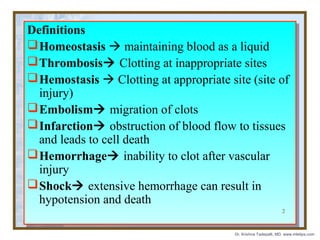
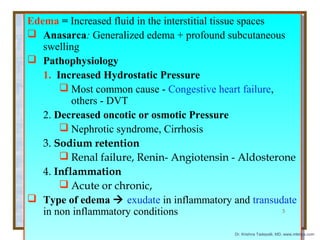
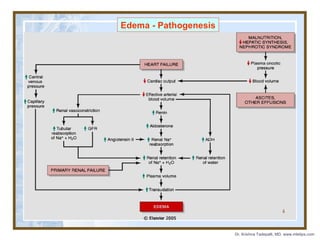
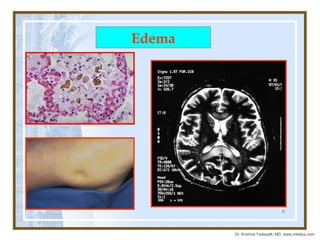
The document discusses hemodynamic disorders including edema, hyperemia, hemorrhage, hemostasis, thrombosis, embolism, and infarction. Edema is defined as increased fluid in the interstitial tissue spaces and can be caused by increased hydrostatic pressure, decreased oncotic pressure, sodium retention, or inflammation. Treatment for edema focuses on reducing sodium intake, using diuretics to increase sodium excretion, and aldosterone antagonists.