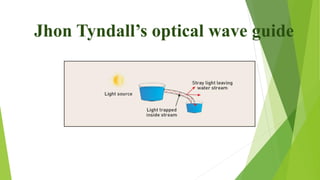
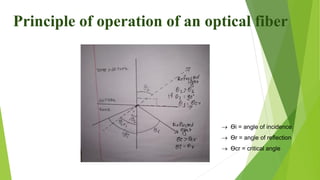
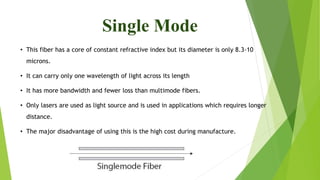
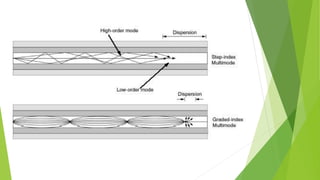
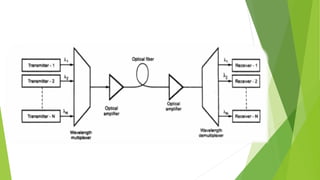
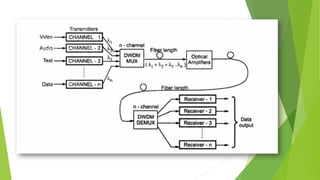
The document provides an overview of fiber optics communication, including its importance, key components, and historical development milestones. It discusses various types of optical fibers, such as single-mode and multimode fibers, along with principles like wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). Additionally, it outlines the advantages and disadvantages of fiber optic communication, highlighting its applications in sectors like medical, military, and networking.