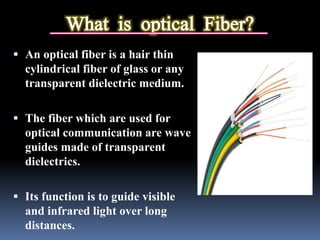
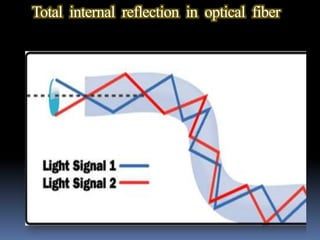
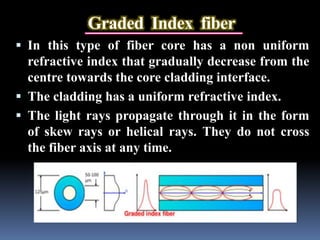
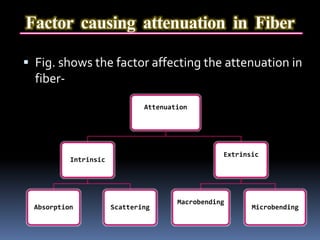
Optical fibers are thin strands of glass that carry light signals for communication. They have a core surrounded by cladding and a protective coating. Optical fibers use total internal reflection to guide light along the core from transmitter to receiver. Fibers are classified by mode (single or multi) and refractive index profile (step or graded). Optical fiber communication systems convert electrical signals to light, transmit the light through fiber, then convert back to electrical signals. Fibers provide advantages like high bandwidth, low loss, and immunity to electromagnetic interference.