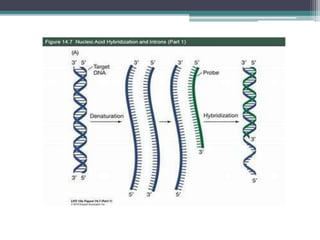
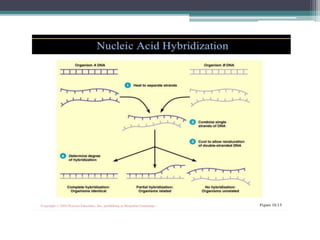
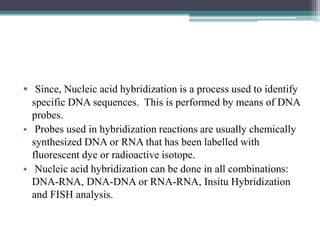
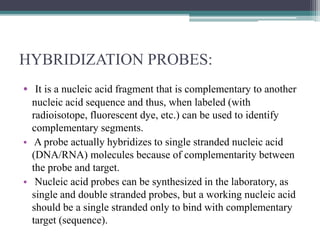
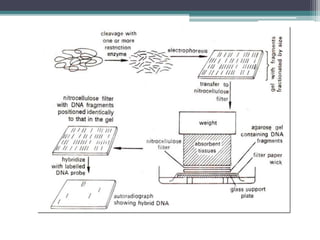
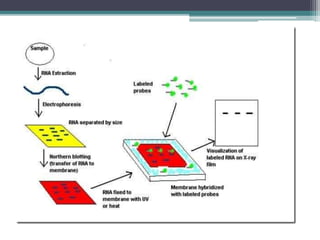
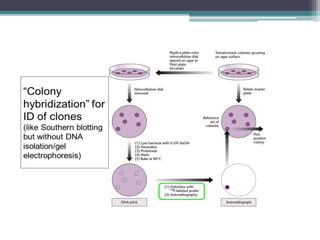
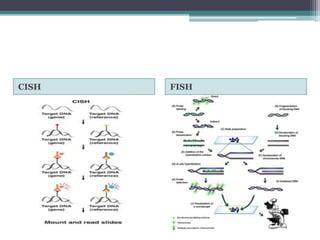
Nucleic acid hybridization is a technique where single-stranded nucleic acid molecules form double-stranded molecules through hydrogen bonding between complementary base sequences. This process can identify specific DNA or RNA sequences through the use of labeled probes. There are different types of hybridization including Southern blot, which uses probes to detect complementary DNA sequences separated by electrophoresis; Northern blot, which detects RNA sequences; and colony hybridization, which isolates plasmids containing a particular sequence.