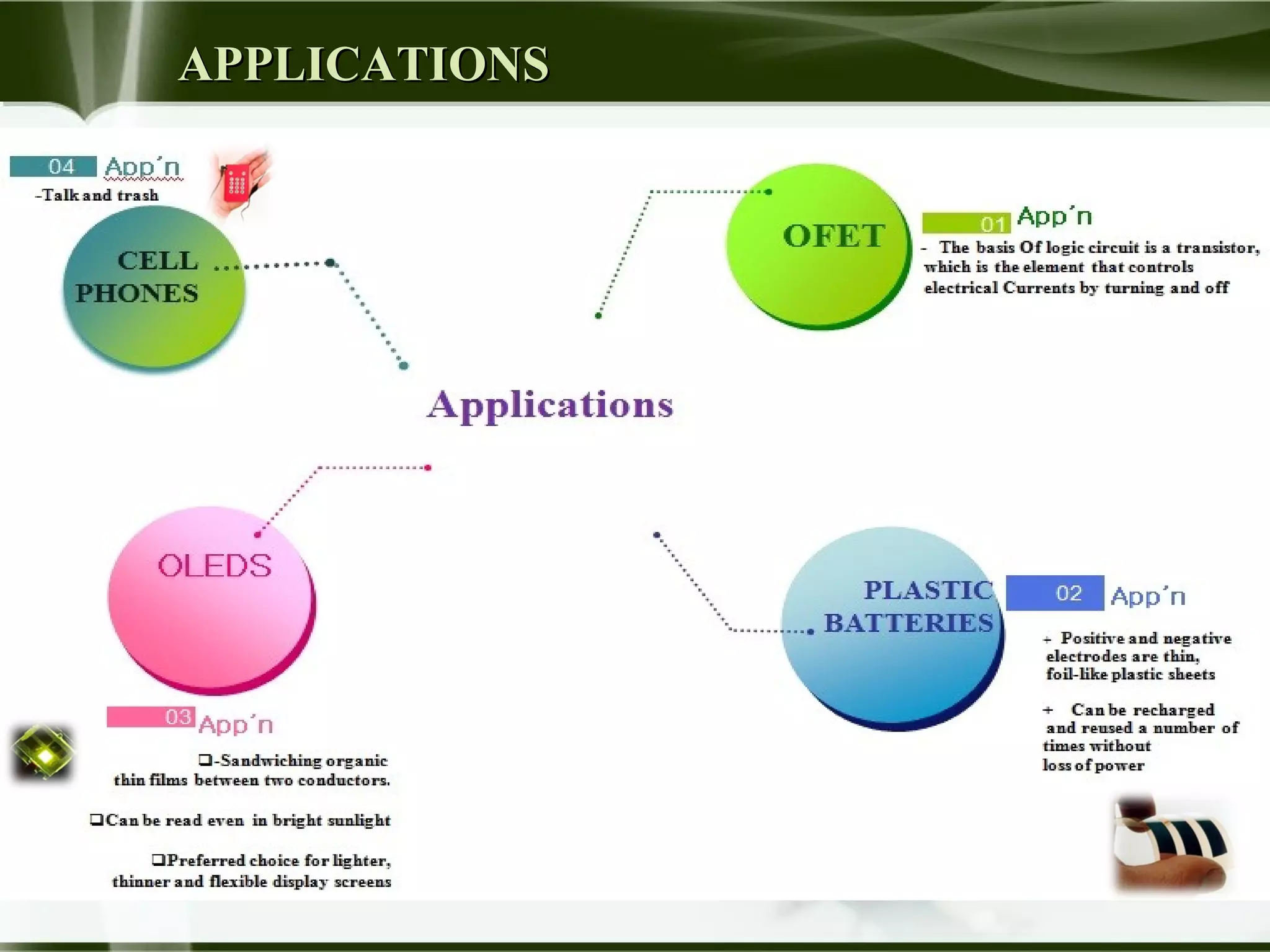
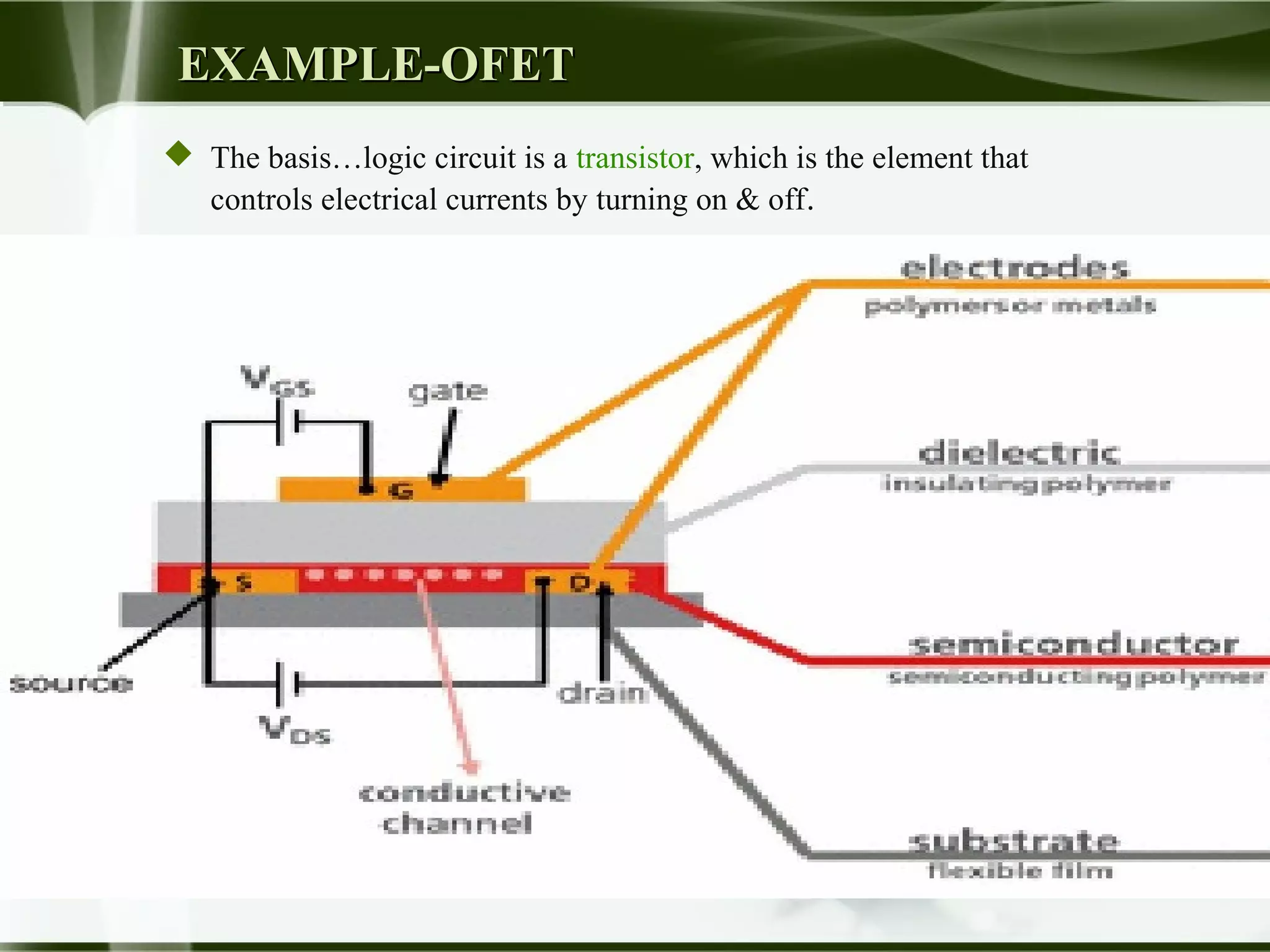
The document discusses the emerging field of polytronics, which uses conductive polymers rather than silicon in electronic devices. It notes that polytronics offers lower costs than silicon chips and more flexibility. The document provides an introduction to polymers and their properties. It outlines some of the history behind polytronics and discusses how polymers can conduct electricity. Examples of applications are given, such as organic field-effect transistors. Advantages of polytronics include lower electronic waste and more affordable access to technology.