Embed presentation
Downloaded 256 times

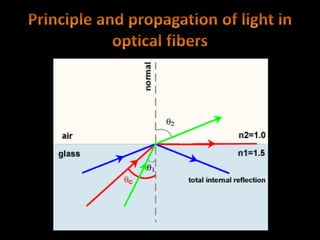
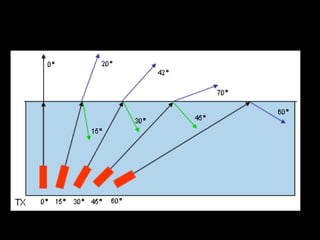



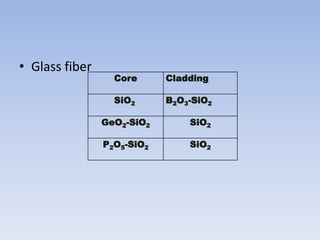

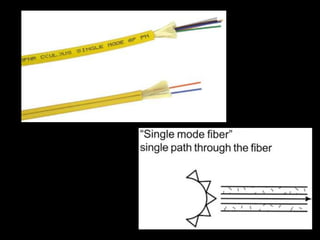
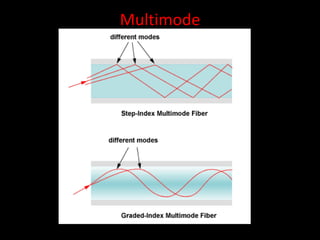

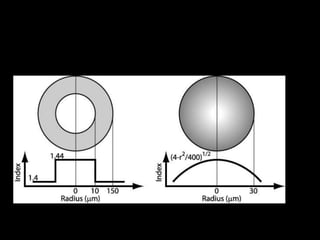
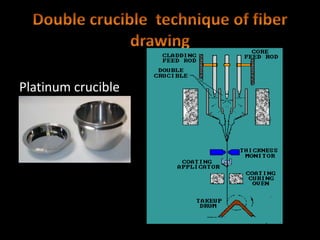


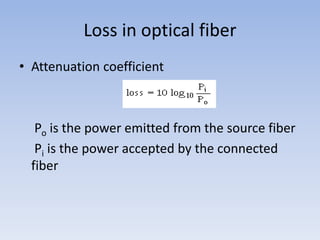
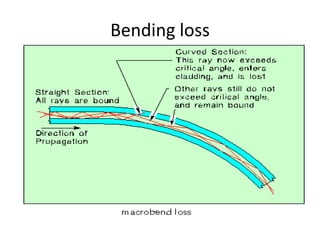
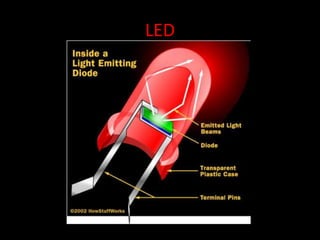
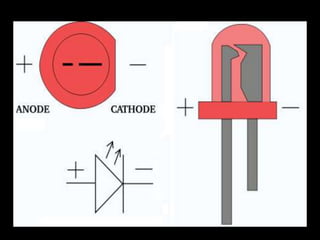

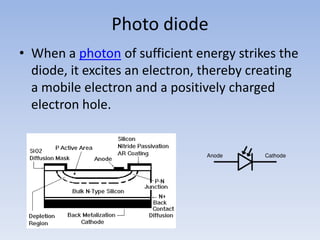

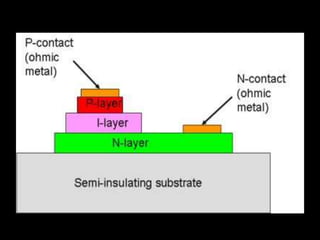
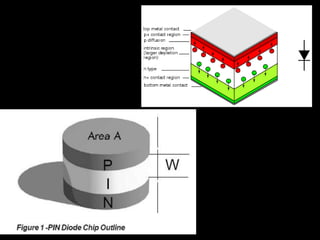
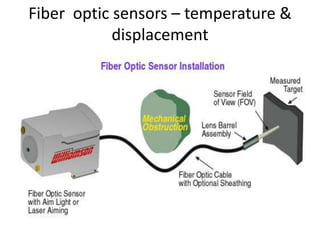


Fiber optics use total internal reflection to transmit light through optical fibers. Fibers come in different materials and have either step index or graded index refractive index profiles. They can operate in single mode or multi-mode. Common light sources are LEDs and lasers, while detectors include photodiodes and PIN diodes. Loss mechanisms in fibers include attenuation, dispersion, and bending loss. Fibers are used in communication systems and sensors can measure temperature and displacement.


































