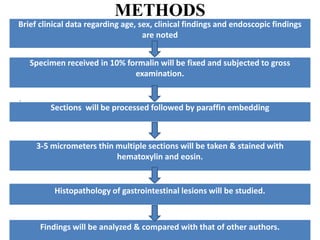
This document outlines a study on the histopathological findings of gastrointestinal endoscopic biopsies. The study will involve collecting approximately 600 biopsy samples from patients undergoing endoscopy at MGMCRI in India from 2016-2018. Biopsy samples will be examined histopathologically and findings will be analyzed. The aim is to study the spectrum of gastrointestinal lesions identified and correlate histological findings with clinical and endoscopic details. Statistical analysis will be performed to compare results with other studies. The study involves collection of human biopsy samples and aims to improve diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases.