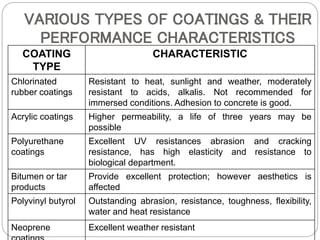
This document discusses materials used for repair, surface coatings, and polyester resins. It describes various types of materials used for repair like cement, polymers, epoxy resins and chemicals. It also discusses essential parameters for surface coatings like bonding strength, durability and permeability. Different types of surface coatings like solvent-based, solvent-free and water-based are described. Properties and applications of polyester resins are provided.