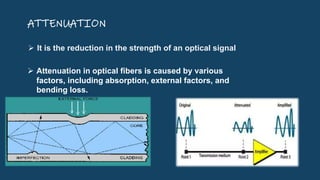
Optical fiber uses the principle of total internal reflection to transmit data signals over large distances at high speeds. It has a core made of glass or plastic surrounded by cladding and a protective coating. A communication system uses an optical fiber as the transmission medium between a transmitter that converts electrical signals to light signals and a receiver that converts the light signals back to electrical signals. Optical fibers have various applications in telecommunications, medicine, military uses, and more due to advantages like high bandwidth, long transmission distances, and less interference compared to traditional copper cables.