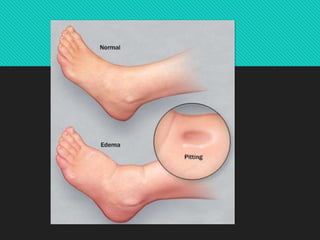
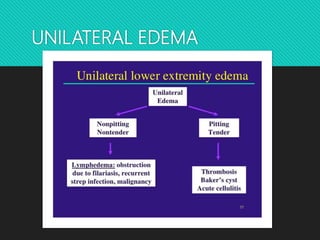
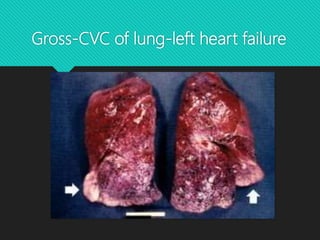
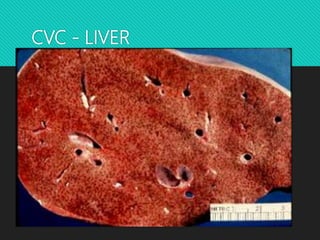
This document discusses edema, hypermia, and congestion. It defines edema as an abnormal accumulation of fluid in tissues and lists several types including renal, cardiac, pulmonary, and cerebral edema. Edema is classified as pitting or non-pitting. Hyperaemia is an active process resulting from arterial dilation while congestion is a passive process from impaired venous drainage. Examples of congestion include central venous congestion of the lung seen in left heart failure and congestion of the liver and spleen seen in right heart failure. Microscopically, congestion shows dilated vessels and hemorrhage.