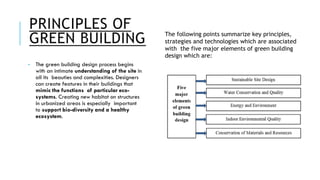
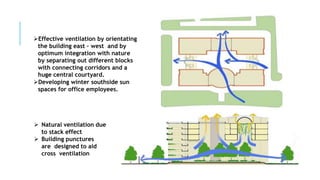
This document summarizes the Indira Paryavaran Bhawan building in New Delhi, India's first net zero energy building. Some key points:
- It was constructed by the Ministry of Environment and Forests as a new office building in New Delhi covering 9565 sqm.
- The design aimed to make it a net zero energy building, achieving 40% energy savings and generating enough renewable energy on-site to meet annual needs.
- Sustainability features included a large 930kwp rooftop solar power system, 55% water savings, preservation of local ecology, and green building certifications.