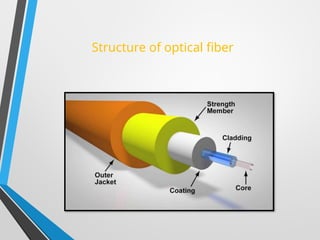
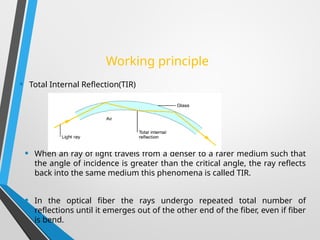
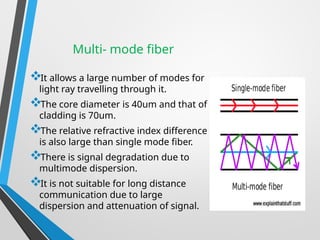
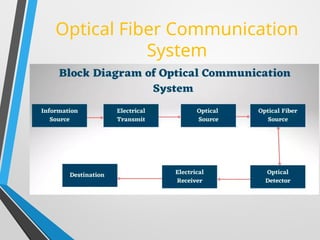
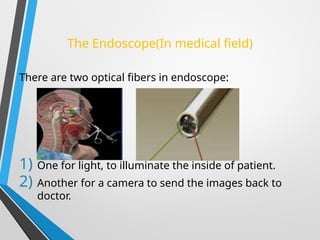
The presentation discusses optical fiber cables, explaining their structure, working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Optical fibers are thin glass fibers that guide light for communication, utilizing total internal reflection, with classifications based on mode and refractive index. Despite high installation costs and limitations, optical fibers offer immense bandwidth and are crucial in various sectors including telecommunications and medicine.