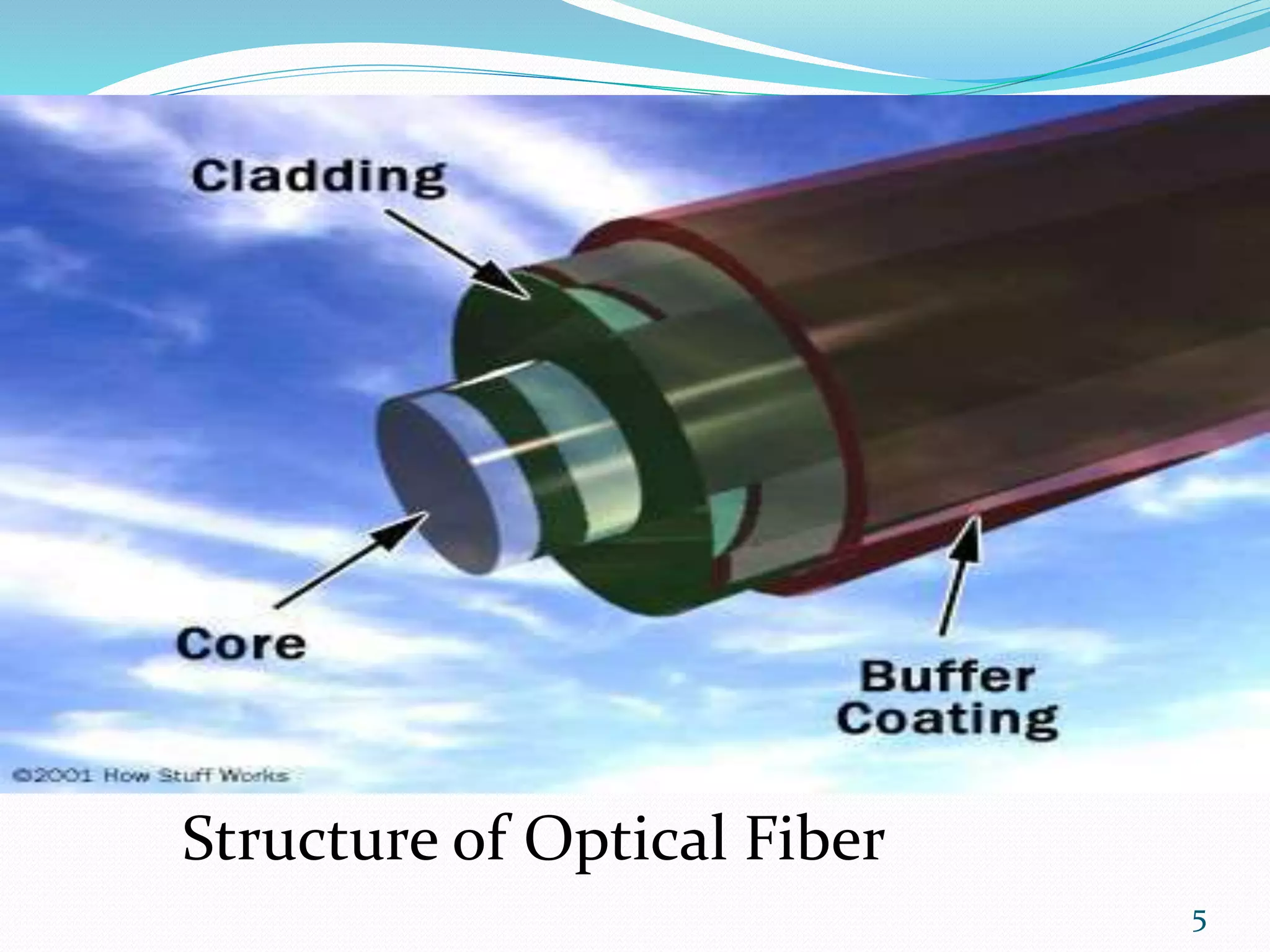
This document discusses different types of optical fibers. It begins by outlining the evolution of optical fiber technology from 1880 to 1980. It then defines an optical fiber as a thin cylindrical fiber of glass that transmits light via total internal reflection. The structure of an optical fiber is described as having a core that carries light, a cladding with a lower refractive index than the core, and a buffer coating. Optical fibers are classified based on the number of propagation modes as either single-mode or multi-mode fibers, and based on refractive index profile as either step-index or graded-index fibers.