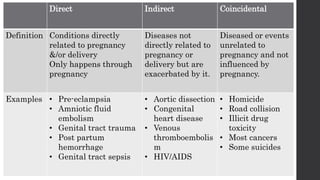
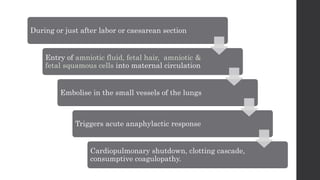
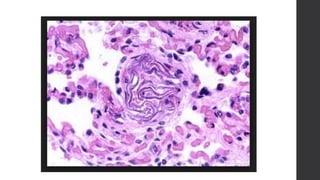
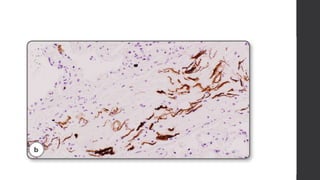
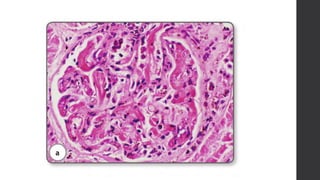
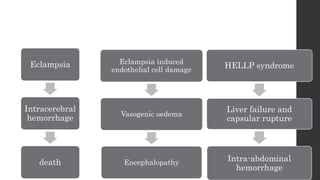
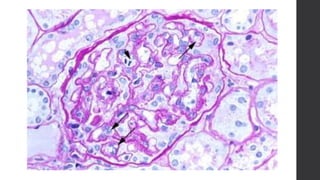
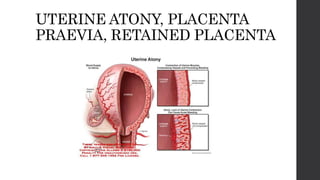
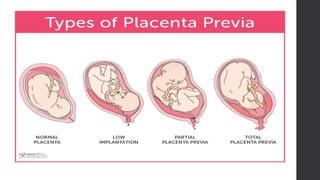
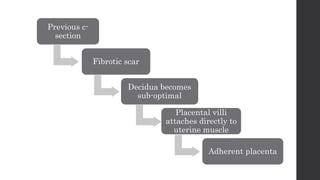
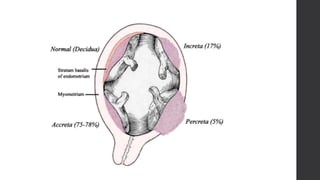
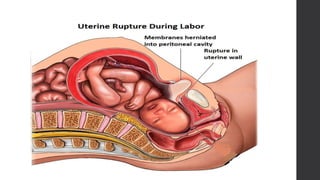
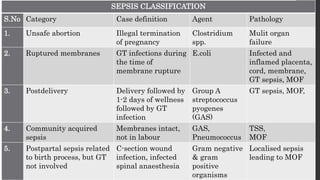
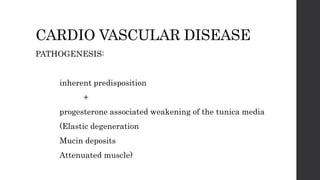
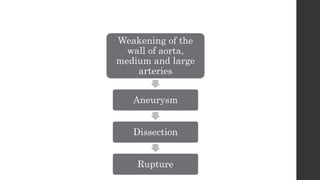
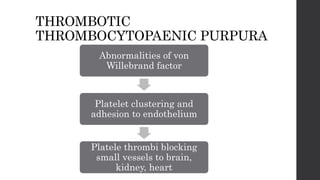
Maternal death can be classified as direct, indirect, or coincidental based on the cause. Direct causes are conditions directly related to pregnancy and delivery, such as pre-eclampsia, postpartum hemorrhage, and sepsis. Indirect causes do not directly involve pregnancy but are exacerbated by it, like venous thromboembolism and cardiac diseases. Autopsies aim to determine the precise cause of death through examination of organs like the lungs, brain, kidneys, and placenta as well as sterile blood cultures and histopathological analysis. Understanding the cause is important for improving maternal healthcare and assessing claims of clinical negligence.