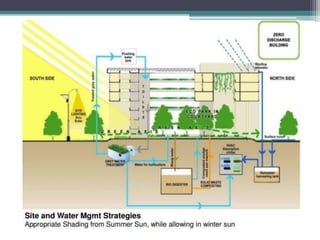
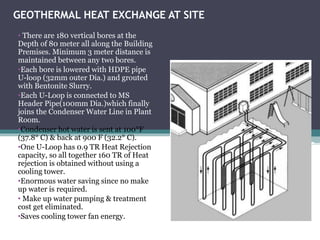
This document provides case studies on several buildings that utilize passive cooling and heating systems to reduce energy usage. It summarizes the sustainable features of the Druk White Lotus School in Ladakh, India which uses passive solar heating and natural ventilation. It also describes the Indira Paryavaran Bhawan in Delhi which saves 40% energy and 55% water usage through passive design strategies like optimal building orientation and integration with nature. Finally, it discusses the passive cooling techniques used at the TERI campus in Bangalore like good cross ventilation and utilizing thick southern walls.