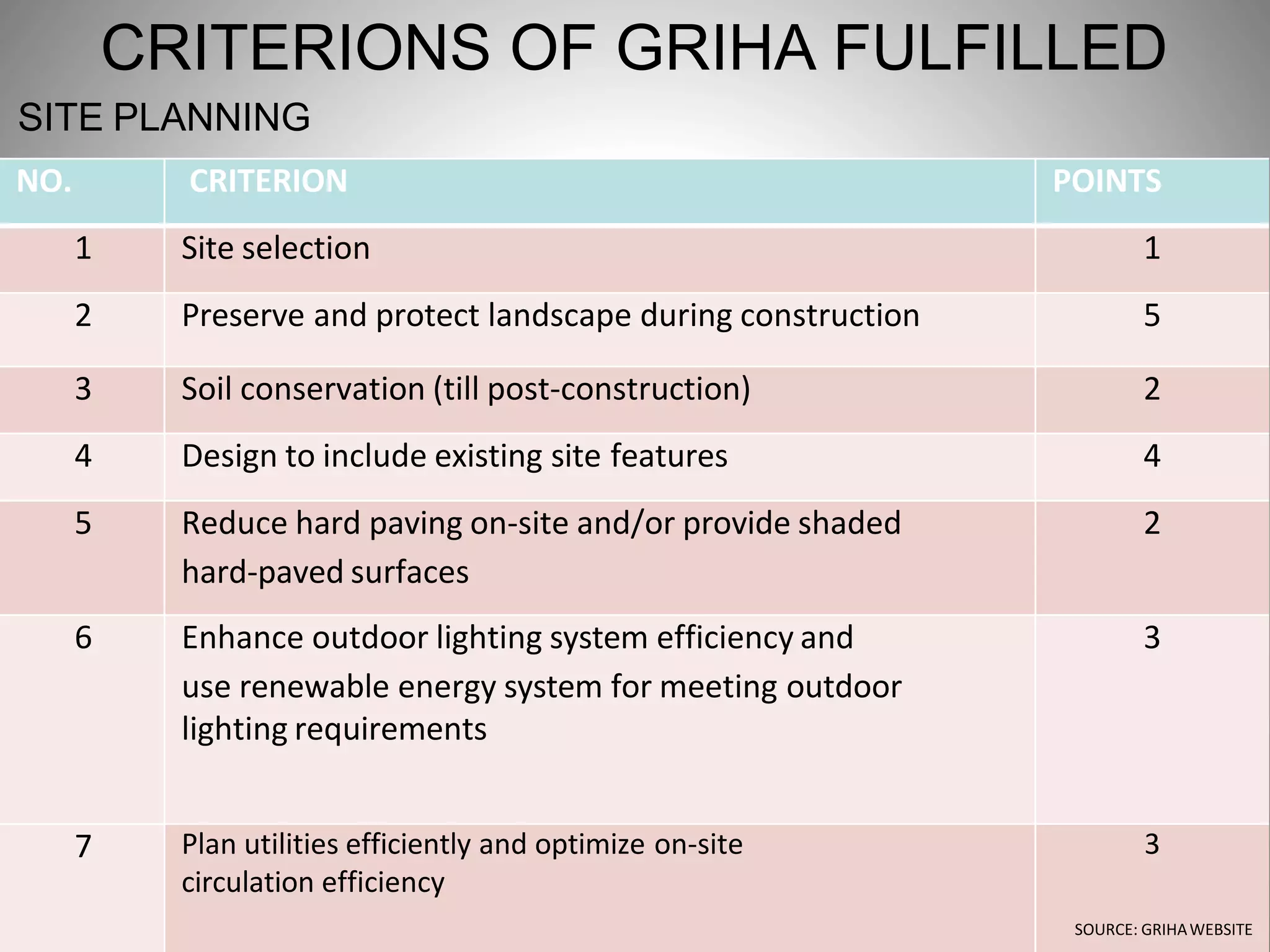
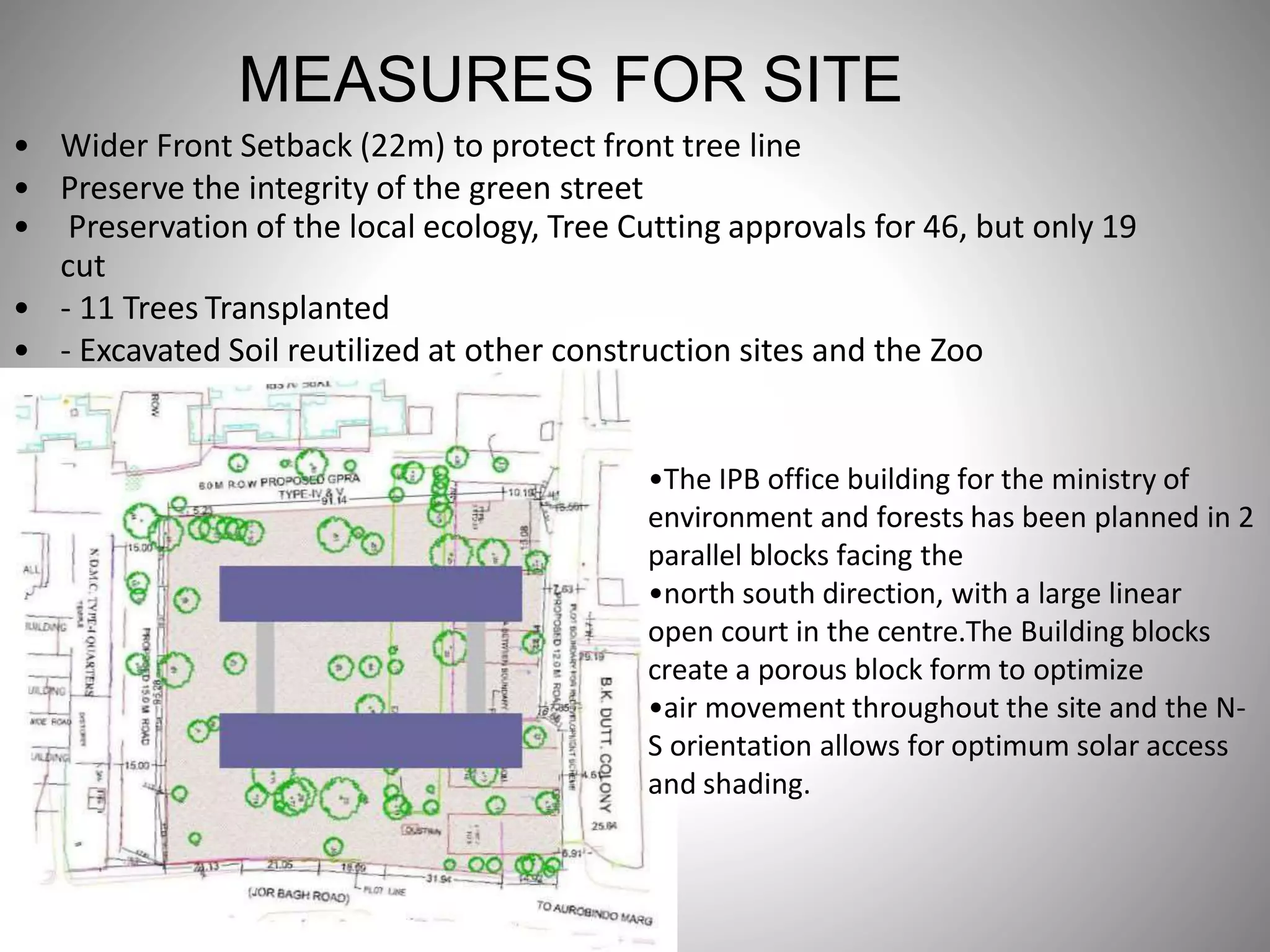
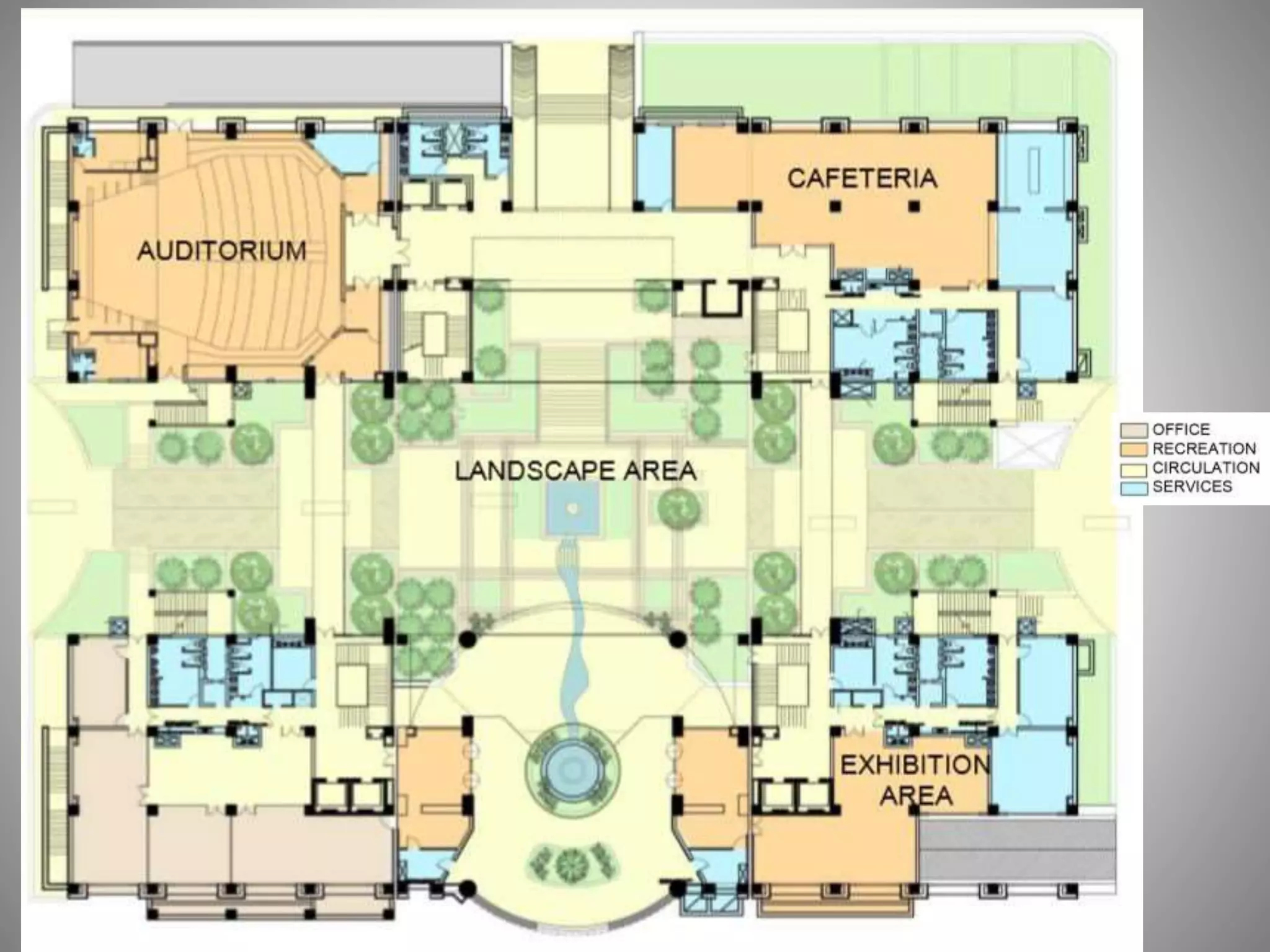
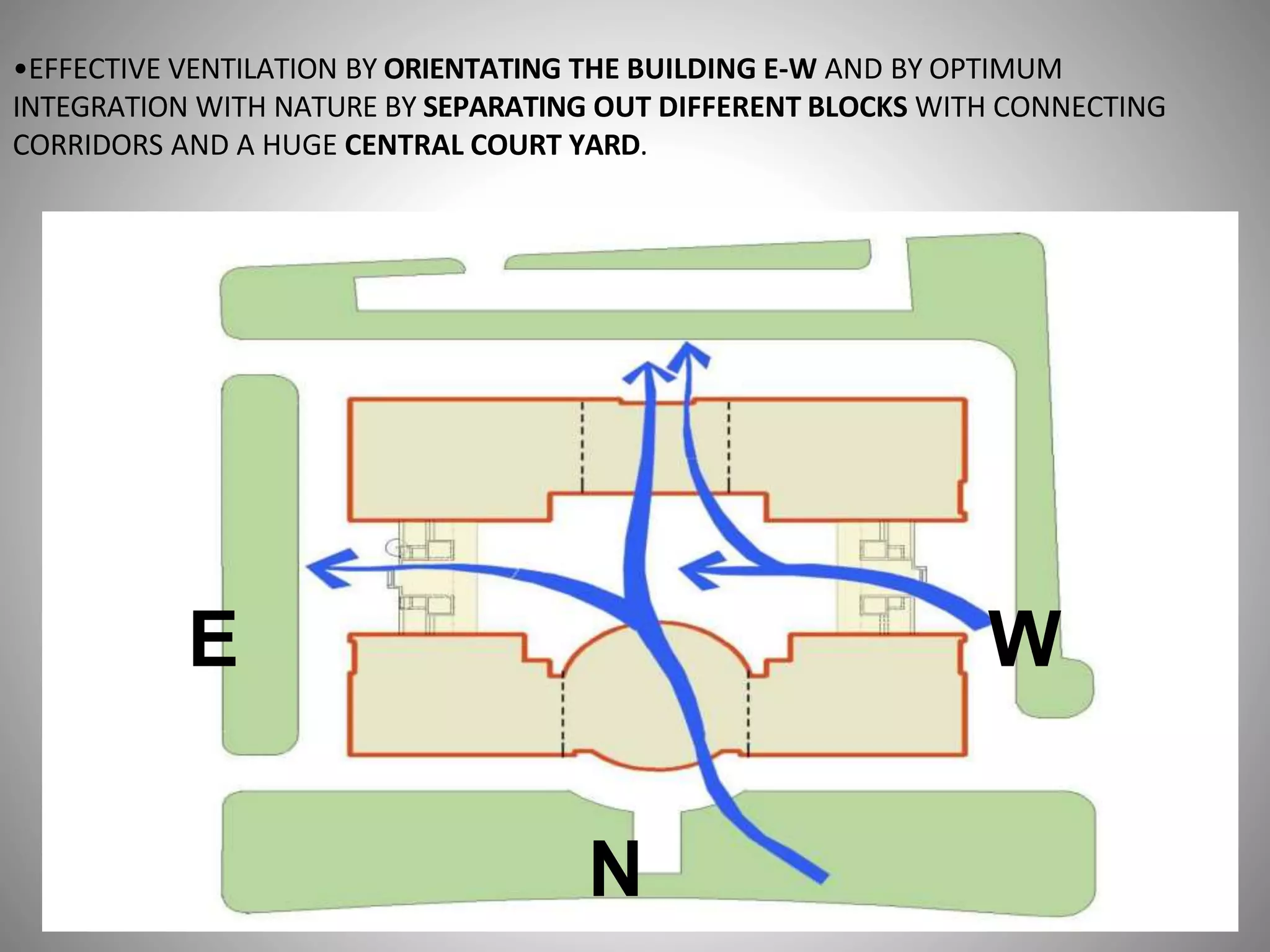
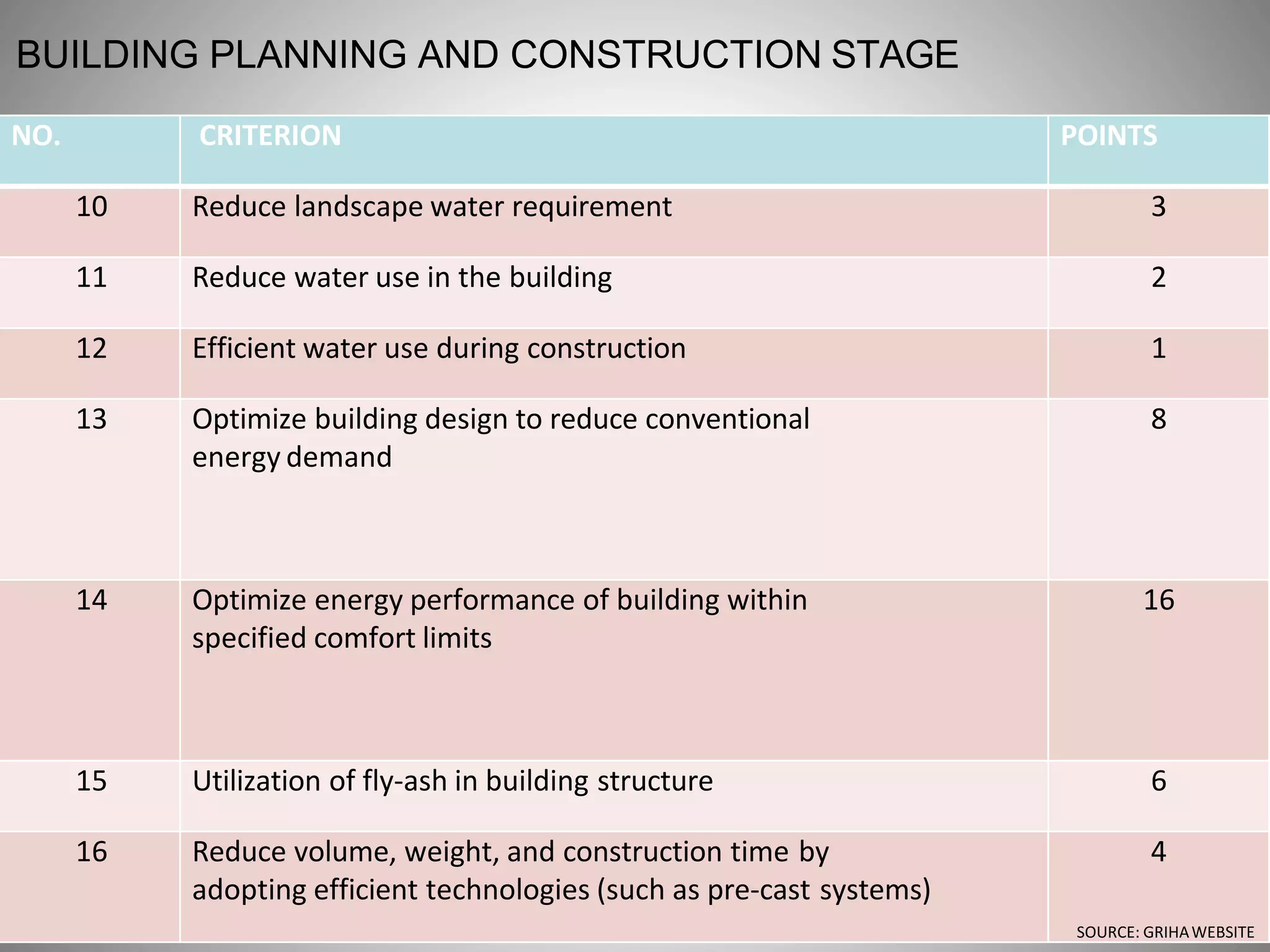
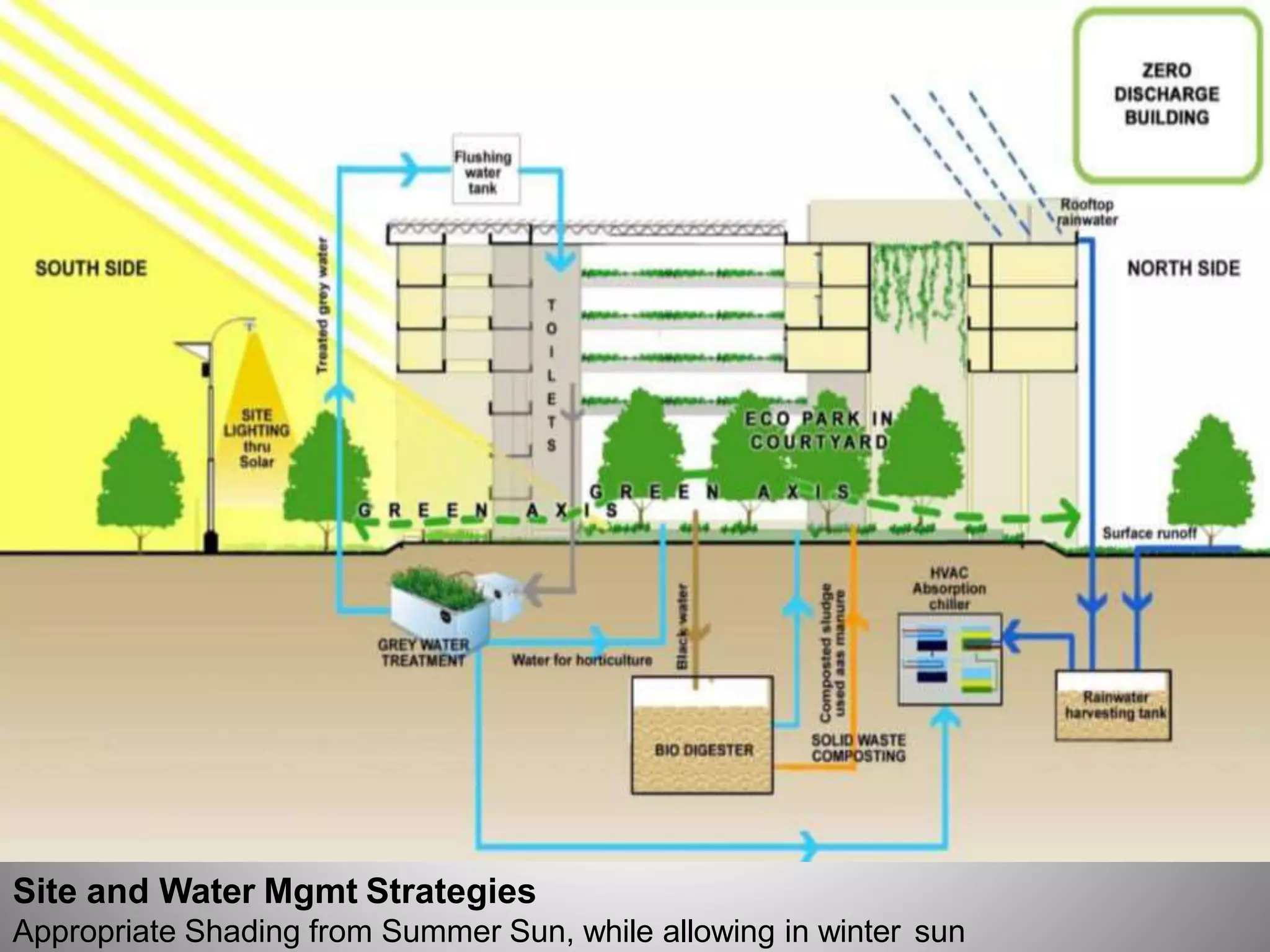
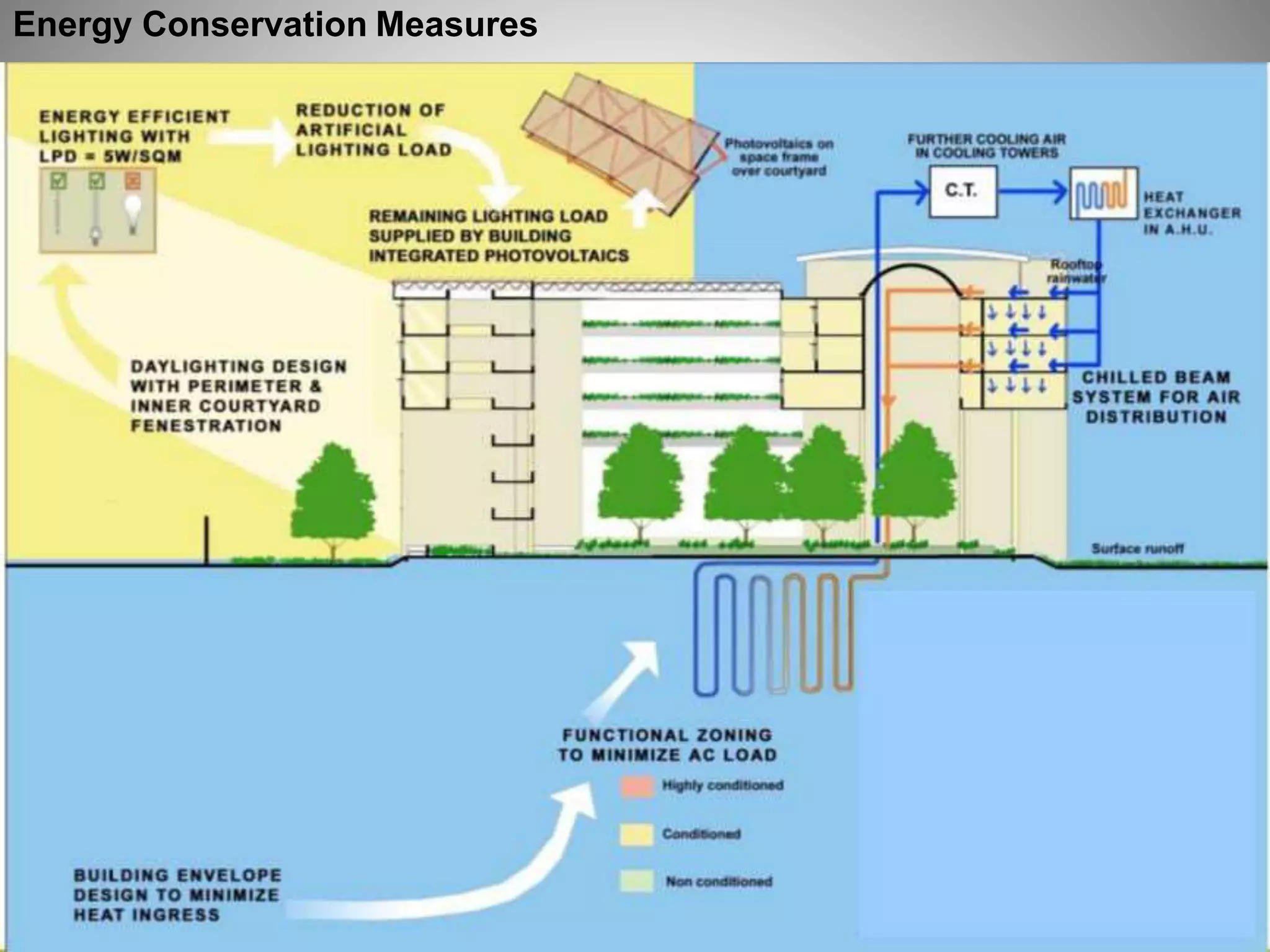
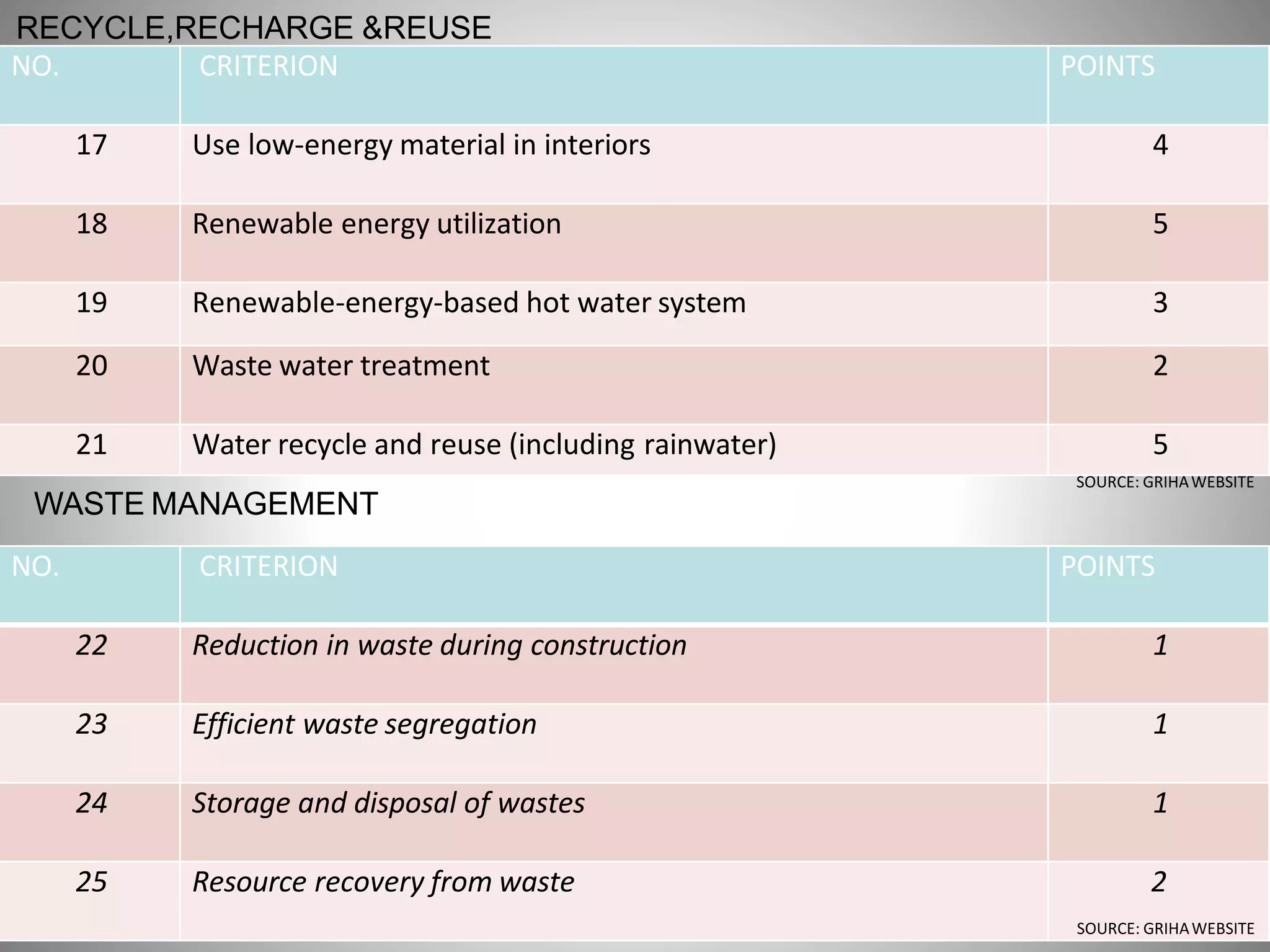
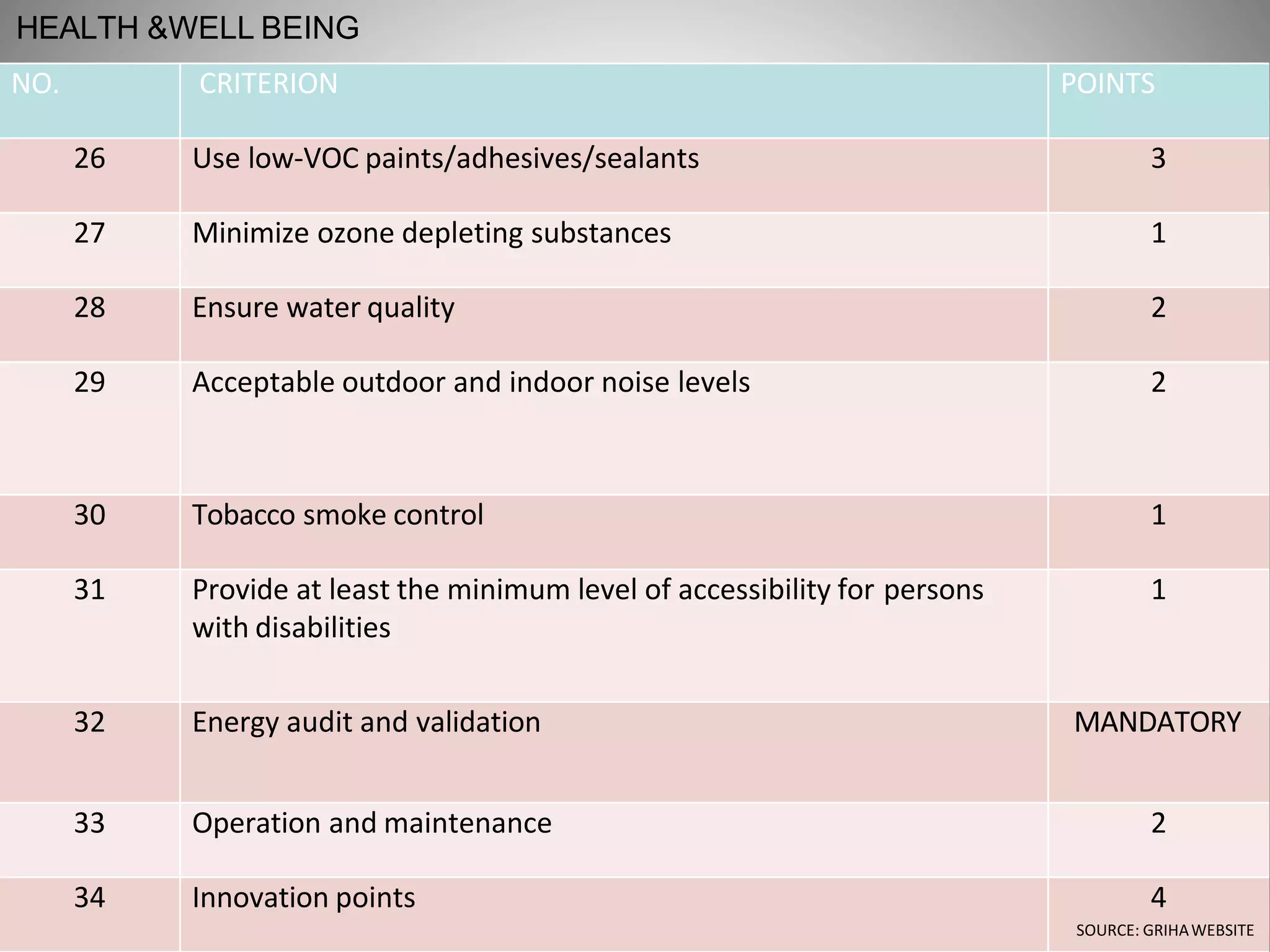
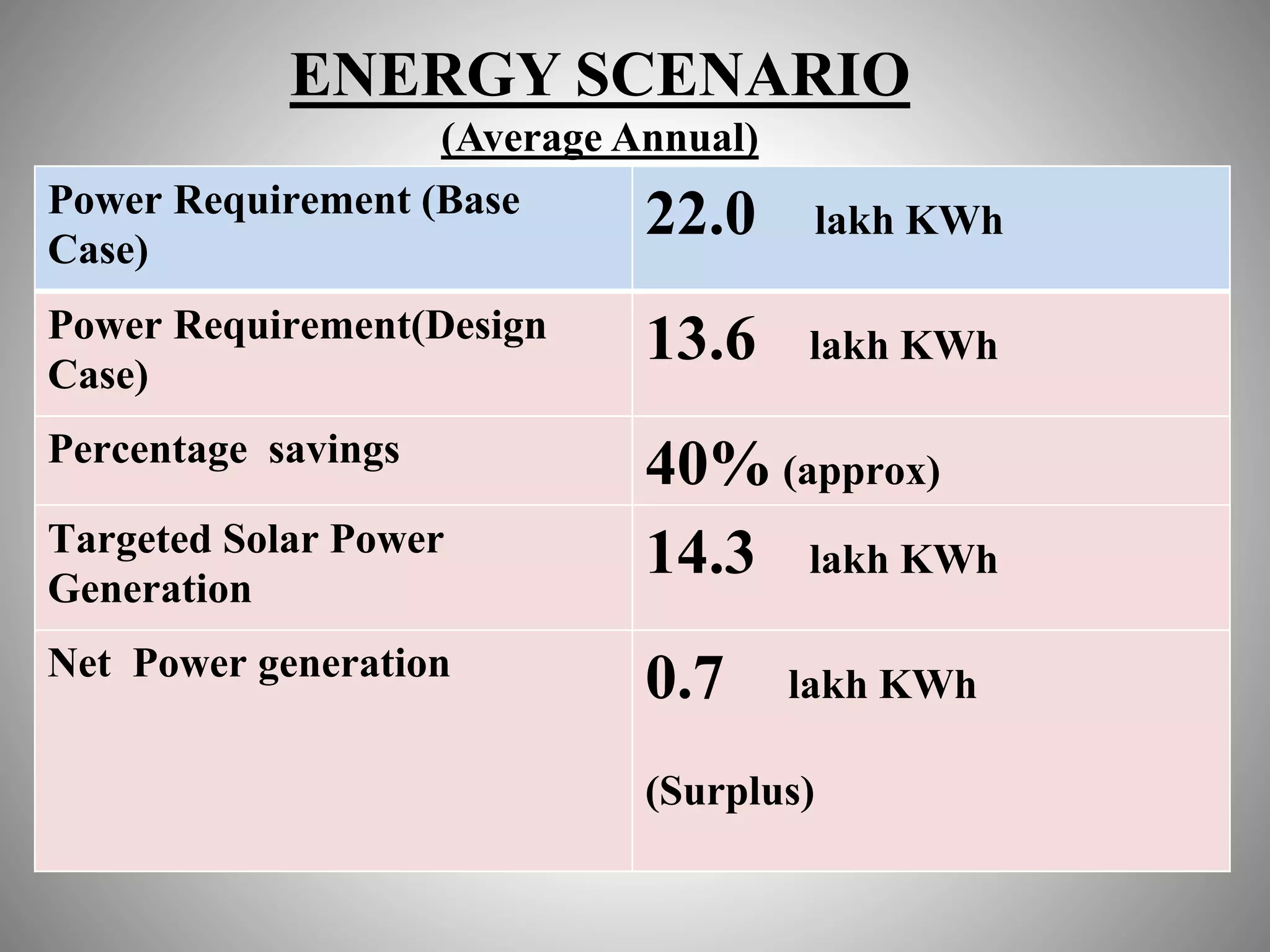
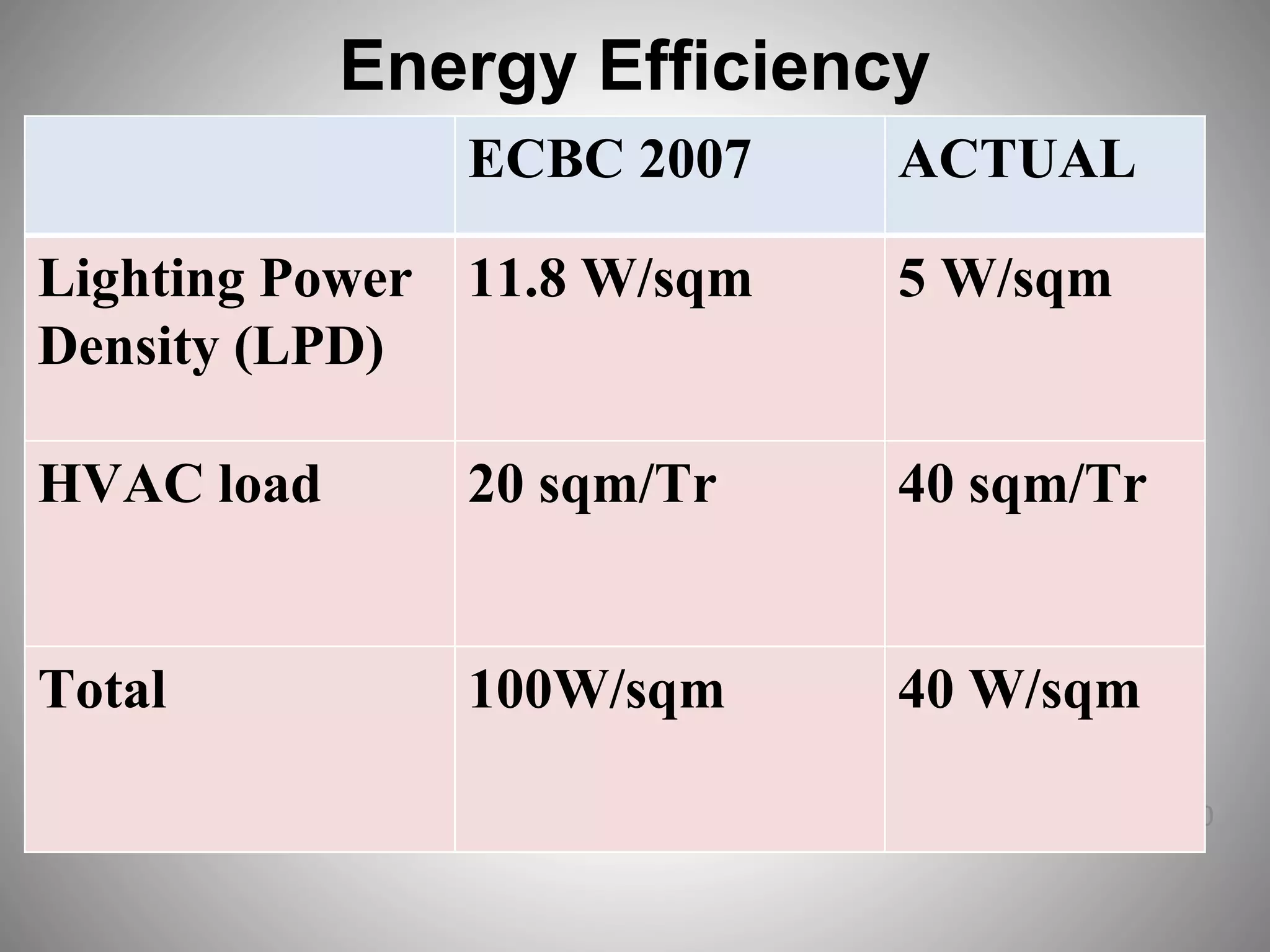
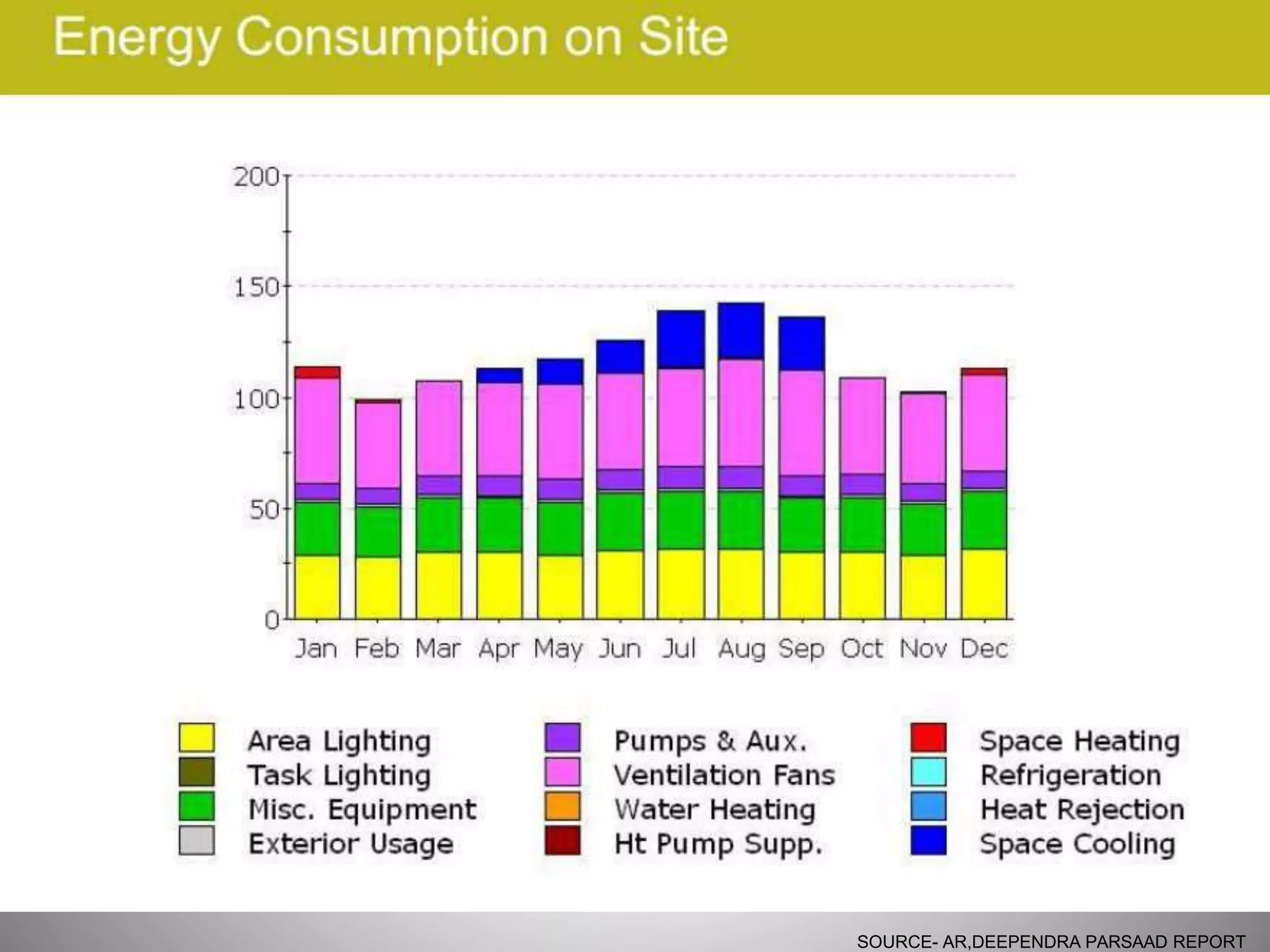
The document describes the Indira Paryavaran Bhawan building project in New Delhi, which was constructed as a net zero energy green building for the Ministry of Environment and Forests. Some key details include:
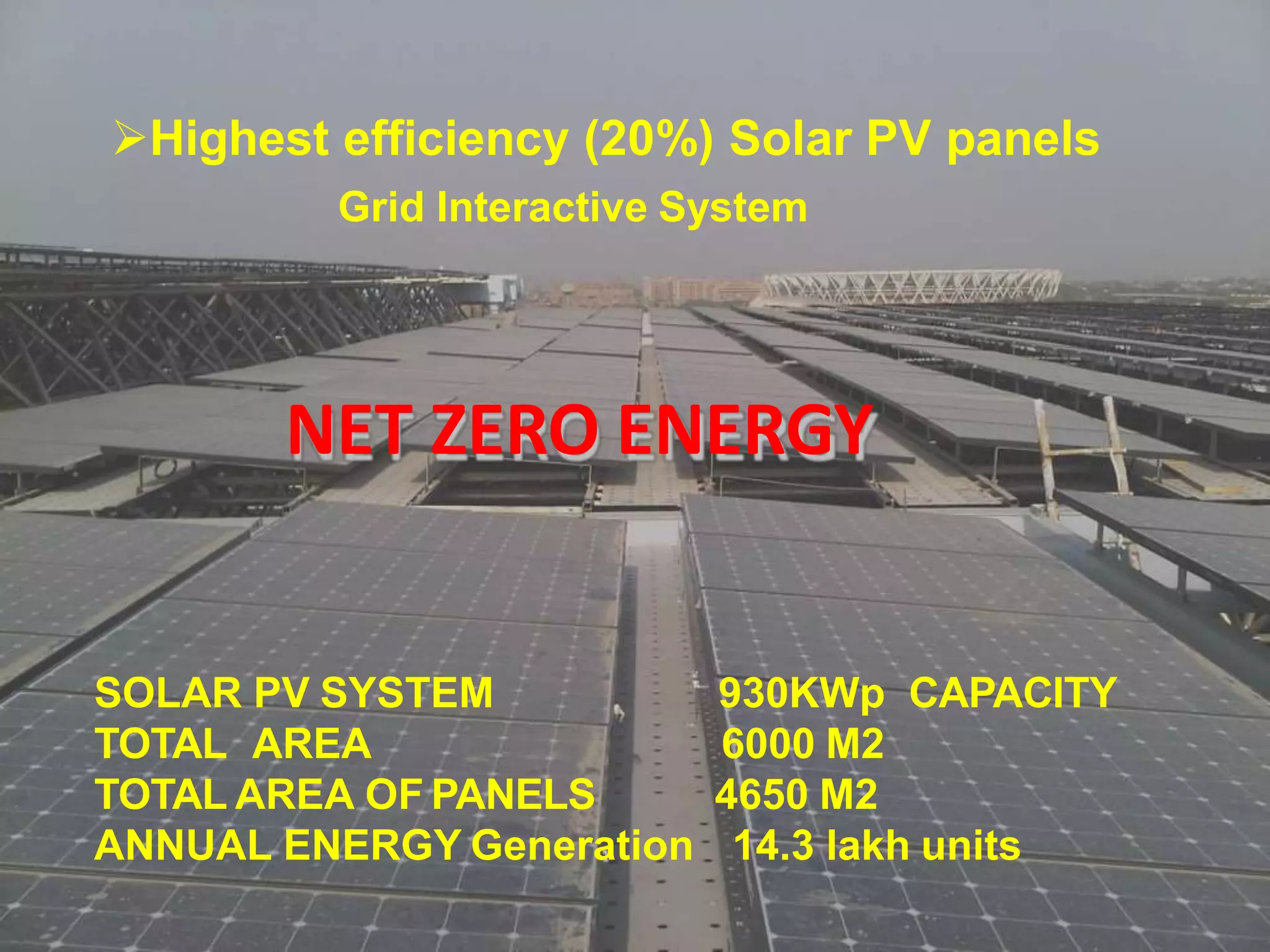
- The building was designed to reduce energy usage by 40% and achieve net zero electricity and water usage.
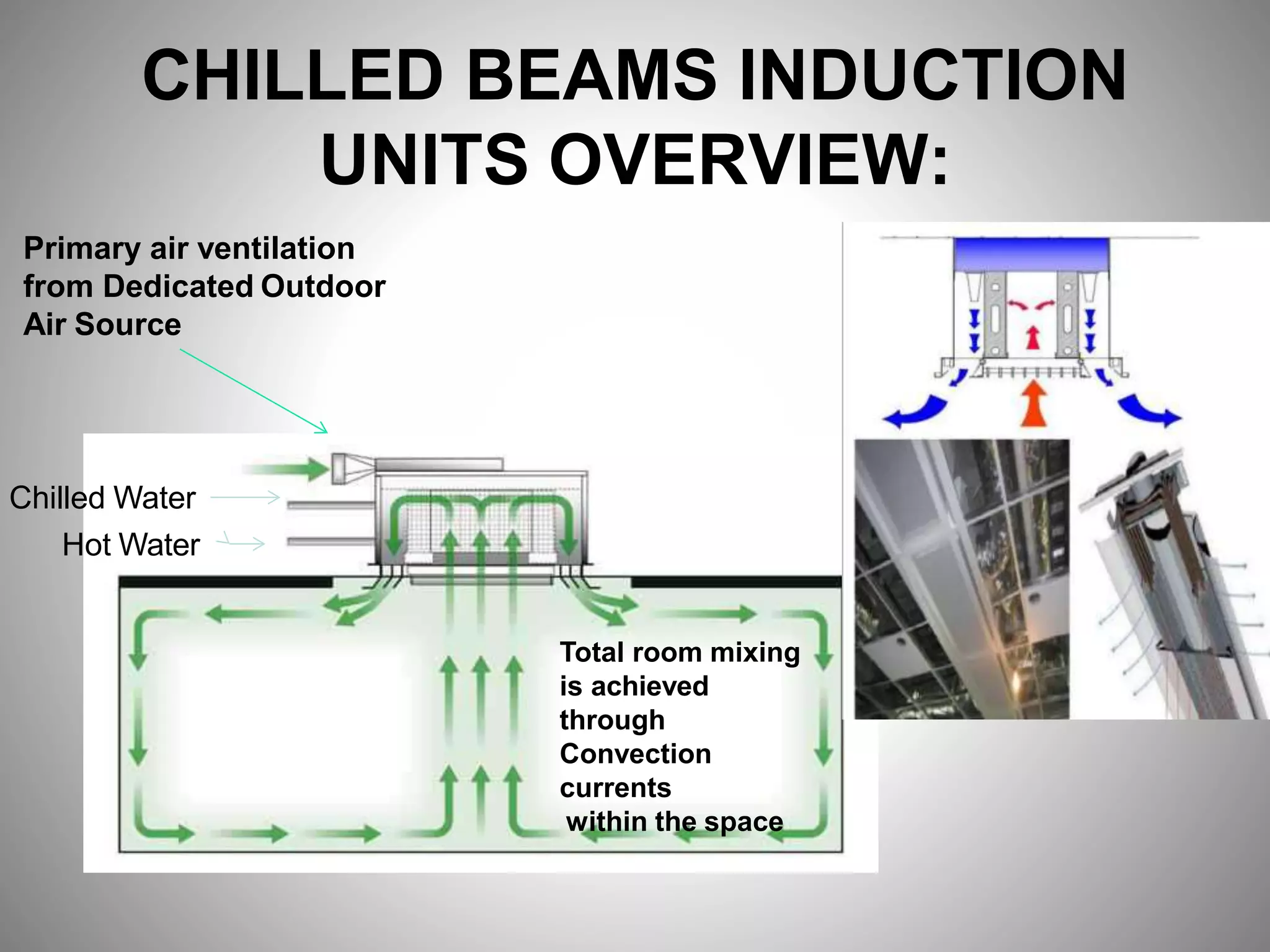
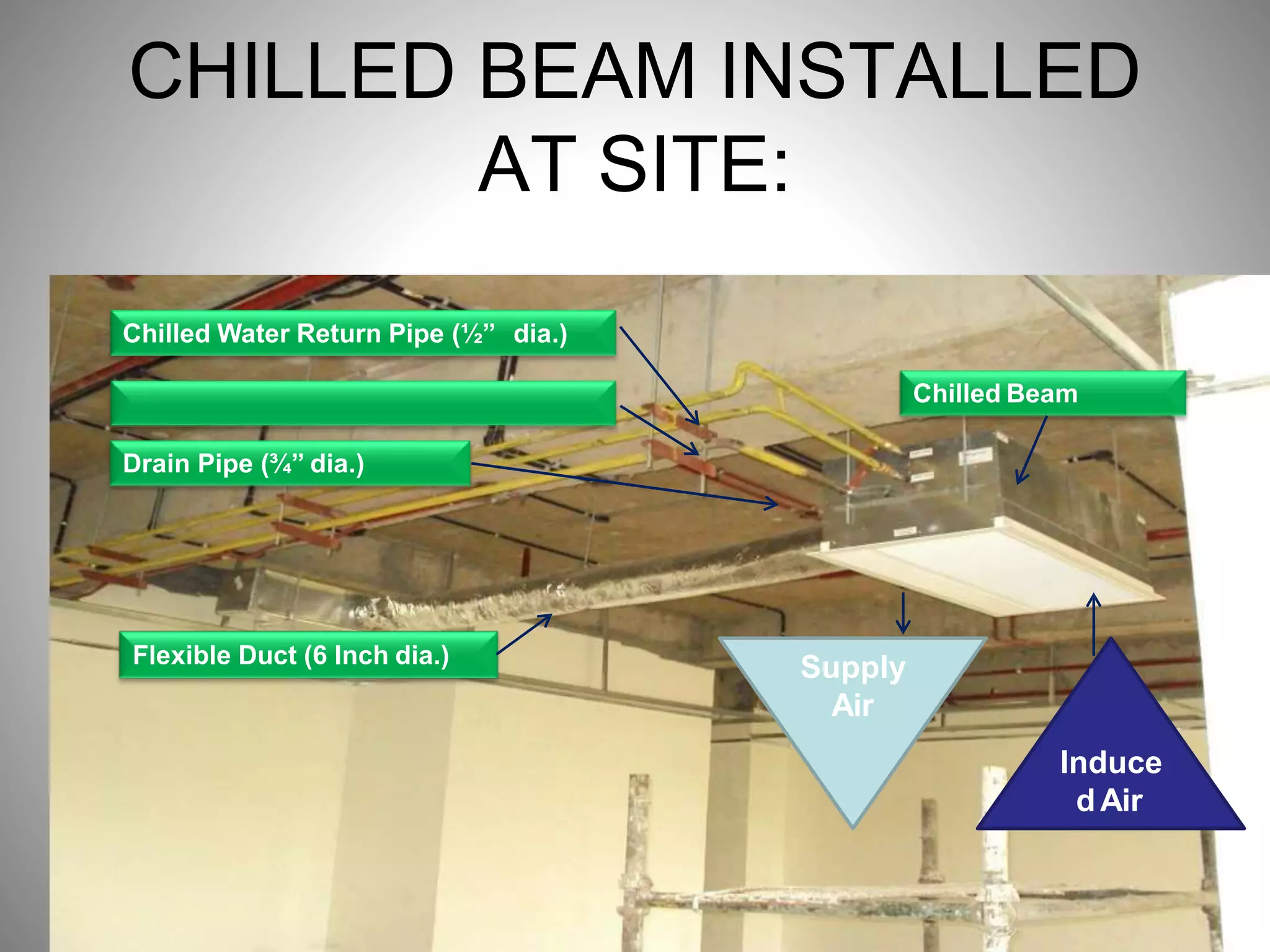
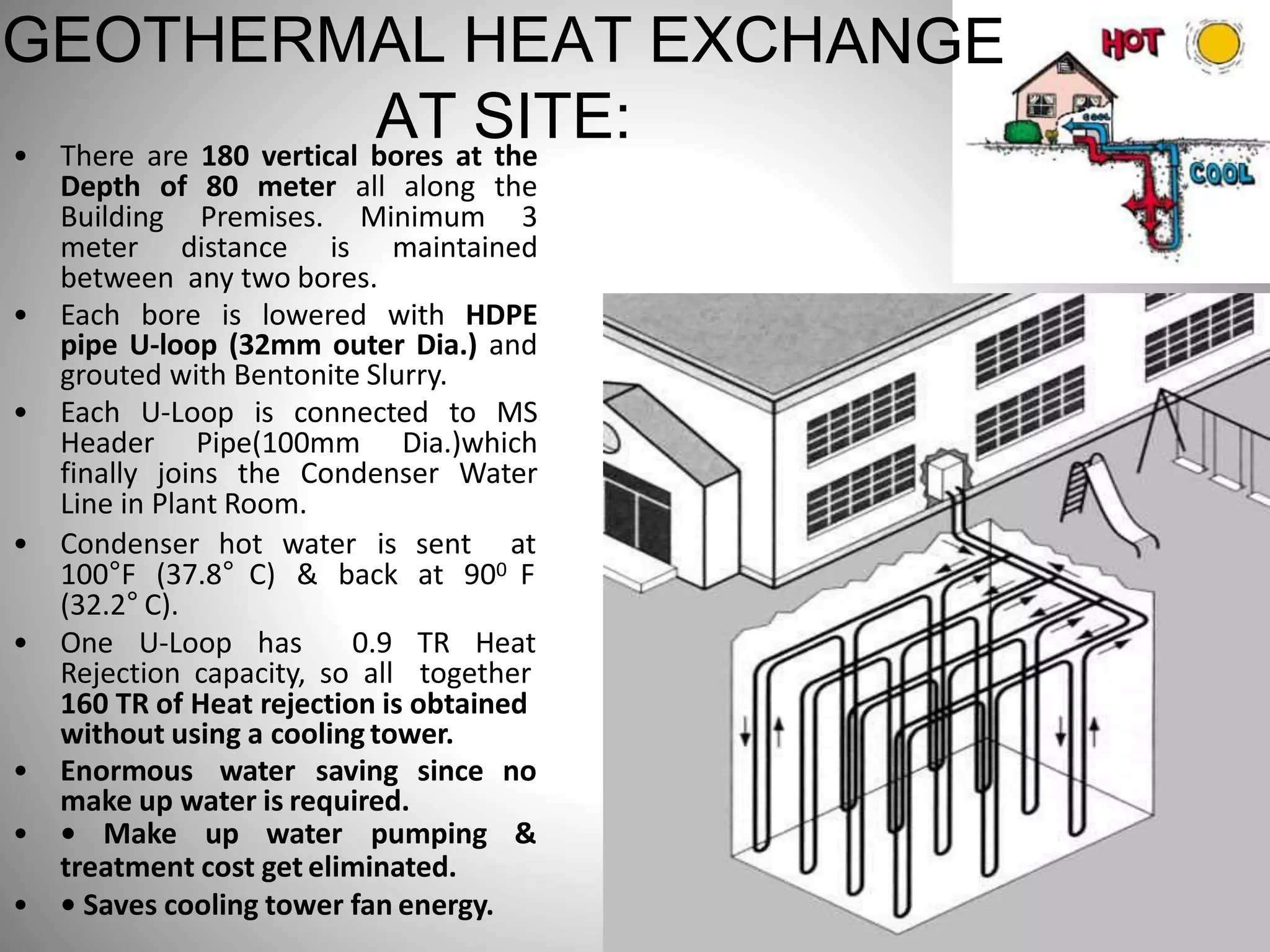
- Sustainable design features included a large solar power system, geothermal heating/cooling, and rainwater harvesting.
- Materials like fly ash bricks, AAC blocks, and local stone helped minimize environmental impact during construction.