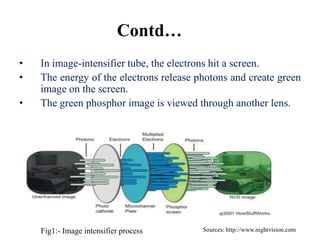
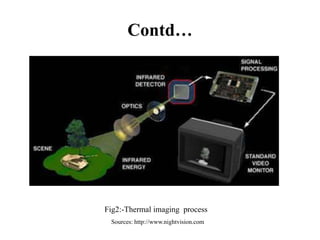
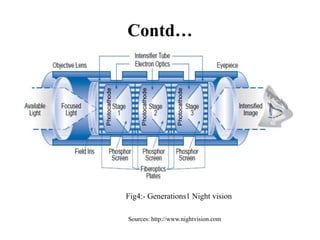
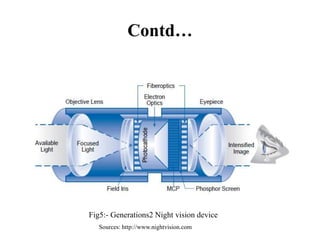
The document provides an overview of night vision technology, detailing its types, workings, devices, generations, and applications. It explains biological versus technical night vision and the functioning of image intensifiers and thermal imaging. The document concludes with the importance of night vision technology in military and civilian applications, particularly for security and combating terrorism.