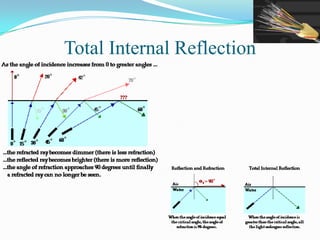
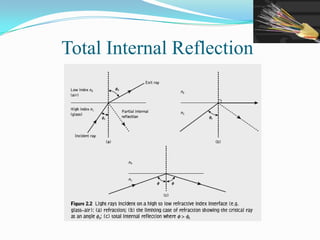
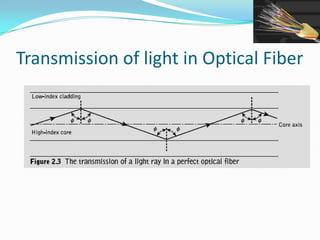
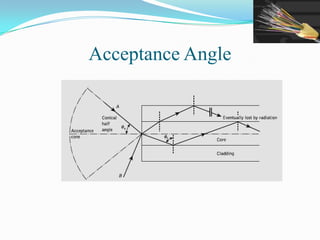
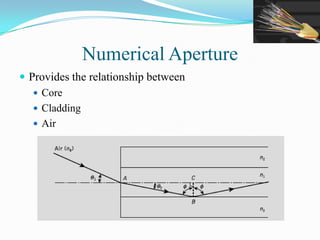
This document discusses optical waveguides and optical fibers. It covers their classification by geometry and mode structure, as well as by refractive index distribution. It also discusses how purification of materials has allowed optical fiber losses to decrease from over 1000 dB/km initially to below 0.2 dB/km currently. Total internal reflection is described as the mechanism that allows light propagation in optical fibers. Acceptance angle and numerical aperture are also defined as they relate to light entering and propagating within an optical fiber.