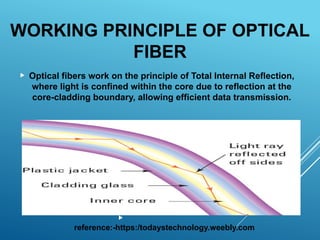
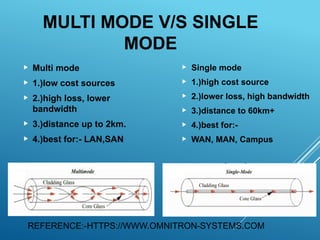
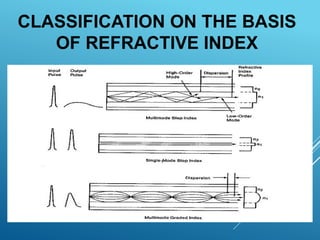
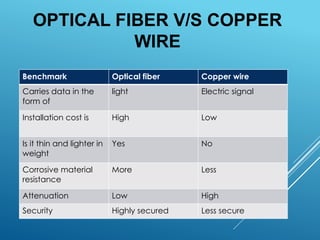
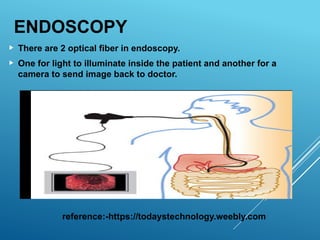
Optical fibers are thin, flexible, transparent fibers that efficiently transmit data through light via total internal reflection, widely used in telecommunications due to their high bandwidth and low signal loss. They can be classified into plastic and glass fibers based on material, and single-mode vs multi-mode based on transmission characteristics. Despite advantages like high capacity and security, they have drawbacks such as fragility and higher installation costs.